Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate how the amplification of HMGA2 contributes to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell proliferation.
Methods
The amplification and expression of HMGA2 were examined by FISH, qRT-PCR and Western blot in AML cases. The effect of HMGA2 knockdown on cell proliferation was analyzed with XTT, colony-forming assays and BrdUrd incorporation assays. The effects of HMGA2 knockdown on cell cycle were studied by flow cytometry analysis. The progression of AML cells in vivo was examined by the xenografted tumor model. The interaction between Akt pathway and HMGA2 was examined by Western blot.
Results
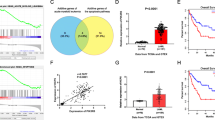
HMGA2 is amplified in AML, and the levels of HMGA2 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expressed in AML cells were significantly higher than those in normal cells, which may be related to NR and prognosis of AML patients. Reduction in HMGA2 expression in AML cells inhibited cell proliferation through a decrease in the protein expression of pAkt and pmTOR, compared with control cells.
Conclusions
HMGA2 is predominantly amplified and expressed in AML cells, and that aberrant expression of HMGA2 induces AML cell proliferation through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Inhibition of HMGA2 expression represents an attractive target for AML therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcaro A, Guerreiro AS (2007) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in human cancer: genetic alterations and therapeutic implications. Curr Genom 8(5):271–306
Ayoubi TA, Jansen E, Meulemans SM, Van de Ven WJ (1999) Regulation of HMGIC expression: an architectural transcription factor involved in growth control and development. Oncogene 18(36):5076–5087
Bustin M, Reeves R (1996) High-mobility-group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 54:35–100
Di Cello F, Hillion J, Hristov A, Wood LJ, Mukherjee M, Schuldenfrei A, Kowalski J, Bhattacharya R, Ashfaq R, Resar LM (2008) HMGA2 participates in transformation in human lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res 6(5):743–750
Elkahloun AG, Krizman DB, Wang Z, Hofmann TA, Roe B, Meltzer PS (1997) Transcript mapping in a 46-kb sequenced region at the core of 12q13.3 amplification in human cancers. Genomics 42(2):295–301
Estey E, Döhner H (2006) Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 368(9550):1894–1907
Fedele M, Visone R, De Martino I, Troncone G, Palmieri D, Battista S, Ciarmiello A, Pallante P, Arra C, Melillo RM, Helin K, Croce CM, Fusco A (2006) HMGA2 induces pituitary tumorigenesis by enhancing E2F1 activity. Cancer Cell 9(6):459–471
Finelli P, Giardino D, Rizzi N, Buiatiotis S, Virduci T, Franzin A, Losa M, Larizza L (2000) Non random trisomies of chromosomes 5, 8 and 12 in the prolactinoma subtype of pituitary adenomas: conventional cytogenetics and interphase FISH study. Int J Cancer 86(3):344–350
Fish RJ, Kruithof EK (2004) Short-term cytotoxic effects and long-term instability of RNAi delivered using lentiviral vectors. BMC Mol Biol 5:9
Fusco A, Fedele M (2007) Roles of HMGA proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(12):899–910
Kong D, Su G, Zha L, Zhang H, Xiang J, Xu W, Tang Y, Wang Z (2014) Coexpression of HMGA2 and Oct4 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in human gastric cancer. Med Oncol 31(8):130
Li Z, Gilbert JA, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Qiu Q, Ramanujan K, Shavlakadze T, Eash JK, Scaramozza A, Goddeeris MM, Kirsch DG, Campbell KP, Brack AS, Glass DJ (2012) An HMGA2-IGF2BP2 axis regulates myoblast proliferation and myogenesis. Dev Cell 23(6):1176–1188
Liu B, Pang B, Hou X, Fan H, Liang N, Zheng S, Feng B, Liu W, Guo H, Xu S, Pang Q (2014) Expression of high-mobility group AT-hook protein 2 and its prognostic significance in malignant gliomas. Hum Pathol 45(8):1752–1758
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Malek A, Bakhidze E, Noske A, Sers C, Aigner A, Schäfer R, Tchernitsa O (2008) HMGA2 gene is a promising target for ovarian cancer silencing therapy. Int J Cancer 123(2):348–356
Mantovani F, Covaceuszach S, Rustighi A, Sgarra R, Heath C, Goodwin GH, Manfioletti G (1998) NF-kappaB mediated transcriptional activation is enhanced by the architectural factor HMGI-C. Nucleic Acids Res 26(6):1433–1439
Martelli AM, Tazzari PL, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F, Blalock WL, Billi AM, Manzoli L, McCubrey JA, Cocco L (2007) Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin module for acute myelogenous leukemia therapy: from bench to bedside. Curr Med Chem 14(19):2009–2023
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Mori M (2008) Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA family. Clin Cancer Res 14(8):2334–2340
Palmieri D, D’Angelo D, Valentino T, De Martino I, Ferraro A, Wierinckx A, Fedele M, Trouillas J, Fusco A (2012) Downregulation of HMGA-targeting microRNAs has a critical role in human pituitary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 31(34):3857–3865
Raskin L, Fullen DR, Giordano TJ, Thomas DG, Frohm ML, Cha KB, Ahn J, Mukherjee B, Johnson TM, Gruber SB (2013) Transcriptome profiling identifies HMGA2 as a biomarker of melanoma progression and prognosis. J Invest Dermatol 133(11):2585–2592
Ravandi F, Burnett AK, Agura ED, Kantarjian HM (2007) Progress in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 110(9):1900–1910
Reeves R (2001) Molecular biology of HMGA proteins: hubs of nuclear function. Gene 277(1–2):63–81
Reeves R, Beckerbauer L (2001) HMGI/Y proteins: flexible regulators of transcription an chromatin structure. Biochim Biophys Acta 1519(1–2):13–29
Rizzi C, Cataldi P, Iop A, Isola M, Sgarra R, Manfioletti G, Giancotti V (2013) The expression of the high-mobility group A2 protein in colorectal cancer and surrounding fibroblasts is linked to tumor invasiveness. Hum Pathol 44(1):122–132
Schoenmakers EF, Wanschura S, Mols R, Bullerdiek J, Van den Berghe H, Van de Ven WJ (1995) Recurrent rearrangements in the high mobility group protein gene, HMGI-C, in benign mesenchymal tumours. Nat Genet 10(4):436–444
Yuan TL, Cantley LC (2008) PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene 27(41):5497–5510
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81100379 and No. 81302079), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2013B022000102), the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No. A2014292), and the Key Clinical Disciplines of Guangdong Province (No. 20111219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L., Wei, X., Zheng, L. et al. Amplified HMGA2 promotes cell growth by regulating Akt pathway in AML. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 389–399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2036-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2036-9