Abstract
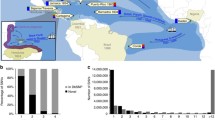
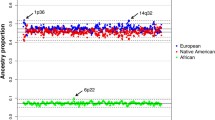
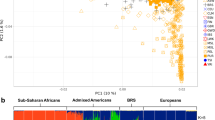
Admixed populations present unique opportunities to discover the genetic factors underlying many multifactorial diseases. The geographical position and complex history of South Africa has led to the establishment of the unique admixed population known as the South African Coloured. Not much is known about the genetic make-up of this population, and the historical record is patchy. We genotyped 959 individuals from the Western Cape area, self-identified as belonging to this population, using the Affymetrix 500k genotyping platform. This resulted in nearly 75,000 autosomal SNPs that could be compared with populations represented in the International HapMap Project and the Human Genome Diversity Project. Analysis by means of both the admixture and linkage models in STRUCTURE revealed that the major ancestral components of this population are predominantly Khoesan (32–43%), Bantu-speaking Africans (20–36%), European (21–28%) and a smaller Asian contribution (9–11%), depending on the model used. This is consistent with historical data. While of great historical and genealogical interest, this information is also essential for future admixture mapping of disease genes in this population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari M (2005) Not white enough, not black enough: racial identity in the South African Coloured community. Ohio University Press
Affymetrix (2006) BRLMM: an improved genotype calling method for the GeneChip Human Mapping 500K Array Set. Affymetrix
Babb C, van der Merwe L, Beyers N, Pheiffer C, Walzl G, Duncan K, van Helden P, Hoal EG (2007) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and sputum conversion time in pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Tuberculosis 87:295–302
Barreiro LB, Neyrolles O, Babb CL, Tailleux L, Quach H, McElreavey K, Helden PD, Hoal EG, Gicquel B, Quintana-Murci L (2006) Promoter variation in the DC-SIGN encoding gene CD209 is associated with tuberculosis. PLoS Med 3:e20
Barth F (1969) Ethnic groups and boundaries: the social organization of culture difference. Little, Brown and company, Boston
Boonzaaier E, Malherbe C, Smith A, Berens P (1996) The Cape Herders: a history of the Khoikhoi of Southern Africa. David Philip Publishers, Cape Town
Botha MC (1972) Blood group gene frequencies. An indication of the genetic constitution of population samples in Cape Town. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 115:Suppl 27
Campbell MC, Tishkoff SA (2008) African genetic diversity: implications for human demographic history, modern human origins, and complex disease mapping. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 9:403–433
Cann HM, de Toma C, Cazes L, Legrand MF, Morel V, Piouffre L, Bodmer J, Bodmer WF, Bonne-Tamir B, Cambon-Thomsen A, Chen Z, Chu J, Carcassi C, Contu L, Du R, Excoffier L, Ferrara GB, Friedlaender JS, Groot H, Gurwitz D, Jenkins T, Herrera RJ, Huang X, Kidd J, Kidd KK, Langaney A, Lin AA, Mehdi SQ, Parham P, Piazza A, Pistillo MP, Qian Y, Shu Q, Xu J, Zhu S, Weber JL, Greely HT, Feldman MW, Thomas G, Dausset J, Cavalli-Sforza LL (2002) A human genome diversity cell line panel. Science 296:261–262
Cilliers SP (1963) The Coloureds of South Africa: a factual survey. Banier Publishers (Pty) Ltd, Cape Town
Conrad DF, Jakobsson M, Coop G, Wen X, Wall JD, Rosenberg NA, Pritchard JK (2006) A worldwide survey of haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat Genet 38:1251–1260
Cooke GS, Campbell SJ, Bennett S, Lienhardt C, McAdam KP, Sirugo G, Sow O, Gustafson P, Mwangulu F, van HP, Fine P, Hoal EG, Hill AV (2008) Mapping of a novel susceptibility locus suggests a role for MC3R and CTSZ in human tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:203–207
Elphick R (1985) Khoikhoi and the founding of White South Africa. Ravan Press, Johannesburg
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Frazer KA, Ballinger DG, Cox DR, Hinds DA, Stuve LL, Gibbs RA, Belmont JW, Boudreau A, Hardenbol P, Leal SM, Pasternak S, Wheeler DA, Willis TD, Yu F, Yang H, Zeng C, Gao Y, Hu H, Hu W, Li C, Lin W, Liu S, Pan H, Tang X, Wang J, Wang W, Yu J, Zhang B, Zhang Q, Zhao H, Zhao H, Zhou J, Gabriel SB, Barry R, Blumenstiel B, Camargo A, Defelice M, Faggart M, Goyette M, Gupta S, Moore J, Nguyen H, Onofrio RC, Parkin M, Roy J, Stahl E, Winchester E, Ziaugra L, Altshuler D, Shen Y, Yao Z, Huang W, Chu X, He Y, Jin L, Liu Y, Shen Y, Sun W, Wang H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Xiong X, Xu L, Waye MMY, Tsui SKW, Xue H, Wong JT-F, Galver LM, Fan JB, Gunderson K, Murray SS, Oliphant AR, Chee