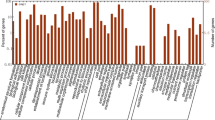
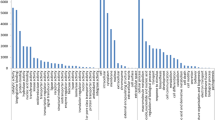
Abstract
We performed de novo transcriptome sequencing for Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius accessions using the 454 GS FLX Titanium System and discovered annotation-based genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) using next-generation ginseng transcriptome data without reference genome sequence. The comprehensive transcriptome characterization with the mature roots of four ginseng accessions generated 297,170 reads for ‘Cheonryang’ cultivar, 305,673 reads for ‘Yunpoong’ cultivar, 311,861 reads for the G03080 breeding line, and 308,313 reads for P. quinquefolius. In transcriptome assembly, the lengths of the sample read were 156.42 Mb for ‘Cheonryang’, 161.95 Mb for ‘Yunpoong’, 165.07 Mb for G03080 breeding line, and 166.48 Mb for P. quinquefolius. A total of 97 primer pairs were designed with the homozygous SNP presented in all four accessions. SNP genotyping using high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis was performed to validate the putative SNP markers of 97 primer pairs. Out of the 73 primer pairs, 73 primer pairs amplified the target sequence and 34 primer pairs showed polymorphic melting curves in samples from 11 P. ginseng cultivars and one P. quinquefolius accession. Among the 34 polymorphic HRM-SNP primers, four primers were useful to distinguish ginseng cultivars. In the present study, we demonstrated that de novo transcriptome assembly and mapping analyses are useful in providing four HRM-SNP primer pairs that reliably show a high degree of polymorphism among ginseng cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador V, Monte E, Garcı́a-Martı́nez JL, Prat S (2001) Gibberellins signal nuclear import of PHOR1, a photoperiod-responsive protein with homology to Drosophila armadillo. Cell 106:343–354
Azevedo C, Santos-Rosa MJ, Shirasu K (2001) The U-box protein family in plants. Trends Plant Sci 6:354–358
Bajgain P, Richardson BA, Price JC, Cronn RC, Udall JA (2011) Transcriptome characterization and polymorphism detection between subspecies of big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata). BMC Genom 12:370
Barbazuk WB, Emrich SJ, Chen HD, Li L, Schnable PS (2007) SNP discovery via 454 transcriptome sequencing. Plant J 51:910–918
Broders KD, Woeste KE, SanMiguel PJ, Westerman RP, Boland GJ (2011) Discovery of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the uncharacterized genome of the ascomycete Ophiognomonia clavigignenti-juglandacearum from 454 sequence data. Mol Ecol Resour 11:693–702
Bundock PC, Eliott FG, Ablett G, Benson AD, Casu RE, Aitken KS, Henry RJ (2009) Targeted single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery in a highly polyploid plant species using 454 sequencing. Plant Biotechnol J 7:347–354
Chagné D, Gasic K, Crowhurst RN, Han Y, Bassett HC, Bowatte DR, Lawrence TJ, Rikkerink EHA, Gardiner SE, Korban SS (2008) Development of a set of SNP markers present in expressed genes of the apple. Genomics 92:353–358
Cheng Y, Zhang JT (2005) Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:143–149
Cheung F, Haas BJ, Goldberg SMD, May GD, Xiao Y, Town CD (2006) Sequencing Medicago truncatula expressed sequenced tags using 454 Life Sciences technology. BMC Genomics 7:272–282
Flint-Garcia SA, Thuillet AC, Yu J, Pressoir G, Romero SM, Mitchell SE, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2005) Maize association population: a high-resolution platform for quantitative trait locus dissection. Plant J 44:1054–1064
Ganopoulos I, Argiriou A, Tsaftaris A (2011) Microsatellite high resolution melting (SSR-HRM) analysis for authenticity testing of protected designation of origin (PDO) sweet cherry products. Food Control 22:532–541
Ganopoulos I, Madesis P, Darzentas N, Argiriou A, Tsaftaris A (2012) Barcode high resolution melting (Bar-HRM) analysis for detection and quantification of PDO “Fava Santorinis”(Lathyrus clymenum) adulterants. Food Chem 133:505–512
