Abstract
Purpose
Human umbilical endothelial cells (HUVECs) have been proved as an effective whole-cell vaccine inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. However, HUVECs divide a very limited number of passages before entering replicative senescence, which limits its application for clinical situation. Here, we fused HUVECs with human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line A549s and investigated the anti-tumor immunity of the hybrids against mice Lewis lung cancer.
Methods
HUVECs were fused with A549s using polyethylene glycol and were sorted by flow cytometry. The fusion cells (HUVEC–A549s) were confirmed by testing the expression of telomerase and VE-cadherin, the senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity, and tube formation ability. HUVEC–A549s were then irradiated and injected into the C57BL/6 mice of protective, therapeutic, and metastatic models. The mechanism of the anti-tumor immunity was explored by analyzing mice sera, spleen T lymphocytes, tumor microenvironment, and histological changes.
Results
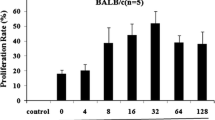
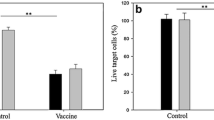
HUVEC–A549s coexpressed tumor and endothelial markers and maintained the vascular function of tube forming at passage 30 without showing signs of senescence. HUVEC–A549s could induce protective and therapeutic anti-tumor activity for LL2 model and presented stronger activity against metastasis than HUVECs. Both humoral and cellular immunity were participated in the anti-angiogenic activity, as HUVECs-neutralizing IgG and HUVECs-toxic lymphocytes were increased. Angiogenic mediators (VEGF and TGF-β) and tumor microenvironment cells MDSCs and Tregs were also diminished.
Conclusions
Our findings might provide a novel strategy for HUVECs-related immunotherapy, and this vaccine requires lower culture condition than primary HUVECs while enhancing the anti-tumor immunity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anno K, Hayashi A, Takahashi T, Mitsui Y, Ide T, Tahara H (2007) Telomerase activation induces elongation of the telomeric single-stranded overhang, but does not prevent chromosome aberrations in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 353(4):926–932
Avigan D, Vasir B, Gong J, Borges V, Wu Z, Uhl L, Atkins M, Mier J, McDermott D, Smith T, Giallambardo N, Stone C, Schadt K, Dolgoff J, Tetreault JC, Villarroel M, Kufe D (2004) Fusion cell vaccination of patients with metastatic breast and renal cancer induces immunological and clinical responses. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4699–4708
Bayne LJ, Beatty GL, Jhala N, Clark CE, Rhim AD, Stanger BZ (2012) Tumor-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates myeloid inflammation and T cell immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 21:822–835
Beck A, Haeuw JF, Wurch T, Goetsch L, Bailly C, Corvaia N (2010) The next generation of antibody-drug conjugates comes of age. Discov Med 10(53):329–339
Bocker W, Yin Z, Drosse I, Haasters F, Rossmann O, Wierer M, Popov C, Locher M, Mutschler W, Docheva D, Schieker M (2008) Introducing a single-cell-derived human mesenchymal stem cell line expressing hTERT after lentiviral gene transfer. J Cell Mol Med 12(4):1347–1359
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS (1997) Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390:404–407
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Chang MW, Grillari J, Mayrhofer C, Fortschegger K, Allmaier G, Marzban G, Katinger H, Voglauer R (2005) Comparison of early passage, senescent and hTERT immortalized endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 309(1):121–136
Chen XY, Zhang W, Zhang W, Wu S, Bi F, Su YJ, Tan XY, Liu JN, Zhang J (2006) Vaccination with viable human umbilical vein endothelial cells prevents metastatic tumors by attack on tumor vasculature with both cellular and humoral immunity. Clin Cancer Res 12(19):5834–5840
Chen F, Zhuang X, Lin L, Yu P, Wang Y, Shi Y, Hu G, Sun Y (2015) New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: challenges and opportunities. BMC Med 13(1):278
Di Ianni M, Del Papa B, De Ioanni M, Moretti L, Bonifacio E, Cecchini D, Sportoletti P, Falzetti F, Tabilio A (2008) Mesenchymal cells recruit and regulate T regulatory cells. Exp Hematol 36(3):309–318
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O (1995) A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92(20):9363–9367
Domagala-Kulawik J, Osinska I, Hoser G (2014) Mechanisms of immune response regulation in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 3(1):15–22
Duan HX, Cheng LM, Wang J, Hu LS, Lu GX (2006) Angiogenic potential difference between two types of endothelial progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood. Cell Biol Int 30(12):1018–1027
Edgell CJ, McDonald CC, Graham JB (1983) Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 80(12):3734–3737
Folkman J (1996) Fighting cancer by attacking its blood supply. Sci Am 275:150–154
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9(3):162–174
Gautam A, Densmore CL, Waldrep JC (2000) Inhibition of experimental lung metastasis by aerosol delivery of PEI-p53 complexes. Mol Ther 2(4):318–323
Gifford SM, Grummer MA, Pierre SA, Austin JL, