Abstract
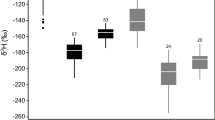
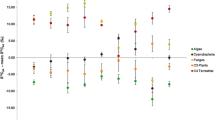
Aquatic food webs are subsidized by allochthonous resources but the utilization of these resources by consumers can be difficult to quantify. Stable isotope ratios of hydrogen (deuterium:hydrogen; δD) potentially distinguish allochthonous inputs because δD differs between terrestrial and aquatic primary producers. However, application of this tracer is limited by uncertainties regarding the trophic fractionation of δD and the contributions of H from environmental water (often called “dietary water”) to consumer tissue H. We addressed these uncertainties using laboratory experiments, field observations, modeling, and a literature synthesis. Laboratory experiments that manipulated the δD of water and food for insects, cladoceran zooplankton, and fishes provided strong evidence that trophic fractionation of δD was negligible. The proportion of tissue H derived from environmental water was substantial yet variable among studies; estimates of this proportion, inclusive of lab, field, and literature data, ranged from 0 to 0.39 (mean 0.17 ± 0.12 SD). There is a clear need for additional studies of environmental water. Accounting for environmental water in mixing models changes estimates of resource use, although simulations suggest that uncertainty about the environmental water contribution does not substantially increase the uncertainty in estimates of resource use. As long as this uncertainty is accounted for, δD may be a powerful tool for estimating resource use in food webs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birchall J, O’Connell TC, Heaton THE, Hedges REM (2005) Hydrogen isotope ratios in animal body protein reflect trophic level. J Anim Ecol 74:877–881
Birge EA, and Juday C (1927) The organic content of the water of small lakes. Proc Am Philos Soc 66:357–372
Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Pace ML, Van de Bogert M, Bade DL, Bastviken D, Gille C, Hodgson JR, Kitchell JF, Kritzberg ES (2005) Ecosystem subsidies: terrestrial support of aquatic food webs from 13C addition to contrasting lakes. Ecology 86:2737–2750
Chu SP (1942) The influence of the mineral composition of the medium on the growth of plankton algae. I. Methods and cultural media. J Ecol 30:284–325
Cole JJ, Caraco NF, Kling GW, Kratz TK (1994) Carbon dioxide supersaturation in the surface waters of lakes. Science 265:1568–1570
Cole JJ, Carpenter SR, Kitchell JF, Pace ML (2002) Pathways of organic carbon utilization in small lakes: results from a whole-lake 13C addition and coupled model. Limnol Oceanogr 47:1664–1675
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1981) Hydrogen isotope ratios of mouse tissues are influenced by a variety of factors other than diet. Science 214:1374–1375
Doucett RR, Marks JC, Blinn DW, Caron M, Hungate BA (2007) Measuring terrestrial subsidies to aquatic food webs using stable isotopes of hydrogen. Ecology 88:1587–1592
Ehleringer JR, Hall AE, Farquhar GD (eds) (1993) Stable isotopes and plant carbon-water relations. Academic Press, San Diego
Estep MF, Dabrowski H (1980) Tracing food webs with stable hydrogen isotopes. Science 209:1537–1538
Grey J, Jones RI, Sleep D (2001) Seasonal changes in the importance of the source of organic matter to the diet of zooplankton in Loch Ness, as indicated by stable isotope analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 46:505–513
Hobson KA, Wassenaar LI (2008) Tracking animal migration with stable isotopes. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hobson KA, Atwell L, Wassenaar LI (1999) Influence of drinking water and diet on the stable-hydrogen isotope ratios of animal tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8003–8006
Huxel GR, McCann K (1998) Food web stability: the influence of trophic flows across habitats. Am Nat 152:460–469
Karlsson J, Jonsson A, Meili M, Jansson M (2003) Control of zooplankton dependence on allochthonous organic carbon in humic and clear-water lakes in northern Sweden. Limnol Oceanogr 48:269–276
Kendall C, McDonnell JJ (eds) (1998) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Macko SA, Estep MLF, Lee WY (1983) Stable hydrogen isotope analysis of foodwebs on laboratory and field populations of marine amphipods. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 72:243–249
Malej A, Faganeli J, Pezdic J (1993) Stable isotope and biochemical fractionation in the marine pelagic food chain: the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca and net zooplankton. Mar Biol 116:565–570