MS, Montpetit A, Chagnon F, Ferretti V, Leboeuf M, Olivier JF, Phillips MS, Roumy S, Sallée C, Verner A, Hudson TJ, Kwok PY, Cai D, Koboldt DC, Miller RD, Pawlikowska L, Taillon-Miller P, Xiao M, Tsui LC, Mak W, Song YQ, Tam PKH, Nakamura Y, Kawaguchi T, Kitamoto T, Morizono T, Nagashima A, Ohnishi Y, Sekine A, Tanaka T, Tsunoda T, Deloukas P, Bird CP, Delgado M, Dermitzakis ET, Gwilliam R, Hunt S, Morrison J, Powell D, Stranger BE, Whittaker P, Bentley DR, Daly MJ, de Bakker PIW, Barrett J, Chretien YR, Maller J, McCarroll S, Patterson N, Pe’er I, Price A, Purcell S, Richter DJ, Sabeti P, Saxena R, Schaffner SF, Sham PC, Varilly P, Altshuler D, Stein LD, Krishnan L, Smith AV, Tello-Ruiz MK, Thorisson GA, Chakravarti A, Chen PE, Cutler DJ, Kashuk CS, Lin S, Abecasis GR, Guan W, Li Y, Munro HM, Qin ZS, Thomas DJ, McVean G, Auton A, Bottolo L, Cardin N, Eyheramendy S, Freeman C, Marchini J, Myers S, Spencer C, Stephens M, Donnelly P, Cardon LR, Clarke G, Evans DM, Morris AP, Weir BS, Tsunoda T, Mullikin JC, Sherry ST, Feolo M, Skol A, Zhang H, Zeng C, Zhao H, Matsuda I, Fukushima Y, Macer DR, Suda E, Rotimi CN, Adebamowo CA, Ajayi I, Aniagwu T, Marshall PA, Nkwodimmah C, Royal CDM, Leppert MF, Dixon M, Peiffer A, Qiu R, Kent A, Kato K, Niikawa N, Adewole IF, Knoppers BM, Foster MW, Clayton EW, Watkin J, Gibbs RA, Belmont JW, Muzny D, Nazareth L, Sodergren E, Weinstock GM, Wheeler DA, Yakub I, Gabriel SB, Onofrio RC, Richter DJ, Ziaugra L, Birren BW, Daly MJ, Altshuler D, Wilson RK, Fulton LL, Rogers J, Burton J, Carter NP, Clee CM, Griffiths M, Jones MC, McLay K, Plumb RW, Ross MT, Sims SK, Willey DL, Chen Z, Han H, Kang L, Godbout M, Wallenburg JC, L’Archevêque P, Bellemare G, Saeki K, Wang H, An D, Fu H, Li Q, Wang Z, Wang R, Holden AL, Brooks LD, McEwen JE, Guyer MS, Wang VO, Peterson JL, Shi M, Spiegel J, Sung LM, Zacharia LF, Collins FS, Kennedy K, Jamieson R, Stewart J (2007) A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 449:851–861
Greeff JM (2007) Deconstructing Jaco: genetic heritage of an Afrikaner. Ann Hum Genet 71:674–688
Heese JA (1971) Die Herkoms van die Afrikaner, 1657–1867. A Balkema, Cape Town
Hoal EG, Lewis L-A, Jamieson SE, Tanzer F, Rossouw M, Victor T, Hillerman R, Beyers N, Blackwell JM, van Helden PD (2004) SLC11A1 (NRAMP1) but not SLC11A2 (NRAMP2) polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in a high-incidence community in South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 8:1464–1471
Keegan T (1996) Colonial South Africa and the origins of the racial order. David Philip Publishers, Cape Town
Kritzinger FE, den BS, Verver S, Enarson DA, Lombard CJ, Borgdorff MW, Gie RP, Beyers N (2009) No decrease in annual risk of tuberculosis infection in endemic area in Cape Town, South Africa. Trop Med Int Health 14:136–142
Li JZ, Absher DM, Tang H, Southwick AM, Casto AM, Ramachandran S, Cann HM, Barsh GS, Feldman M, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Myers RM (2008) Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation. Science 319:1100–1104
McKeigue PM (1997) Mapping genes underlying ethnic differences in disease risk by linkage disequilibrium in recently admixed populations. Am J Hum Genet 60:188–196
Möller M, Kwiatkowski R, Nebel A, van Helden PD, Hoal EG, Schreiber S (2007) Allelic variation in BTNL2 and susceptibility to tuberculosis in a South African population. Microbes Infect 9:522–528
Möller M, Nebel A, Valentonyte R, van Helden PD, Schreiber S, Hoal EG (2009) Investigation of chromosome 17 candidate genes in susceptibility to TB in a South African population. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 89:189–194
Montana G, Pritchard JK (2004) Statistical tests for admixture mapping with case–control and cases-only data. Am J Hum Genet 75:771–789
Mountain A (2003) The first people of the Cape, 1st edn. David Philips Publishers, Cape Town
Mountain A (2004) An unsung heritage. David Philip Publishers, Cape Town
Nurse GT, Weiner JS, Jenkins T (1985) The peoples of Southern Africa and their affinities. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D (2006) Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2:e190
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Quintana-Murci L, Harmant C, Quach H, Balanovsky O, Zaporozhchenko V, Bormans C, van Helden PD, Hoal EG, Behar DM (2010) Strong maternal Khoisan contribution to the South African Coloured population: a case of gender-biased admixture. Am J Hum Genet 86:611–620
Rosenberg N (2004) DISTRUCT: a program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol Ecol Notes 4:137–138
Rosenberg NA, Li LM, Ward R, Pritchard JK (2003) Informativeness of genetic markers for inference of ancestry. Am J Hum Genet 73:1402–1422
