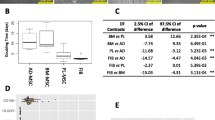
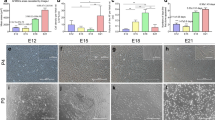
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can be isolated from different adult sources and, even if the minimal criteria for defining MSCs have been reported, the scientific question about the potential distinctions among MSCs derived from different sources is still open. In particular, it is debated whether MSCs of different origin have the same grade of stemness or whether the source affects their undifferentiated status. Here, we report not only the isolation and the traditional characterization of MSCs derived from amniotic fluid (AF-MSCs) and skin (S-MSCs) but also a molecular characterization based on mRNAs and miRNAs profiling. Our results show that, even if both AF- and S-MSCs are mostly regulated by the same pathways (such as Wnt, MAPK and TGF-β), there are some important differences at the molecular level that directly affect important cellular features, such as the ability to differentiate into adipocytes. In conclusion, even if further studies are necessary to improve the knowledge about the role of each dysregulated miRNAs gene, these differences may actually strengthen the question about the importance of tissue origin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akle KA, Adinolfi M, Welsh KI, Leibowitz S (1981) Immunogenicity of human amniotic epithelial cells after transplantation into volunteers. Lancet 2:1003–1005
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Büssing I, Slack FJ, Grosshans H (2008) let-7 microRNAs in development, stem cells and cancer. Trends Mol Med 14:400–409
Campanati A, Orciani M, Gorbi S, Regoli F, Di Primio R, Offidani A (2012) Effect of biologic therapies targeting tumour necrosis factor-α on cutaneous mesenchymal stem cells in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 167:68–76
Choy L, Derynck R (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits adipocyte differentiation by Smad3 interacting with CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and repressing C/EBP transactivation function. J Biol Chem 278:9609–9619
Cleary MA, van Osch GJ, Brama PA (2013) TGFβ and Wnt crosstalk: embryonic to in vitro cartilage development from mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med
Cloonan N, Forrest AR, Kolle G, Gardiner BB, Faulkner GJ, Brown MK, Taylor DF, Steptoe AL, Wani S, Bethel G, Robertson AJ, Perkins AC, Bruce SJ, Lee CC, Ranade SS, Peckham HE, Manning JM, McKernan KJ, Grimmond SM (2008) Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat Methods 5:613–619
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Gigante A, Manzotti S, Bevilacqua C, Orciani M, Di Primio R, Mattioli-Belmonte M (2008) Adult mesenchymal stem cells for bone and cartilage engineering: effect of scaffold materials. Eur J Histochem 52:169–174
Guan L, Yu J, Zhong L, Huang B, Luo T, Zhang M, Lin S, Li W, Ge J, Chen X, Liu Q, Zeng MZ, Song X (2011) Biological safety of human skin-derived stem cells after long-term in vitro culture. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 5:97–103
Guo X, Wang XF (2009) Signaling cross-talk between TGFβ/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res 19:71–88
Halfon S, Abramov N, Grinblat B, Ginis I (2011) Markers distinguishing mesenchymal stem cells from fibroblasts are downregulated with passaging. Stem Cells Dev 20:53–66
Hirata-Tominaga K, Nakamura T, Okumura N, Kawasaki S, Kay EP, Barrandon Y, Koizumi N, Kinoshita S (2013) Corneal endothelial cell fate is maintained by LGR5 via the regulation of hedgehog and wnt pathway. Stem Cells 31:1396–1407
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Heinrich EM, Dimmeler S (2012) MicroRNAs and stem cells: control of pluripotency, reprogramming, and lineage commitment. Circ Res 110:1014–1022
Kandyba E, Leung Y, Chen YB, Widelitz R, Chuong CM, Kobielak K (2013) Competitive balance of intrabulge BMP/Wnt signaling reveals a robust gene network ruling stem cell homeostasis and cyclic activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:1351–1356
Kim MJ, Shin KS, Jeon JH, Lee DR, Shim SH, Kim JK, Cha DH, Yoon TK, Kim GJ (2011) Human chorionic-plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative analysis of their potential as placenta-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Res 346:53–64
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet 11:597–610
Kuang W, Tan J, Duan Y, Duan J, Wang W, Jin F, Yuan X, Liu Y (2009) Cyclic strech induced miR-146° upregulation delays C2C12 myogenic differentiation through inhibition of Numb. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:259–263
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 12:15–20
Li G, Luna C, Qiu J, Epstein DL, Gonzalez P (2011) Role of miR-204 in the regulation of apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress response, and inflammation in human trabecular meshwork cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:2999–3007
