Abstract
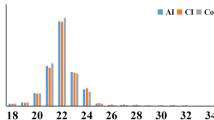
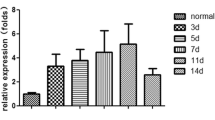
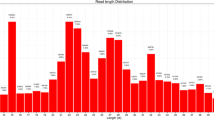
The pathogenesis of angiostrongyliasis, resulting from the third-stage and the fourth-stage Angiostrongylus cantonensis larvae invasion of the human central nervous system, remains elusive. MicroRNAs are important regulators of gene expression and involved in many biological processes. The aim of this study was to determine and characterize miRNAs of third (L3) and fourth (L4) larvae of A. cantonensis by Solex deep sequencing. A total of 629 conserved miRNAs (526 and 376 miRNAs in L3 and L4 larvae of A. cantonensis, respectively) and three novel candidate miRNA from L3 and L4 larva of A. cantonensis were identified with bioinformatic analysis. There were 163 miRNAs upregulated and 54 miRNAs downregulated (fold changes ≥5.0) in the L4 of A. cantonensis compared with that of L3 of A. cantonensis. Interestingly, Gene Ontology “biological process” classifications revealed that 26 miRNAs of significantly differential expression are associated with the immune system, which implies that these miRNAs might participate in the pathogenesis of angiostrongyliasis by regulating genes involved in immune response pathways. Furthermore, the differential expression patterns of 26 conserved miRNAs between L3 and L4 of A. cantonensis were verified. The results of real-time PCR and Northern blot showed that the aca-miR-124 and aca-miR-146a-5p have a low level expression in L3 larvae but high level expression in L4 larvae. Transfection of aca-miR-124 mimics alone significantly downregulated the mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-1β and TNF-a in the N9 cells, compared to the combination transfection of aca-miR-124 mimics and inhibitor (P < 0.05), suggesting that miR-124 of A. cantonensis have an important role in the suppression of microglia activation. In conclusion, the study presents a general picture of the expression of small RNAs in L3 and L4 of A. cantonensis and highlights conserved miRNAs differentially expressed between L3 and L4 larvae. Our data revealed that miRNAs of parasite may mediate important roles in A. cantonensis immune evasion and aca-miR-146a-5p can serve as a potential biomarker to diagnose angiostrongyliasis.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander R, Lodish H, Sun L (2011) MicroRNAs in adipogenesis and as therapeutic targets for obesity. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15:623–636
Ali AB, Van den Enden E, Van Gompel A, Van Esbroeck M (2008) Eosinophilic meningitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis in a Belgian traveler. Travel Med Infect Dis 6:41–44
Alicata JE (1965) Biology and distribution of the rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, and its relationship to eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and other neurological disorders of man and animals. Adv Parasitol 3:223–248
Ambros V, Bartel B, Bartel DP, Burge CB, Carrington JC, Chen X, Dreyfuss G, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Marshall M, Matzke M, Ruvkun G, Tuschl T (2003) A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 9:277–279
Aravin AA, Lagos-Quintana M, Yalcin A, Zavolan M, Marks D, Snyder B, Gaasterland T, Meyer J, Tuschl T (2003) The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev Cell 5:337–350
Bartel DP (2004) microRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, Sharon E, Spector Y, Bentwich Z (2005) Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37:766–770
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF et al (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303:83–86
Chen MX, Ai L, Xu MJ, Zhang RL, Chen SH, Zhang YN, Guo J, Cai YC, Tian LG, Zhang LL, Zhu XQ, Chen JX (2011) Angiostrongylus cantonensis: identification and characterization of microRNAs in male and female adults. Exp Parasitol 128:116–120
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 15:3674–3678
Conrad AT, Dittel BN (2011) Taming of macrophage and microglial cell activation by microRNA-124. Cell Res 21:213–216
Enik ÊS, Mona S, Andor P (2008) microRNAs and immunity: novel players in t he regulation of normal immune function and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol 18:131–140
Friedländer MR, Chen W, Adamidi C, Maaskola J, Einspanier R, Knespel S, Rajewsky N (2008) Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat Biotechnol 26:407–415
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D140–D144
Guarnieri DJ, DiLeone RJ (2008) microRNAs: a new class of gene regulators. Ann Med 40:197–208
Hagen JW, Lai EC (2008) microRNA control of cell–cell signaling during development and disease. Cell Cycle 7:2327–2332
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
He H, Cheng M, Yang X, Meng J, He A, Zheng X, Li Z, Guo P, Pan Z, Zhan X (2009) Preliminary molecular characterization of the human pathogen Angiostrongylus cantonensis. BMC Mol Biol 10:97
Hussain M, Taft RJ, Asgari S (2008) An insect virus-encoded microRNA regulates viral replication. J Virol 82:9164–9170
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA et al (2009) Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137:1005–1017
Lanford RE, Hildebrandt-Eriksen ES, Petri A et al (2010) Therapeutic silencing of microRNA-122 in primates with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Science 327:198–201
Lau NC, Lai EC (2005) Diverse roles for RNA in gene regulation. Genome Biol 6:315
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:858–862
Lee RC, Ambros V (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294:862–864
Lin WC, Li SC, Lin WC, Shin JW, Hu SN, Yu XM, Huang TY, Chen SC, Chen HC, Chen SJ, Huang PJ, Gan RR, Chiu CH, Tang P (2009) Identification of microRNA in the protist Trichomonas vaginalis. Genomics 93:487–493
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E et al (2010) Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol 28:341–347
Mallick B, Ghosh Z, Chakrabarti J (2008) MicroRNA switches in Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372:459–463
Nana-Sinkam SP, Croce CM (2010) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: opportunities for the development of microRNA-based drugs. IDrugs 13:843–846
Perry MM, Moschos SA, Williams AE et al (2008) Rapid changes in microRNA-146a expression negatively regulate the interleukin-1b induced inflammatory response in human lung alveolar epithelial cells. J Immunol 180:5689–5698
Ponomarev ED, Veremeyko T, Barteneva N et al (2011) MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-α-PU.1 pathway. Nat Med 17:64–70
Prucca CG, Slavin I, Quiroga R et al (2008) Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia is regulated by RNA interference. Nature 456:750–754
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Shi R, Chiang VL (2005) Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. Biotechniques 39:519–525
Tan KS, Armugam A, Sepramaniam S, Lim KY, Setyowati KD et al (2009) Expression profile of microRNAs in young stroke patients. PLoS ONE 4:e7689
Wang QP, Wu ZD, Wei J, Owen RL, Lun ZR, Eur J (2012) Human Angiostrongylus cantonensis: an update. Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:389–395
Xu MJ, Liu Q, Nisbet AJ, Cai XQ, Yan C, Lin RQ, Yuan ZG, Song HQ, He XH, Zhu XQ (2010) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in Clonorchis sinensis of human health significance. BMC Genomics 11:521
Xue X, Sun J, Zhang Q et al (2008) Identification and characterization of novel microRNAs from Schistosoma japonicum. PLoS One 3:e4034
Zhang B, Stellwag EJ, Pan X (2009) Large-scale genome analysis reveals unique features of microRNAs. Gene 443:100–109
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81261160324, 81271855) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB530004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhengyu Li and Xiaoguang Chen contribute to this work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Chen, X., Zen, X. et al. MicroRNA expression profile in the third- and fourth-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus cantonensis . Parasitol Res 113, 1883–1896 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3836-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3836-6