Garvin MR, Saitoh K, Gharrett AJ (2010) Application of single nucleotide polymorphisms to non-model species: a technical review. Mol Ecol Resour 10:915–934
Gebert M, Dresselhaus T, Sprunck S (2008) F-actin organization and pollen tube tip growth in Arabidopsis are dependent on the gametophyte-specific Armadillo repeat protein ARO1. Plant Cell Online 20:2798–2814
Geraldes A, DiFazio SP, Slavov GT, Ranjan P, Muchero W, Hannemann J, Gunter LE, Wymore AM, Grassa CJ, Farzaneh N, Porth I, McKown AD, Skyba O, Li E, Fujita M, Klápště J, Martin J, Schackwitz W, Pennacchio C, Rokhsar D, Friedmann MC, Wasteneys GO, Guy RD, El-Kassaby YA, Mansfield SD, Cronk QCB, Ehlting J, Douglas CJ, Tuskan GA (2013) A 34 K SNP genotyping array for Populus trichocarpa: design, application to the study of natural populations and transferability to other Populus species. Mol Ecol Resour 13:306–323
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Graham IA, Besser K, Blumer S, Branigan CA, Czechowski T, Elias L, Guterman I, Harvey D, Isaac PG, Khan AM (2010) The genetic map of Artemisia annua L. identifies loci affecting yield of the antimalarial drug artemisinin. Science 327:328–331
Hoffmann M, Hurlebaus J, Weilke C (2007) Novel methods for high-performance melting curve analysis using the LightCycler® 480 system. Biochemica 1:17–19
Hu SY (1976) The genus Panax (ginseng) in Chinese medicine. Econ Bot 30:11–28
Hyun DY (2012) Screening method for salinity tolerance in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Korea Patent 10-1128911
Jaakola L, Suokas M, Häggman H (2010) Novel approaches based on DNA barcoding and high-resolution melting of amplicons for authenticity analyses of berry species. Food Chem 123:494–500
Jo IH, Bang KH, Kim YC, Lee JW, Seo AY, Seong BJ, Kim HH, Kim DH, Cha SW, Cho YG, Kim HS (2011) Rapid identification of ginseng cultivars (Panax ginseng Meyer) using novel SNP-based probes. J Ginseng Res 35:504–513
Joo SS, Won TJ (2005) Reciprocal activity of ginsenosides in the production of proinflammatory repertoire, and their potential roles in neuroprotection in vitro. Planta Med 71:476–481
Kim JH, Kende H (2004) A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13374–13379
Kim SH, Park KS (2003) Effects of Panax ginseng extract on lipid metabolism in humans. Pharmacol Res 48:511–513
Kim OT, Bang KH, In DS, Lee JW, Kim YC, Shin YS, Hyun DY, Lee SS, Cha SW, Sung NS (2007) Molecular authentication of ginseng cultivars by comparison of internal transcribed spacer and 5.8S rDNA sequences. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1:163–167
Koepke T, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Jiwan D, Harper A, Whiting M, Oraguzie N, Dhingra A (2012) Rapid gene-based SNP and haplotype marker development in non-model eukaryotes using 3′UTR sequencing. BMC Genomics 13:18
Lai E, Riley J, Purvis I, Roses A (1998) A 4-Mb high-density single nucleotide polymorphism-based map around human APOE. Genomics 54:31–38
Lee JW, Bang KH, Kim YC, Seo AY, Jo IH, Lee JH, Kim OT, Hyun DY, Cha SW, Cho JH (2012) CAPS markers using mitochondrial consensus primers for molecular identification of Panax species and Korean ginseng cultivars (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer). Mol Biol Rep 39:729–736
Loridon K, Burgarella C, Chantret N, Martins F, Gouzy J, Prospéri J-M, Ronfort J (2013) Single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery and diversity in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Mol Ecol Resour 13:84–95
Martinowich K, Hattori D, Wu H, Fouse S, He F, Hu Y, Fan G, Sun YE (2003) DNA methylation-related chromatin remodeling in activity-dependent BDNF gene regulation. Science 302:890–893
Novaes E, Drost DR, Farmerie WG, Pappas GJ, Grattapaglia D, Sederoff RR, Kirst M (2008) High-throughput gene and SNP discovery in Eucalyptus grandis, an uncharacterized genome. BMC Genomics 9:312
Park CK, Jeon BS, Yang JW (2003) The chemical components of Korean ginseng. Food Ind Nutr 8:10–23
