Abstract
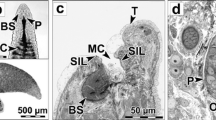
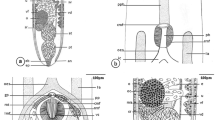
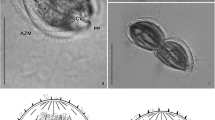
Diplozoons are representatives of blood-feeding ectoparasites from the family Diplozoidae (Polyopisthocotylea, Monogenea). Although these worms have been the subject of numerous taxonomical, phylogenetic, and ecological studies, the detailed study of their excretory system has remained relatively neglected. Our observations focused on the morphological and ultrastructural features of the excretory apparatus of four diplozoid species: Diplozoon paradoxum, Eudiplozoon nipponicum, Paradiplozoon bliccae, and Paradiplozoon homoion. Observations were obtained using two microscope methods: light microscopy, equipped with differential interference contrast (Nomarski DIC) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ultrastructure of two basic compartments which forms the excretory apparatus, flame cells with filtration apparatus, and canal cells forming the protonephridial ducts is revealed in this study. A unique consecutive sequence of longitudinal semi-thin sections of the excretory pore of E. nipponicum is visualized there for the first time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baguñà J, Riutort M (2004) Molecular phylogeny of the Platyhelminthes. Can J Zool 82:168–193
Brusca RC, Brusca GJ (2003) Invertebrates. 2nd edition, Sinauer Associates, 936 pp. ISBN 0-87893-097-3
Bychovski BE, Nagibina LF (1959) Systematics of the genus Diplozoon Nordmann (Monogenoidea). Zool Zhur 28:362–377
Collins JJ, King RS, Cogswell A, Williams DL, Newmark PA (2011) An atlas for Schistosoma mansoni organs and life-cycle stages using cell type-specific markers and confocal microscopy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5(3):e1009
Culioli JL (2006) Epidermis and protonephridia of a free-living platyhelminth, Mesocastrada führmanni Voltz, 1898 (Rhabdocoela, Typhloplanoida): an ultrastructural study. Zool Anz 244:163–169
Ergens R, Lom J (1970) Causative agents of parasitic diseases of fish. Academia, Praha, 384 pp
Faust EC (1919) The excretory system in Digenea. I. Biol Bull 36:315–321
Galaktionov KV, Dobrovolskij A (2013) The biology and evolution of trematodes: an essay on the biology, morphology, life cycles, transmissions, and evolution of digenetic trematodes. Springer Science & Business Media, 592 pp
Gelnar M, Svobodová Z, Vykusová B (1989) Eudiplozoon nipponicum (Goto, 1891)—a new parasite of carp in Czechoslovak ponds (in Czech). Bull Czech Fish 1:5–12
Goto S (1891) On Diplozoon nipponicum n. sp. J. Coli. Sei. Imp, Univ. Tokyo 4: 151–192
Hertel LA (1993) Excretion and osmoregulation in the flatworms. Trans Am Microsc Soc 112:10–17
Howells RE (1969) Observations on the nephridial system of the cestode Moniezia expansa (Rud., 1805). Parasitology 59:449–459
Justine JL (1998) Non-monophyly of the monogeneans? Int J Parasitol 28:1653–1657
Kearn GC (1974) A comparative study of the glandular and excretory systems of the oncomiracidia of the monogenean skin parasites Entobdella hippoglossi, E. diadema and E. soleae. Parasitology 69:257–269
Konstanzová V, Koubková B, Kašný M, Ilgová J, Dzika E, Gelnar M (2015) Ultrastructure of the digestive tract of Paradiplozoon homoion (Monogenea). Parasitol Res 114:1485–1494. doi:10.1007/s00436-015-4331-4
Košková E, Špakulová M, Koubková B, Reblánová M, Orosová M (2011) Comparative karyological analysis of four diplozoid species (Monogenea, Diplozoidae), gill parasites of cyprinid fishes. Parasitol Res 108:935–941
Lindroos P (1983) The excretory ducts of Diphyllobothrium dendriticum (Nitzsch 1824) plerocercoids: ultrastructure and marker distribution. Z Parasitenkd 69:229–237
Littlewood DTJ, Rohde K, Clough KA (1999) The interrelationships of all major groups of Platyhelminthes: phylogenetic evidence from morphology and molecules. Biol J Linn Soc 66:75–114
Martin WE, Bils RF (1964) Trematode excretory concretions: formation and fine structure. J Parasitol 50:337–344
Matějusová I, Koubková B, D’Amelio S, Cunningham CO (2001) Genetic characterization of six species of diplozoids (Monogenea; Diplozoidae). Parasitology 123:465–474
Mattison RG, Hanna REB, Nizami WA (1992) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of the protonephridial system of juvenile Paramphistomum epiclitum and Fischoederius elongatus (Paramphistomidae: Digenea) during migration in Indian ruminants. Int J Parasitol 22:1103–1115
McCullough JS, Fairweather I (1991) Ultrastructure of excretory system of Trilocularia acanthiaevulgaris (Cestoda, Tetraphyllidea). Parasitol Res 77:157–160
Naem S, Budke CM, Craig TM (2012) Morphological characterization of adult Fascioloides magna (Trematoda: Fasciolidae): first SEM report. Parasitol Res 110:971–978
