Abstract
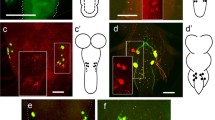
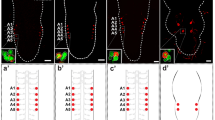
The distribution of leucokinin (LK) neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) of Drosophila melanogaster was described by immunolabelling many years ago. However, no detailed underlying information of the input or output connections of their neurites was then available. Here, we provide a more accurate morphological description by employing a novel LK-specific GAL4 line that recapitulates LK expression. In order to analyse the possible afferent and efferent neural candidates of LK neurons, we used this lk-GAL4 line together with other CNS-Gal4 lines, combined with antisera against various neuropeptides or neurotransmitters. We found four kinds of LK neurons in the brain. (1) The lateral horn neurons connect the antennal glomerula to the mushroom bodies. (2) The suboesophageal neurons connect the gustatory receptors to the suboesophageal ganglia and ventral nerve cord. (3) The anterior neurons innervate the corpus cardiacum of the ring gland but LK expression is surprisingly not detectable from the third instar onwards in these neurons. (4) A set of abdominal ganglion neurons connect to the dorsal median tract in larvae and send their axons to a segmental muscle 8. Thus, the methods employed in our study can be used to identify individual neuropeptidergic neurons and thereby characterize functional cues or developmental transformations in their differentiation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acebes A, Ferrús A (2001) Increasing the number of synapses modifies olfactory perception in Drosophila. J Neurosci 21:6264–6273
Cantera R, Nässel DR (1992) Segmental peptidergic innervation of abdominal targets in larval and adult dipteran insects revealed with antiserum against leucokinin I. Cell Tissue Res 269:459–471
Chen Y, Veenstra JA, Davis NT, Hagedorn HH (1994) A comparative study of leucokinin-immunoreactive neurons in insects. Cell Tissue Res 276:69–83
Clark E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1997) Reciprocal localization of Nod and kinesin fusion proteins indicates microtubule polarity in the Drosophila oocyte, epithelium neuron and muscle. Development 124:461–470
Connolly JB, Roberts IJ, Armstrong JD, Kaiser K, Forte M (1996) Associative learning disrupted by impaired Gs signalling in Drosophila mushroom bodies. Science 274:2104–2107
Fischler W, Kong P, Marella S, Scott K (2007) The detection of carbonation by the Drosophila gustatory system. Nature 448:1054–1058
Friggi-Grelin F, Coulom H, Meller M, Gómez D, Hirsh J, Birman S (2003) Targeted gene expression in Drosophila dopaminergic cells using regulatory sequences from tyrosine hydroxylase. J Neurobiol 54:618–627
Gendre N, Lüer K, Friche S, Grillenzoni N, Ramaekers A, Technau GM, Stocker RF (2004) Integration of complex larval chemosensory organs into the adult nervous system of Drosophila. Development 131:83–92
Herrero P, Magariños M, Torroja L, Canal I (2003) Neurosecretory identity conferred by the apterous gene: lateral horn leucokinin neurons in Drosophila. J Comp Neurol 457:123–132
Herrero P, Magariños M, Molina I, Benito J, Dorado B, Turiégano E, Canal I, Torroja L (2007) Squeeze involvement in the specification of Drosophila leucokinergic neurons: different regulatory mechanisms endow the same neuropeptide selection. Mech Dev 124:427–440
Johard HA, Enell LE, Gustafsson E, Trifilieff P, Veenstra JA, Nässel DR (2008) Intrinsic neurons of Drosophila mushroom bodies express short neuropeptide F: relations to extrinsic neurons expressing different neurotransmitters. J Comp Neurol 507:1479–1496
Keene AC, Waddell S (2007) Drosophila olfactory memory: single genes to complex neural circuits. Nat Rev 8:341–354
Landgraf M, Sánchez-Soriano N, Technau GM, Urban J, Prokop A (2003) Charting the Drosophila neuropile: a strategy for the standardised characterisation of genetically amenable neurites. Dev Biol 260:207–225
Mahr A, Aberle H (2006) The expression pattern of the Drosophila vesicular glutamate transporter: a marker protein for motoneurons and glutamatergic centers in the brain. Gene Expr Patterns 6:299–309
Marella S, Fischler W, Kong P, Asgarian S, Rueckert E, Scott K (2006) Imaging taste responses in the fly brain reveals a functional map of taste category and behaviour. Neuron 49:285–295
Melcher C, Pankratz MJ (2005) Candidate gustatory interneurons modulating feeding behaviour in the Drosophila brain. PLoS Biol 3:e305