Rafalski A (2002) Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100
Robertson T, Bibby S, O’Rourke D, Belfiore T, Agnew-Crumpton R, Noormohammadi AH (2010) Identification of chlamydial species in crocodiles and chickens by PCR-HRM curve analysis. Vet Microbiol 145:373–379
Seeb JE, Carvalho G, Hauser L, Naish K, Roberts S, Seeb LW (2011) Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery and applications of SNP genotyping in nonmodel organisms. Mol Ecol Resour 11:1–8
Shin HR, Kim JY, Yun TK, Morgan G, Vainio H (2000) The cancer-preventive potential of Panax ginseng: a review of human and experimental evidence. Cancer Causes Control 11:565–576
Stone SL, Anderson EM, Mullen RT, Goring DR (2003) ARC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes the ubiquitination of proteins during the rejection of self-incompatible Brassica pollen. Plant Cell Online 15:885–898
Sun H, Wang H, Kwon WS, Kim YJ, In JG, Yang DC (2011) A simple and rapid technique for the authentication of the ginseng cultivar, Yunpoong, using an SNP marker in a large sample of ginseng leaves. Gene 487:75–79
Varshney RK, Nayak SN, May GD, Jackson SA (2009) Next-generation sequencing technologies and their implications for crop genetics and breeding. Trends Biotechnol 27:522–530
Wang LCH, Lee TF (2000) Effect of ginseng saponins on cold tolerance in young and elderly rats. Planta Med 66:144–147
Wang DG, Fan JB, Siao CJ, Berno A, Young P, Sapolsky R, Ghandour G, Perkins N, Winchester E, Spencer J (1998) Large-scale identification, mapping, and genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the human genome. Science 280:1077–1082
Wang H, Sun H, Kwon WS, Jin H, Yang DC (2009) Molecular identification of the Korean ginseng cultivar “Chunpoong” using the mitochondrial nad7 intron 4 region. Mitochondrial DNA 20:41–45
Wittwer CT, Reed GH, Gundry CN, Vandersteen JG, Pryor RJ (2003) High-resolution genotyping by amplicon melting analysis using LCGreen. Clin Chem 49:853–860
Wu SB, Wirthensohn MG, Hunt P, Gibson JP, Sedgley M (2008) High resolution melting analysis of almond SNPs derived from ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 118:1–14
Xie JT, Mehendale SR, Li X, Quigg R, Wang X, Wang C-Z, Wu JA, Aung HH, A Rue P, Bell GI (2005) Anti-diabetic effect of ginsenoside Re in ob/ob mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1740:319–325
Yun TK, Lee YS, Lee YH, Kim SI, Yun HY (2001) Anticarcinogenic effect of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer and identification of active compounds. J Korean Med Sci 16:S6–S18
Zhai J, Wang Y, Sun C, Jiang S, Wang K, Zhang Y, Zhang H-B, Zhang M (2013) A plant-transformation-competent BIBAC library of ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer) for functional genomics research and characterization of genes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis. Mol Breed 31:685–692
Zhou ZC, Dong Y, Sun HJ, Yang AF, Chen Z, Gao S, Jiang JW, Guan XY, Jiang B, Wang B (2014) Transcriptome sequencing of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) and the identification of gene-associated markers. Mol Ecol Resour 14:127–138
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted with the support of the “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ010104)”, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea. This study was supported by the 2014 Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of National Institute of Horticultural and Herbal Science, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Data accessibility
Raw sequence data: NCBI Sequence Read Archive: SRX446688, SRX446744, SRX446787, SRX446788.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, IH., Lee, SH., Kim, YC. et al. De novo transcriptome assembly and the identification of gene-associated single-nucleotide polymorphism markers in Asian and American ginseng roots. Mol Genet Genomics 290, 1055–1065 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0974-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0974-6