Abstract
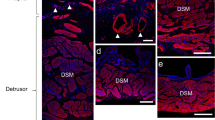
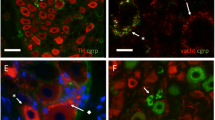
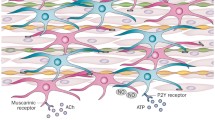
Morphological and functional studies have confirmed that interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are involved in many enteric motor neurotransmission pathways. Recent investigations have demonstrated that human and guinea pig prostate glands possess a distinct cell type with morphological and immunological similarities to ICCs. These prostate ICCs have a close relationship with nerve bundles and smooth muscle cells. Prostate smooth muscle tone is largely induced by stimulation from the sympathetic nervous system, which releases excitatory norepinephrine (NE) to act on the α1-adrenoceptor. We have performed morphological and functional experiments to determine the role of ICCs in sympathetic neurotransmission in the guinea pig prostate based on the hypothesis that prostate ICCs act as mediators of sympathetic neurotransmission. Immunohistochemistry revealed many close points of contact between ICCs and sympathetic nerve bundles and smooth muscle cells. Double-labeled sections revealed that α1-adrenoceptor and the gap junction protein connexin 43 were expressed in prostate ICCs. Surprisingly, prostate ICCs co-expressed tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase, two markers of sympathetic neurons. Functionally, the application of NE evoked a large single inward current in isolated prostate ICCs in a dose-dependent manner. The inward current evoked by NE was mediated via the activation of α1-adrenoceptors, because it was abolished by the non-specific α-adrenoceptor antagonist, phentolamine and the specific α1-adrenoceptor antagonist, prazosin. Thus, ICCs in the guinea pig prostate are target cells for prostate sympathetic nerves and possess the morphological and functional characteristics required to mediate sympathetic signals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arver S, Sjöstrand NO (1982) Functions of adrenergic and cholinergic nerves in canine effectors of seminal emission. Acta Physiol Scand 115:67–77
Beckett EA, Takeda Y, Yanase H, Sanders KM, Ward SM (2005) Synaptic specializations exist between enteric motor nerves and interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine stomach. J Comp Neurol 493:193–206
Burns AJ, Lomax AE, Torihashi S, Sanders KM, Ward SM (1996) Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate inhibitory neurotransmission in the stomach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12008–12013
Davidson RA, McCloskey KD (2005) Morphology and localization of interstitial cells in the guinea-pig bladder: structural relationships with smooth muscle and neurons. J Urol 173:1385–1390
Eckert RE, Schreier U, Drescher P, Madsen PO, Derouet H, Becht E, Steffens J, Ziegler M (1995) Regulation of prostatic smooth muscle contractility by intracellular second messengers: implications for the conservative treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Int 54:6–21
Epperson A, Hatton WJ, Callaghan B, Doherty P, Walker RL, Sanders KM, Ward SM, Horowitz B (2000) Molecular markers expressed in cultured and freshly isolated interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol 279:C529–C539
Exintaris B, Klemm MF, Lang RJ (2002) Spontaneous slow wave and contractile activity of the guinea pig prostate. J Urol 168:315–322
Harrington AM, Hutson JM, Southwell BR (2005) Immunohistochemical localization of substance P NK1 receptor in guinea pig distal colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:727–737
Horiguchi K, Sanders KM, Ward SM (2003) Enteric motor neurons form synaptic-like junctions with interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine gastric antrum. Cell Tissue Res 311:299–313
Horowitz B, Ward SM, Sanders KM (1999) Cellular and molecular basis for electrical rhythmicity in gastrointestinal muscles. Annu Rev Physiol 61:19–43
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Klüppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A (1995) W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 373:347–349
Iino S, Horiguchi K, Nojyo Y, Ward SM, Sanders KM (2009) Interstitial cells of Cajal contain signalling molecules for transduction of nitrergic stimulation in guinea pig caecum. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:542–550
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, You HJ, Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, Kim MJ, Lee KP, So I, Kim KW (2004) Substance P induces inward current and regulates pacemaker currents through tachykinin NK1 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal of murine small intestine. Eur J Phamacol 495:35–42
Kunisawa Y, Kawabe K, Niijima T, Honda K, Takenaka T (1985) A pharmacological study of alpha adrenergic receptor subtypes in smooth muscle of human urinary bladder base and prostatic uretha. J Urol 134:396–398