Minagawa M, Wada E (1984) Stepwise enrichment of 15-N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between 15-N and animal age. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1135–1140
Pace ML, Cole JJ, Carpenter SR, Kitchell JF, Hodgson JR, Van de Bogert MC, Bade DL, Kritzberg ES, Bastviken D (2004) Whole-lake carbon-13 additions reveal terrestrial support of aquatic food webs. Nature 427:240–243
Pace ML, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Coloso JJ, Kitchell JF, Hodgson JR, Middelburg JJ, Preston NP, Solomon CT, Weidel BC (2007) Does terrestrial organic carbon subsidize the planktonic food web in a clear-water lake? Limnol Oceanogr 52:2177–2189
Podlesak DW, Torregrossa AM, Ehleringer JR, Dearing MD, Passey BH, Cerling TE (2008) Turnover of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the body water, CO2, hair, and enamel of a small mammal. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:19–35
Polis GA, Anderson WB, Holt RD (1997) Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: the dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:289–316
Schimmelmann A, Deniro MJ (1986) Stable isotopic studies on chitin. 3. The D/H and O-18/O-16 ratios in arthropod chitin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:1485–1496
Schimmelmann A, DeNiro MJ (1993) Preparation of organic and water hydrogen for stable isotope analysis—effects due to reaction vessels and zinc reagent. Anal Chem 65:789–792
Sessions AL, Burgoyne TW, Schimmelmann A, Hayes JM (1999) Fractionation of hydrogen isotopes in lipid biosynthesis. Org Geochem 30:1193–1200
Sharp Z (2008) Principles of stable isotope geochemistry. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Smith BN, Epstein S (1970) Biogeochemistry of stable isotopes of hydrogen and carbon in salt marsh biota. Plant Physiol 46:738–742
Smith BN, Ziegler H (1990) Isotopic fractionation of hydrogen in plants. Bot Acta 103:335–342
Solomon CT, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Pace ML (2008) Support of benthic invertebrates by detrital resources and current autochthonous primary production: results from a whole-lake 13C addition. Freshwater Biol 53:42–54
Stiller M, Nissenbaum A (1980) Variations of stable hydrogen isotopes in plankton from a fresh-water lake. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:1099–1101
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Sedell JR, Cushing CE (1980) The river continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2000) Improved method for determining the stable-hydrogen isotopic composition (delta D) of complex organic materials of environmental interest. Environ Sci Technol 34:2354–2360
Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2003) Comparative equilibration and online technique for determination of non-exchangeable hydrogen of keratins for use in animal migration studies. Isotopes Environ Health Stud 39:211–217
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Acknowledgments
S. Paskewitz, S. Dodson, and K. Forshay provided advice and assistance for maintaining lab cultures of mosquitoes, zooplankton, and phytoplankton, and N. Bankston helped maintain the phytoplankton cultures as well as the zooplankton cultures and experiment. Samples for the fish study were provided by D. Josephson and C. Kraft (Little Moose Hatchery, Old Forge, New York), A. Smith and K. Staigmiller (Washoe Park Trout Hatchery, Anaconda, Montana), and B. Couch (Buford Trout Hatchery, Cumming, Georgia). Unpublished data used to calculate ω for insects from Californian streams were supplied by J. Finlay. S. Carpenter suggested the equation for compounding of environmental water, and, along with J. Coloso, J. Kitchell, and M. J. Vander Zanden, offered comments that substantially improved this research. Comments from J. Gaeta improved the manuscript. Funding was provided by an NSF-DDIG award (DEB-0708666) to C. T. S. and M. J. Vander Zanden, and by a collaborative NSF award (DEB-0414258) to S. Carpenter, J. J. C., M. L. P., J. Kitchell, and J. Hodgson. The experiments described here comply with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Sebastian Diehl.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solomon, C.T., Cole, J.J., Doucett, R.R. et al. The influence of environmental water on the hydrogen stable isotope ratio in aquatic consumers. Oecologia 161, 313–324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-009-1370-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-009-1370-5