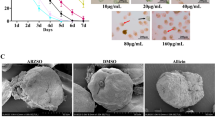
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the in vitro and in vivo efficacies of chemotherapy employing albendazole liposome (L-ABZ), Huaier aqueous extract, and a Huaier aqueous extract/L-ABZ combination against Echinococcus granulosus. Protoscolices of E. granulosus were incubated in vitro with the two drugs, either separately or in combination, at the following final concentrations: 2 mg/mL Huaier aqueous extract, 10 μg/mL L-ABZ, and 2 mg/mL Huaier aqueous extract + 10 μg/mL L-ABZ. Huaier aqueous extract and L-ABZ displayed slower protoscolicidal activity when applied separately than when used in combination. The maximum protoscolicidal effect was found with the combination Huaier aqueous extract + L-ABZ. Despite the low Huaier aqueous extract + L-ABZ concentrations used, protoscolex viability dropped rapidly. In vivo studies were performed on mice injected with protoscolices of E. granulosus. Huaier aqueous extract and L-ABZ were administered three times a week for a period of 4 months by the oral route. Huaier aqueous extract in E. granulosus-infected mice was effective. Combined application of both drugs did increase the treatment efficacy. In conclusion, the outcomes obtained clearly demonstrated that in vitro and in vivo treatment with Huaier aqueous extract and L-ABZ is effective against E. granulosus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Eshy SA (2006) Clinical characteristics, diagnosis and surgical management of hydatid cysts. West Afr J Med 25:144–152
Anadol D, Ozcelik U, Kiper N, Gocmen A (2001) Treatment of hydatid disease. Paediatr Drugs 3:123–135
Casado N, Perez-Serrano J, Denegri G, Rodriguez-Caabeiro F (1996) Development of chemotherapeutic model for the in vitro screening of drugs against Echinoccus granulosus cysts: the effects of an albendazole–albendazole sulphoxide combination. Int J Parasitol 26:59–65
Dziri C, Haouet K, Fingerhut A, Zaouche A (2009) Management of cystic echinococcosis complications and dissemination: where is the evidence? World J Surg 33:1266–1273
Eckert J, Deplazes P (2004) Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:107–135
El-On J (2003) Benzimidazole treatment of cystic echinococcosis. Acta Trop 85:243–252
Falagas ME, Bliziotis IA (2007) Albendazole for the treatment of human echinococcosis: a review of comparative clinical trials. Am J Med Sci 334:171–179
Hemphill A, Spicher M, Stadelmann B, Mueller J, Naguleswaran A, Gottstein B, Walker M (2007) Innovative chemotherapeutical treatment options for alveolar and cystic echinococcosis. Parasitology 134:1657–1670
Horiuchi A, Satou T, Akao N, Koike K, Fujita K, Nikaido T (2005) The effect of free and polyethylene glycol-liposome-entrapped albendazole on larval mobility and number in Toxocara canis infected mice. Vet Parasitol 129:83–87
Ingold K, Bigler P, Thormann W, Cavaliero T, Gottstein B, Hemphill A (1999) Efficacies of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfone against in vitro-cultivated Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1052–1061
Liu LF, Durairajan SS, Lu JH, Koo I, Li M (2012) In vitro screening on amyloid precursor protein modulation of plants used in Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese medicine for memory improvement. J Ethnopharmacol 141:754–760
Manterola C, Mansilla JA, Fonseca F (2005) Preoperative albendazole and scolices viability in patients with hepatic echinococcosis. World J Surg 29:750–753
Perez-Serrano J, Casado N, Guillermo D, Rodriguez-Caabeiro F (1994) The effects of albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide combination-therapy on Echinococcus granulosus in vitro. Int J Parasitol 24:219–224
Polat C, Dervisoglu A, Hokelek M, Yetim I, Buyukkarabacak Y, Ozkutuk Y, Erzurumlu K (2005) Dual treatment of albendazole in hepatic hydatidosis: new therapeutic modality in 52 cases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:421–425
Puryan K, Karadayi K, Topcu O, Canbay E, Sumer Z, Turan M, Karayalcin K, Sen M (2005) Chlorhexidine gluconate: an ideal scolicidal agent in the treatment of intraperitoneal hydatidosis? World J Surg 29:227–230
Ren J, Zheng C, Feng G, Liang H, Xia X, Fang J, Duan X, Zhao H (2009) Inhibitory effect of extract of fungi of Huaier on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci 29:198–201
Siles-Lucas M, Hemphill A (2002) Cestode parasites: application of in vivo and in vitro models for studies on the host–parasite relationship. Adv Parasitol 51:133–230
Stettler M, Rossignol JF, Fink R, Walker M, Gottstein B, Merli M, Theurillat R, Thormann W, Dricot E, Segers R, Hemphill A (2004) Secondary and primary murine alveolar echinococcosis: combined albendazole/nitazoxanide chemotherapy exhibits profound anti-parasitic activity. Int J Parasitol 34:615–624
Thatte U, Bagadey S, Dahanukar S (2000) Modulation of programmed cell death by medicinal plants. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand) 46:199–214
Wang E, Bussom S, Chen J, Quinn C, Bedognetti D, Lam W, Guan F, Jiang Z, Mark Y, Zhao Y, Stroncek DF, White J, Marincola FM, Cheng YC (2011) Interaction of a traditional Chinese Medicine (PHY906) and CPT-11 on the inflammatory process in the tumor microenvironment. BMC Med Genomics 4:38
Wen H, New RR, Muhmut M, Wang JH, Wang YH, Zhang JH, Shao YM, Craig PS (1996) Pharmacology and efficacy of liposome-entrapped albendazole in experimental secondary alveolar echinococcosis and effect of co-administration with cimetidine. Parasitology 113(Pt 2):111–121
Zhang N, Kong X, Yan S, Yuan C, Yang Q (2010) Huaier aqueous extract inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Sci 101:2375–2383
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30960338), National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (no. 2009BAI82B06), Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps foundation (2011BB019, 2011BA0158), and Shihezi University foundation (Rezx200925, LHJJ2010B10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hailong Lv and Yufeng Jiang contribute equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, H., Jiang, Y., Liao, M. et al. In vitro and in vivo treatments of Echinococcus granulosus with Huaier aqueous extract and albendazole liposome. Parasitol Res 112, 193–198 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3125-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3125-1