Lam M, Shigemasa Y, Exintaris B, Lang RJ, Hashitani H (2011) Spontaneous Ca2+ signaling of interstitial cells in the guinea pig prostate. J Urol 186:2478–2486
Lavin ST, Southwell BR, Murphy R, Jenkinson KM, Furness JB (1998) Activation of neurokinin 1 receptors on interstitial cells of Cajal of the guinea-pig small intestine by substance P. Histochem Cell Biol 110:263–271
Maeda H, Yamagata A, Nishikawa S, Yoshinaga K, Kobayashi S, Nishi K, Nishikawa S (1992) Requirement of c-kit for development of intestinal pacemaker system. Development 116:369–375
McCloskey KD, Gurney AM (2002) Kit-positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 168:832–869
Nemeth L, Puri P (2001) Three-dimensional morphology of c-Kit-positive cellular network and nitrergic innervation in the human gut. Arch Pathol Lab Med 125:899–904
Nguyen DT, Dey A, Lang RJ, Ventura S, Exintaris B (2011) Contractility and pacemaker cells in the prostate gland. J Urol 185:347–351
Ohkawa H (1983) Sympathetic neuromuscular transmission in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig prostate gland. Int J Fertil 28:68–77
Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Cretoiu D, Radu E (2005) The connective connection: interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) and ICC-like cells establish synapses with immunoreactive cells. Electron microscope study in situ. J Cell Mol Med 9:714–730
Salmhofer H, Neuhuber WL, Ruth P, Huber A, Russwurm M, Allescher HD (2001) Pivotal role of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the nitric oxide signaling pathway of rat small intestine. Morphological evidence. Cel1 Tissue Res 305:331–340
Sanders KM (1996) A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 111:492–515
Seki K, Komuro T (2001) Immunocytochemical demonstration of the gap junction proteins connexin 43 and connexin 45 in the musculature of the rat small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 306:417–422
Seki K, Zhou DS, Komuro T (1998) Immunohistochemical study of the c-kit expressing cells and connexin 43 in the guinea-pig digestive tract. J Auton Nerv Syst 68:182–187
Seki N, Suzuki H (1989) Electrical and mechanical activity of rabbit prostate smooth muscles in response to nerve stimulation. J Physiol (Lond) 419:651–663
Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McCloskey KD, Thornbury KD, McHale NG (2000) Specialised pacemaking cells in the rabbit urethra. J Physiol (Lond) 526:359–366
Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McCloskey KD, McHale NG, Thornbury KD (2001) Role of IP3 in modulation of spontaneous activity in pacemaker cells of rabbit urethra. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:1349–1356
Sergeant GP, Thornbury KD, McHale NG, Hollywood MA (2002) Characterization of norepinephrine-evoked inward currents in interstitial cells isolated from the rabbit urethra. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:885–894
Shafik A, Shafik I, el-Sibai O (2005) Identification of c-kit-positive cells in the human prostate: the interstitial cells of Cajal. Arch Androl 51:345–351
Spray DC, Bennett MV (1985) Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 47:281–303
Van der Aa F, Roskams T, Blyweert W, De Ridder D (2003) Interstitial cells in the human prostate: a new therapeutic target? Prostate 56:250–255
Wang XY, Paterson C, Huizinga JD (2003) Cholinergic and nitrergic innervation of ICC-DMP and ICC-IM in the human small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:531–543
Wang YF, Daniel EE (2001) Gap junctions in gastrointestinal muscle contain multiple connexins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:533–543
Ward SM, Morris G, Reese L, Wang XY, Sanders KM (1998) Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate enteric inhibitory neurotransmission in the lower esophageal and pyloric sphincters. Gastroenterology 115:314–329
Ward SM, Beckett EAH, Wang XY, Baker F, Khoyi M, Sanders KM (2000) Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate cholinergic neurotransmission from enteric motor neurons. J Neurosci 20:1393–1403
Ward SM, Sanders KM, Hirst GD (2004) Role of interstitial cells of Cajal in neural control of gastrointestinal smooth muscles. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:112–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was funded by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, project no. 81060064.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jp., Ding, Gf. & Wang, Qz. Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate excitatory sympathetic neurotransmission in guinea pig prostate. Cell Tissue Res 352, 479–486 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1572-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1572-3