Niewiadomska K, Czubaj A (2000) Ultrastructure of the excretory system in the metacercaria of Diplostomum pseudospathaceum Niew., 1984 (Digenea). Acta Parasitol 45:307–321
Nordmann V (1832) Mikrographische Beiträge zur Naturgeschischte der wirbellosen Thiere. Erstes Heft. X + 118 pp., 10 pl., Berlin
Poddubnaya LG, Xylander WER, Gibson DI (2012) Ultrastructural characteristics of the protonephridial terminal organ and associated ducts of adult specimens of the Aspidogastrea, Digenea and Monogenea, with comments on the relationships between these groups. Syst Parasitol 82:89–104
Poddubnaya LG, Kuchta R, Bristow GA, Scholz T (2015) Ultrastructure of the anterior organ and posterior funnel-shaped canal of Gyrocotyle urna Wagener, 1852 (Cestoda: Gyrocotylidea). Folia Parasitol 62:027
Reichenbach-Klinke HH (1961) Die Gattung Diplozoon v. Nordmann. Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde 20:541–557
Rohde K (1973) Ultrastructure of the protonephridial system of Polystomoides malayi Rohde and P. renschi Rohde (Monogenea: Polystomatidae). Int J Parasitol 3:329–333
Rohde K (1975) Fine structure of the Monogenea, especially Polystomoides Ward. Adv Parasitol 13:1–33
Rohde K (1987) Ultrastructure of flame cells and protonephridial capillaries of Craspedella and Didymorchis (Plathelminthes, Rhabdocoela). Zoomorphology 106:346–351
Rohde K (1989a) Ultrastructure of the protonephridial system of Gyrodactylus (Monogenea, Gyrodactylidae). Zool Anz 223:311–322
Rohde K (1989b) Ultrastructure of the protonephridial system of Lobatostoma manteri (Trematoda: Aspidogastrea). J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 21:599–610
Rohde K (1991) The evolution of protonephridia of the Platyhelminthes. Hydrobiologia 227:315–321
Rohde K (1993) Ultrastructure of protonephridia in the Monogenea, implications for the phylogeny of the group. Bull Fr Pêche Piscic 328:115–119
Rohde K, Justine JL, Watson NA (1989) Ultrastructure of the flame bulbs of the monopisthocotylean Monogenea Loimosina wilsoni (Loimoidae) and Calceostoma herculeana (Calceostomatidae). Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 64:433–442
Rohde K, Watson NA, Roubal FR (1992) Ultrastructure of the protonephridial system of Anoplodiscus cirrusspiralis (Monogenea Monopisthocotylea). Int J Parasitol 22:443–457
Ruppert EE, Fox RS, Barnes RD (2004) Invertebrate zoology (7 ed.). Brooks/Cole. pp. 213–215. ISBN 0-03-025982-7
Silveira M, Corinna A (1976) Fine structural observations on the protonephridium of the terrestrial triclad Geoplana pasipha. Cell Tissue Res 168:455–463
Smyth JD, Halton DW (1983) The physiology of trematodes. Cambridge University Press, UK, 432 pp
Smyth JD, McManus DP (2007) The physiology and biochemistry of cestodes. Cambridge University Press, UK, 412 pp
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Trump BF, Smuckler EA, Benditt EP (1961) A method for staining epoxy sections for light microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 5:343–348
Valverde-Islas LE, Arrangoiz E, Vega E, Robert L, Villanueva R, Reynoso-Ducoing O, Willms K, Zepeda-Rodríguez A, Fortoul TI, Ambrosio JR (2011) Visualization and 3D reconstruction of flame cells of Taenia solium (Cestoda). PLoS One 6(3):e14754
Wiles M (1968) The occurrence of Diplozoon paradoxum Nordmann, 1832 (Trematoda: Monogenea) in certain waters of northern England and its distribution on the gills of certain Cyprinidae. Parasitology 58:61–70
Wilson RA, Webster LA (1974) Protonephridia. Biol Rev 49:127–160
Xylander WER (1987) The protonephridial system in Cestoda: evolutionary changes and their possible functional significance. Ver Dtsch Zoologischen Ges 80:257–258
Xylander WER (1992) Investigations on the protonephridial system of postlarval Gyrocotyle urna and Amphilina foliacea (Cestoda). Int J Parasitol 22:287–300
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Faculty of Science, Masaryk University Brno. A big thank you goes to Professor Iva Dyková for her support with TEM observations, helpful comments, and kind approach. The authors also thank the Laboratory of Electron Microscopy, Biology Centre of ASCR, České Budějovice, Czech Republic, and Petra Masařová for TEM sample preparation. Great thanks go to Gabriela Vágnerová and Eliška Šrámová for their help with fish autopsies and to Peter Daniel Stuart for English correction of this text. VK, BK, and MG were supported by the Czech Science Foundation, no. GAP506/12/1258. MK and JI were supported by the Czech Science Foundation, projects to promote excellence in basic research, no. GBP505/12/G112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstanzová, V., Koubková, B., Kašný, M. et al. Excretory system of representatives from family Diplozoidae (Monogenea). Parasitol Res 115, 1493–1500 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4882-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4882-4