Rossouw M, Nel HJ, Cooke GS, van Helden PD, Hoal EG (2003) Association between tuberculosis and a polymorphic NFkappaB binding site in the interferon gamma gene. Lancet 361:1871–1872
Seldin MF (2007) Admixture mapping as a tool in gene discovery. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17:177–181
Shell R (1994) Children of bondage. Witwatersrand University Press, Johannesburg
Stead WW, Senner JW, Reddick WT, Lofgren JP (1990) Racial differences in susceptibility to infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 322:422–427
Tang H, Peng J, Wang P, Risch NJ (2005) Estimation of individual admixture: analytical and study design considerations. Genet Epidemiol 28:289–301
The International HapMap Consortium (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437:1299–1320
Thorp CR (2000) Hunter-Gatherers and farmers: an enduring frontier in the Caledon Valley, South Africa. Publishers of British Archaeological Reports
Tishkoff SA, Kidd KK (2004) Implications of biogeography of human populations for ‘race’ and medicine. Nat Genet 36:S21–S27
Tishkoff SA, Williams SM (2002) Genetic analysis of African populations: human evolution and complex disease. Nat Rev Genet 3:611–621
Tishkoff SA, Reed FA, Friedlaender FR, Ehret C, Ranciaro A, Froment A, Hirbo JB, Awomoyi AA, Bodo JM, Doumbo O, Ibrahim M, Juma AT, Kotze MJ, Lema G, Moore JH, Mortensen H, Nyambo TB, Omar SA, Powell K, Pretorius GS, Smith MW, Thera MA, Wambebe C, Weber JL, Williams SM (2009) The genetic structure and history of Africans and African Americans. Science 324:1035–1044
Van der Ross RE (1993) 100 questions about Coloured South Africans. UWC Printing Department, Cape Town
Zhu X, Zhang S, Tang H, Cooper R (2006) A classical likelihood based approach for admixture mapping using EM algorithm. Hum Genet 120:431–445
Zhu X, Tang H, Risch N (2008) Admixture mapping and the role of population structure for localizing disease genes. Adv Genet 60:547–569
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants on this study, Alan Morris for helpful discussions, and The Meraka Institute (http://www.meraka.org.za/) for computational resources. We are grateful to Karen Small of Strategic Development Information and GIS, City of Cape Town for provision of demographic data. We thank GlaxoSmithKline for the donation of the GeneChip Human Mapping 500K Array Sets from Affymetrix. The experiments performed in this study comply with the current laws of South Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The collective term for people of mixed ancestry in southern Africa is “Coloured” and is recognized and used officially in South Africa. Whilst we acknowledge that in some cultures this term may have acquired a derogatory connotation, this is certainly not intended here.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2010_836_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1 Estimates of the number of ancestral populations (K) for the SAC and combined HapMap and HGDP samples under an admixture model using the STRUCTURE software. The estimated probability of the data given the model is plotted against increasing K for each of the subsets of SNP data used (see Methods) (TIFF 6 kb)
439_2010_836_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Figure S2 Proportion of each individual’s ancestry for the number of ancestral populations from k = 2 to the estimated number of ancestral populations with greatest probability (Fig S1). Plots shown are for random linked SNPs (TIFF 600 kb)
439_2010_836_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Figure S3 Proportion of each individual’s ancestry for the number of ancestral populations from k = 2 to the estimated number of ancestral populations with greatest probability (Fig S1). Plots shown are for unlinked random SNPs (TIFF 256 kb)
439_2010_836_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Figure S4 Proportion of each individual’s ancestry for the number of ancestral populations from k = 2 to the estimated number of ancestral populations with greatest probability (Fig S1). Plots shown are for linked Ancestry Informative Markers (TIFF 356 kb)
439_2010_836_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Figure S5: Proportion of each individual’s ancestry derived using the linkage model in STRUCTURE for the optimal number of ancestral populations (K = 4) (TIFF 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Wit, E., Delport, W., Rugamika, C.E. et al. Genome-wide analysis of the structure of the South African Coloured Population in the Western Cape. Hum Genet 128, 145–153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0836-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0836-1