Abstract
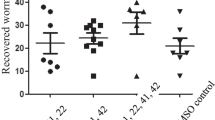
The aim of the study is to understand the anti-Clonorchis sinensis properties of mebendazole and albendazole, and compare to praziquantel and tribendimidine. Two hundred and thirty rats were divided into five batches for experimental treatment. In four batches, each rat was infected orally with 50 or 100 C. sinensis metacercariae. Twenty-eight to 46 days post-infection, groups of rats were treated orally with single doses of mebendazole, albendazole, praziquantel, tribendimidine, or multiple daily doses of albendazole. While in the remaining batch, mebendazole or praziquantel was administered to groups of rats infected each with 50 metacercariae for 7 or 14 days. In each batch of test, untreated but infected rats served as control. All rats were euthanized 2–4 weeks post-drug administration for assessment of efficacy. In the first batch of test, rats treated with mebendazole or tribendimidine at single doses of 150, 75, and 37.5 mg/kg resulted in worm burden reductions of 99.0%, 94.0%, and 73.1%, or 98.0%, 80.6%, and 60.4%, respectively. When rats were treated with albendazole at the same dose levels, no or poor effect was seen. In the second batch of test, promising effect against adult C. sinensis in rats treated with mebendazole or tribendimidine at single doses of 100 and 50 mg/kg were also observed, but under the single dose of 25 mg/kg, only tribendimidine still remained the effect. In the third batch of test, the aforementioned three single dose levels of mebendazole, albendazole and praziquantel were applied. Again, mebendazole exhibited higher effect and albendazole exhibited no or poor effect. While praziquantel, administered at a higher dose of 300 mg/kg, also showed promising effect. In the fourth batch of test, oral administration of albendazole at a daily dose of 150 or 100 mg/kg for 2 or 3 days resulted in moderate or higher efficacy with worm burden reductions of 79.2% and 91.9%, respectively. In the fifth batch of test, single mebendazole doses of 150 or 75 mg/kg exhibited promising effect against 14-day-old C. sinensis in rats with worm burden reductions of 95.3% and 86.4%, respectively, but mebendazole was short of the effect against 7-day-old worms. Under the same dose level, praziquantel possessed an effect against both 7- and 14-day-old juvenile C. sinensis. The results confirm that in infected rats, mebendazole administered orally at a single dose of 150 mg/kg exhibits potential effect against juvenile (14-day-old) and adult C. sinensis. No or less effect is obtained from albendazole under the same dose levels, but extension of treatment course may enhance the effect of albendazole against this species of fluke. The single effective dose ranges of mebendazole and tribendimidine against C. sinensis in rats are similar with a broad window, while the window for praziquantel is narrow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan RJ, Watson TR (1983) The metabolic and pharmacokinetic disposition of mebendazole in the rat. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 8:373–381
Bae PW, Kim SJ, Rim HJ (1984) Experimental studies on the effect of albendazole against Clonorchis sinensis. Korea Univ Med J 21:1–14
Cao WJ, Zhong HL, Feng ML (1985) Treatment of clonorchiasis sinensis with albendazole: 50 cases. Chin Intern Med J 24:353–354
Chai JY, Murrell KD, Lymbery AJ (2005) Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: status and issues. Int J Parasitol 35:1233–1254
CONSIHPD (Coordinating Office of the National Survey on the Important Human Parasitic Diseases) (2005) A national survey on current status of the important parasitic diseases in human population. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 23(5 suppl):332–340
Fan PC, Wu CC, Huang P, Yen CW (2005) Determination of the minimum effective dosages of praziquantel, albendazole, and mebendazole against Clonorchis sinensis infections in rats. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 21:448–451
Gottschall DW, Theodorides VJ, Wang R (1990) The metabolism of benzimidazole anthrelmintics. Parasitol Today 6:115–124
Hu Y, Xiao SH, Aroian R (2009) The new anthelmintic tribendimidine is an L-type (levamisole and pyrantel) nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3(8):e499
Huang Y, Quan YZ, Tu ZG (1991) The pharmacolinetics and biliary excretion of praziquantel in rats by different route of administration. Acta Pharmacol Sin 7:205–208
Huang X, Cai W, Ma Q (1999) Comparison of the efficacy of albendazole-medicated sweets and praziquantel for the treatment of clonorchiasis. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 17:376
Keiser J, Utzinger J (2007) Food-borne trematodiasis: current chemotherapy and advances with artemisinins and synthetic trioxolanes. Trends Parasitol 23:555–562
Keiser J, Utzinger J (2008) Efficacy of current drugs against soil-transmitted helminth infections: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 299:1937–1948
Keiser J, Xiao SH, Xue J, Chan ZS, Odermatt P, Tesana S, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2006) Effect of artesunate and artemether against Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini in rodent models. Int J Antimicrob Agents 28:370–373
Keiser J, Xiao SH, Chollet J, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2007) Evaluation of the in vivo activity of tribendimidine against Schistosoma mansoni, Fasciola hepatica, Clonorchis sinensis, and Opisthorchis viverrini. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:1096–1098
Keiser J, Xiao SH, Smith TA, Utzinger J (2009) Combination chemotherapy against Clonorchis sinensis: experiments with artemether, artesunate, OZ78, praziquantel and tribendimidine in a rat model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 9:3770–3776
Keystone JS, Murdoch JK (1979) Mebendazole. Ann Intern Med 91:582–586
Li BZ, Liu TC, Yu XH, Zhang DS, Wang JC, Liu YZ (1984) Experimental chemotherapy of Clonorchis sinensis at different developing stage in rats with praziquantel. Acta Pharmaceut Sin 19:291–293
Liu JB, Liu YH, Wang QN, Chen RX, Luo XR, Liu ZH (1981) Praziquantel treatment of clonorchiasis and paragonimiasis in experimental animals. Acta Pharmaceut Sin 16:56–58
Liu YH, Wang XG, Gao P, Qian MX (1991) Experimental and clinical trial of albendazole in the treatment of Clonorchiasis sinensis. Chin Med J 104(1):27–31
Liu YS, Wu YM, Du WP, Hu XJ, Wu ZX, Chen YG, Zheng CY, Lonf CP, Li GY, Shi JM (1994) Compare the efficacy of albendazole and praziquantel against clonorchiasis. Chin J Infect Dis 12:117–118
Lun ZR, Gasser RB, Cai DH, Zhu XQ, Yu XB, Fang YY (2005) Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. Lancet Infect Dis 5:31–41
Qiu ZD, Liu YH, Wang QN, Qu ZQ, Liu JB, Chen RX, Zhang CD (1985) Praziquantel in the treatment of 248 cases of clonorchiasis. Chin J Clin Hepatol 1:47–48
Rim HJ (2005) Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol 79:269–281
Rim HJ, Lee YM, Lee JS, Joo KH (1982) Therapeutic field trial with praziquantel (Biltricide®) in a rural population infected with Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 20:1–8
Soh CT (1984) Clonorchis sinensis: experimental and clinical studies with praziquantel in Korea. Arzneimittelforschung 34:1156–1159
Wang XG, Liu YH, Gao P, Guan L, Qian MX, Chen JX, Liu JG, Li CX, Zhou XR, Zhang DF, Sm Wu (1990) Experimental and clinical trials of albendazole in the treatment of clonorchiasis. Chin J Infect Dis 8:197–199
WHO (1995) Control of foodborne trematode infections. Report of a WHO study group. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. No. 849
Witassek F, Allan RJ, Watson TR, Woodtli W, Ammann R, Bircher J (1983) Preliminary observations on the biliary elimination of mebendazole and its metabolites in patients with echinococcosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25:81–84
Xiao SH, Yang YQ, You JQ, Shen BG, Jiao W, Chai JJ (1994) Effect of benzimidazole compounds on mice infected with secondary cysts of Echinococcus granulosus. Chin Med J 107:521–532
Xiao SH, Wu HM, Tanner M, Utzinger J, Wang C (2005) Tribendimidine: a promising, safe and broad-spectrum anthelmintic agent from China. Acta Trop 94:1–14
Xiao SH, Xue J, Tanner M, Zhang YN, Keiser J, Utzinger J, Qiang HQ (2008a) Artemether, artesunate, praziquantel and tribendimidine administered singly at different dosages against Clonorchis sinensis: a comparative in vivo study. Acta Trop 106:54–59
Xiao SH, Xue J, Tanner M, Zhang YN, Keiser J, Utzinger J, Qiang HQ, Liu XY (2008b) The effect of tribendimidine, artesunate, artemether and praziquantel given at a single or multiple doses or combined use in treatment of rats infected with Clonorchis sinensis. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 26:321–326
Xiao SH, Xue J, Xu LL, Qiang HQ, Zhang YN (2009) The in vitro and in vivo effect of tribendimidine and its metabolites against Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 105:1497–1507
Xu FN, Wu WD, Liu XM, Chen DL, Wu ZM, Zhang ZL (1986) Comparative study on different dosage-schedules of praziquantel in treating 376 cases of Clonorchis sinensis infection. Anhui Med J 7:33–35
Yangco BG, De Lerma C, Lyman GH, Price DL (1987) Clinical study evaluating efficacy of praziquantel in clonorchiasis. Antimicrob Agent Chemother 31:135–138
Yu SH, Xu LQ, Jiang ZX, Xu SH, Han JJ, Zhu YG, Chang J, Lin JX, Xu FN (1994a) Report on the first nationwide survey of the distribution of human parasites in China. 1. Regional distribution of parasite species. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 12:241–247 (in Chinese)
Yu SH, Xu LQ, Jiang ZX, Xu SH, Han JJ, Zhu YG, Chang J, Lin JX, Xu FN (1994b) Nationwide survey of human parasite in China. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 25:4–10
Yuan GY, Wang BJ, Wei CM, Zhang R, Guo RC (2008) LC-MS determination of p-(1-dimethylaminoethylimino)aniline: a metabolite of tribendimidine in human plasma. Chromatographia 68:139–142
Zhong HL, Cao WJ, Rossignol JF, Feng ML, Hu RY, Gan SB, Tan W (1986) Albendazole in nematode, cestode, trematode and protozoan (Giardia) infections. Chin Med J Engl 99:912–915
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by the Major National Science and Technology Projects, 2009ZX10004-302 and the Platform of Basic Research for the Important Parasitic Diseases Control Technology Based on Functional Genomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Sh., Xue, J., Xu, Ll. et al. Comparative effect of mebendazole, albendazole, tribendimidine, and praziquantel in treatment of rats infected with Clonorchis sinensis . Parasitol Res 108, 723–730 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2187-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2187-1