Abstract
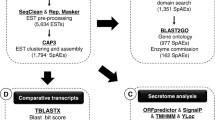
Taking a genomic approach to characterize potential secreted products, we analyzed putative protein sequences from Brugia malayi whole-genome shotgun sequencing project. SignalP analysis was applied to predict protein sequences and to identify potential signal peptides and anchors. We randomly analyzed 552 sequences, of which 88 (15.9%) bear predicted signal sequence coding regions. Through comparisons of sequences with homologs from other species, we found that although some of the sequences with signal sequences have no homologs with others, there are almost the same amounts of the sequences with signals which are highly conserved. Considering the distribution of secretory proteins of B. malayi in three categories has not made big differences, and most of the homologues of free-living nematodes of these secretory proteins also contained either N-signal signal peptides or signal anchors; we speculated that secretory proteins may be in the same evolutional status as the non-secretory proteins.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JE, Maizels RM (1996) Immunology of human helminth infection. Int Archiv Allerg Immunol 109:3–10
Auriault C, Ouaissi MA, Torpier G, Eisen H, Capron A (1981) Proteolytic cleavage of IgG bound to the Fc receptor of Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula. Parasite Immunol 3:33–44
Behnke JM, Barnard CJ, Wakelin D (1992) Understanding chronic nematode infections: evolutionary considerations, current hypotheses and the way forward. Int J Parasitol 22:861–907
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, Heijne GV, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Blaxter M (1998) Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode. Science 282:2041–2046
Falcone FH, Loke P, Zang X, MacDonald AS, Maizels RM, Allen JE (2001) A Brugia malayi homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor reveals an important link between macrophages and eosinophil recruitment during nematode infection. J Immunol 167:5348–5354
Fischer P, Djoha S, Büttner DW, Zipfel PF (2003) Isolation and characterization of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from the filarial parasite Onchocerca volvulus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 128:33–42
Ghedin E, Wang S, Spiro D, Caler E, Zhao Q, Crabtree J, Allen JE, Delcher AL, Guiliano DB, Miranda-Saavedra D, Angiuoli SV, Creasy T, Amedeo P, Haas B, El-Sayed NM, Wortman JR, Feldblyum T, Tallon L, Schatz M, Shumway M, Koo H, Salzberg SL, Schobel S et al (2007) Draft genome of the filarial nematode parasite Brugia malayi. Science 317:1756–1760
Gomez-Escobar N, Gregory WF, Maizels RM (2000) Identification of tgh-2, a filarial nematode homolog of Caenorhabditis elegans daf-7 and human transforming growth factor b, Expressed in microfilarial and adult stages of Brugia malayi. Infect Immun 68:6402–6410
Haffner A, Guilavogui AZ, Tischendorf FW (1998) Onchocerca volvulus: microfilariae secrete elastinolytic and males nonelastinolytic matrix-degrading serine and metalloproteases. Exp Parasitol 90:26–33
Harcus YM, Parkinson J, Fernández C, Daub J, Selkirk ME, Blaxter ML, Maizels RM (2004) Signal sequence analysis of expressed sequence tags from the nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and the evolution of secreted proteins in parasites. Genome Biol 5:R39
Henkle-Dührsen K, Kampkötter A (2001) Antioxidant enzyme families in parasitic nematodes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 114:129–142
Holland MJ, Harcus YM, Riches PL, Maizels RM (2000) Proteins secreted by the parasitic nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis act as adjuvants for Th2 responses. Eur J Immunol 30:1977–1987
Jaubert S, Laffaire JB, Ledger TN, Escoubas P, Amri EZ, Abad P, Rosso MN (2004) Comparative analysis of two 14-3-3 homologues and their expression pattern in the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Int J Parasitol 34:873–880
Kaiser CA, Preuss D, Grisafi P, Botstein D (1987) Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science 235:312–317
Klee EW, Ellis LB (2005) Evaluating eukaryotic secreted protein prediction. BMC Bioinformatics 6:256–262
Knox DP (2007) Proteinase inhibitors and helminth parasite infection. Parasite Immunol 29:57–71
Lun HM, Mak CH, Ko RC (2003) Characterization and cloning of metallo-proteinase in the excretory/secretory products of the infective-stage larva of Trichinella spiralis. Parasitol Res 90:27–37
Maizels RM, Bundy DAP, Selkirk ME, Smith DF, Anderson RM (1993) Immunological modulation and evasion by helminth parasites in human populations. Nature 365:797–805
Newlands GF, Skuce PJ, Knox DP, Smith SK, Smith WD (1999) Cloning and characterization of a beta-galactoside-binding protein (galectin) from the gut of the gastrointestinal nematode parasite Haemonchus contortus. Parasitol 119:483–490
Pastrana DV, Raghavan N, Fitzgerald P, Eisinger SW, Metz C, Bucala R, Schleimer RP, Bickel C, Scott AL (1998) Filarial nematode parasites secrete a homologue of the human cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Infect Immun 66:5955–5563
Robertson L, Robertson WM, Sobczak M, Helder J, Tetaud E, Ariyanayagam MR, Ferguson MAJ, Fairlamb A, Jones JT (2000) Cloning, expression and functional characterisation of a peroxiredoxin from the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 111:41–49
Sajid M, McKerrow JH (2002) Cysteine proteases of parasitic organisms. Mol Biochem Parasitol 120:1–21
Salter JP, Choe Y, Albrecht H, Franklin C, Lim KC, Craik CS, McKerrow JH (2002) Cercarial elastase is encoded by a functionally conserved gene family across multiple species of schistosomes. J Biol Chem 277:24618–24624
Shibui A, Takamoto M, Shi Y, Komiyama A, Sugane K (2001) Cloning and characterization of a novel gene encoding keratin-like protein from nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:59–61
Sommer A, Nimtz M, Conradt HS, Brattig N, Boettcher K, Fischer P, Walter RD, Liebau E (2001) Structural analysis and antibody response to the extracellular glutathione S-transferases from Onchocerca volvulus. Infect Immun 69:7718–7728
Tsuji N, Morales TH, Ozols VV, Carmody AB, Chandrashekar R (1999) Identification of an asparagine amidohydrolase from the filarial parasite Dirofilaria immitis. Int J Parasitol 29:1451–1455
Williamson AL, Brindley PJ, Abbenante G, Prociv P, Berry C, Girdwood K, Pritchard DI, Fairlie DP, Hotez PJ, Dalton JP, Loukas A (2002) Cleavage of hemoglobin by hookworm cathepsin D aspartic proteases and its potential contribution to host specificity. FASEB J 16:1458–1460
Williamson AL, Brindley PJ, Knox DP, Hotez PJ, Loukas A (2003) Digestive proteases of blood-feeding nematodes. Trends Parasitol 19:417–423
Zang X, Maizels RM (2001) Serine proteinase inhibitors from nematodes and the arms race between host and pathogen. Trends Biochem Sci 26:191–197
Zang X, Yazdanbakhsh M, Jiang H, Kanost MR, Maizel MR (1999) A novel serpin expressed by blood-borne microfilariae of the parasitic nematode Brugia malayi inhibits human neutrophil serine proteinases. Blood 94:1418–1428
Acknowledgments
Authors contributed equally. The project was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2008N2005) and Xiamen Municipality (Grant No. 3502Z20074036), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Table 1
Blast results of protein sequences of Brugia malayi (DOC 596 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, X., Chen, X., Wang, Y. et al. Signal sequence analysis of protein sequences from the filarial nematode parasite Brugia malayi and the evolution of secreted proteins in parasites. Parasitol Res 104, 1321–1326 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1331-2