Lin GL, Hankenson KD (2011) Integration of BMP, Wnt, and Notch signalling pathways in osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Biochem 112:3491–3501
Lindroos B, Suuronen R, Miettinen S (2011) The potential of adipose stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Rev 7:269–291
Ling L, Nurcombe V, Cool SM (2009) Wnt signalling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene 433:1–7
Liu Z, Sall A, Yang D (2008) MicroRNA: an emerging therapeutic target and intervention tool. Int J Mol Sci 9:978–999
Nagaoka T, Karasawa H, Castro NP, Rangel MC, Salomon DS, Bianco C (2012) An evolving web of signaling networks regulated by Cripto-1. Growth Factors 30:13–21
Nimmo RA, Slack FJ (2009) An elegant miRror: microRNAs in stem cells, developmental timing and cancer. Chromosoma 118:405–418
Ong WK, Sugii S (2013) Adipose-derived stem cells: fatty potentials for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:1083–1086
Orciani M, Gorbi S, Benedetti M, Di Benedetto G, Mattioli-Belmonte M, Regoli F, Di Primio R (2010a) Oxidative stress defense in human-skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus human keratinocytes: different mechanisms of protection and cell selection. Free Radic Biol Med 49:830–838
Orciani M, Mariggiò MA, Morabito C, Di Benedetto G, Di Primio R (2010b) Functional characterization of calcium-signaling pathways of human skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 23:124–132
Orciani M, Morabito C, Emanuelli M, Guarnieri S, Sartini D, Giannubilo SR, Di Primio R, Tranquilli AL, Mariggiò MA (2011a) Neurogenic potential of mesenchymal-like stem cells from human amniotic fluid: the influence of extracellular growth factors. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 25:115–130
Orciani M, Campanati A, Salvolini E, Lucarini G, Di Benedetto G, Offidani A, Di Primio R (2011b) The mesenchymal stem cell profile in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 165:585–592
Papadopoulos GL, Alexiou P, Maragkakis M, Reczko M, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2009) DIANA-mirPath: integrating human and mouse microRNAs in pathways. Bioinformatics 25:1991–1993
Salvolini E, Orciani M, Lucarini G, Vignini A, Tranquilli AL, Di Primio R (2011) VEGF and nitric oxide synthase immunoexpression in Down’s syndrome amniotic fluid stem cells. Eur J Clin Investig 41:23–29
Saulnier N, Lattanzi W, Puglisi MA, Pani G, Barba M, Piscaglia AC, Giachelia M, Alfieri S, Neri G, Gasbarrini G, Gasbarrini A (2009) Mesenchymal stromal cells multipotency and plasticity: induction toward the hepatic lineage. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci Suppl 1:71–78
Scuteri A, Miloso M, Foudah D, Orciani M, Cavaletti G, Tredici G (2011) Mesenchymal stem cells neuronal differentiation ability: a real perspective for nervous system repair? Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 6:82–92, Review
Talebi S, Aleyasin A, Soleimani M, Massumi M (2012) Derivation of islet-like cells from mesenchymal stem cells using PDX1-transducing lentiviruses. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 59:205–212
Zamani N, Brown CW (2011) Emerging roles for the transforming growth factor-{beta} superfamily in regulating adiposity and energy expenditure. Endocr Rev 32:387–403
Zhang Y, Liang X, Lian Q, Tse HF (2013) Perspective and challenges of mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular regeneration. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 11:505–517
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Lang MF, Yang S, Li W, Shi Y (2010) MicroRNA-let7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:1876–1881
Zhou S, Eid K, Glowacki J (2003) Cooperation between TGF-beta and Wnt pathways during chondrocyte and adipocyte differentiation of human marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 19:463–470
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant FIRB-RBAP10MLK7_003 from Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca, Rome, Italy
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Sequences of the primers used in PCR. (DOC 31 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
MiRs grouped based on expression in S-MSCs compared to AF-MSCs. Group A: miRs similarly expressed in AF-MSCs and S-MSCs; Group B: miRs up-regulated and group C: miRs down-regulated in S-MSCs vs. AF-MSCs. miRNAs subsequently subjected to validation by qRT-PCR are marked in bold. (DOC 17.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazzarini, R., Olivieri, F., Ferretti, C. et al. mRNAs and miRNAs profiling of mesenchymal stem cells derived from amniotic fluid and skin: the double face of the coin. Cell Tissue Res 355, 121–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1725-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1725-4