Nässel DR (2002) Neuropeptides in the nervous system of Drosophila and other insects: multiple roles of neuromodulators and neurohormones. Prog Neurobiol 68:1–84
Nässel DR, Homberg U (2006) Neuropeptides in interneurons of insect brain. Cell Tissue Res 326:1–24
O’Donnell MJ, Rheault MR, Davies SA, Rosay P, Harvey BJ, Maddrell HP, Kaiser K, Dow JAT (1998) Hormonally controlled chloride movement across Drosophila tubules is via ion channels in stellate cells. Am J Physiol 43:R1039–R1049
Rubin GM, Sprading AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila melanogaster with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Santos JG, Vömel M, Struck R, Homberg U, Nässel DR, Wegener C (2007) Neuroarchitecture of peptidergic systems in the larval ventral ganglion of Drosophila melanogaster. PlosOne 2:e695
Schroll C, Riemensperger T, Bucher D, Ehmer J, Voller T, Erbguth K, Gerber B, Hendel T, Nagel G, Buchner F, Fiala A (2006) Light-induced activation of distinct modulatory neurons trigger appetitive or aversive learning in Drosophila larvae. Curr Biol 16:1741–1747
Scott K, Brady R, Cravchik A, Morozov P, Rzhetsky A, Zuker C, Axel R (2001) A chemosensory gene family encoding candidate gustatory and olfactory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 104:661–673
Schwaerzel M, Monastirioti M, Scholz H, Friggi-Grelin F, Birman S, Heisenberg M (2003) Dopamine and octopamine differentiate between aversive and appetitive olfactory memories in Drosophila. J Neurosci 23:10496–10502
Siegmund T, Korge G (2001) Innervations of the ring gland of Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 431:481–491
Sinakevitch I, Strausfeld J (2004) Chemical neuroanatomy of the fly’s movement detection pathway. J Comp Neurol 468:6–23
Stocker RF (1994) The organization of the chemosensory system in Drosophila melanogaster: a review. Cell Tissue Res 275:3–26
Stocker RF, Heimbeck G, Gendre N, Belle JS de (1997) Neuroblast ablation in Drosophila P[GAL4] lines reveals origins of olfactory interneurons. J Neurobiol 32:443–456
Strausfeld NJ (1976) Atlas of an insect brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Taghert PH, Veenstra JA (2003) Drosophila neuropeptide signalling. Adv Genet 49:1–65
Terhzaz S, O’Connell FC, Pollock VP, Kean L, Davies SA, Veenstra JA, Dow JAT (1999) Isolation and characterization of a leucokinin-like peptide of Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol 202:3667–3676
Thorne N, Chromey C, Bray S, Amrein H (2004) Taste perception and coding in Drosophila. Curr Biol 14:1065–1079
Veenstra JA (2008) Regulatory peptides in fruit fly midgut. Cell Tissue Res 334:499–516
Veenstra JA, Pattillo JM, Petzel DH (1997) A single cDNA encodes all three Aedes leucokinins, which stimulate both fluid secretion by the Malpighian tubules and hindgut contractions. J Biol Chem 272:10402–10407
Waddell S, Armstrong JD, Kitamoto T, Kaiser K, Quinn WG (2000) The amnesiac gene product is expressed in two neurons in the Drosophila brain that are critical for memory. Cell 103:805–813
Wang Z, Singhvi A, Kong P, Scott K (2004) Taste representations in the Drosophila brain. Cell 117:981–991
Wong AM, Wang JW, Axel R (2002) Spatial representation of the glomerular map in the Drosophila protocerebrum. Cell 109:229–241
Zhang K, Guo JZ, Peng Y, Xi W, Guo A (2007) Dopamine-mushroom body circuit regulates saliency-based decision-making in Drosophila. Science 316:1901–1904
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Reinhard Stocker, Manolo Calleja, Angel Acebes, Hermann Aberle, Laura Torroja and Richard Axel for kindly providing the fly stocks and to Hermann Aberlee for generously providing V-Glut antisera. We thank Laura Torroja and Isabel Molina for their technical assistance with the transgenic constructs and histological muscle preparations from larvae, Cristina Nuñez de Arce for her help in the laboratory and Carlos Sánchez, Verónica Labrador and Angeles Muñoz for their help with the confocal microscopy. We also thank Phil Mason for improving the English language of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid—Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid (CCG07/UAM/SAL-1551) and from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology (BFU2004-03894).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Haro, M., Al-Ramahi, I., Benito-Sipos, J. et al. Detailed analysis of leucokinin-expressing neurons and their candidate functions in the Drosophila nervous system. Cell Tissue Res 339, 321–336 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0890-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0890-y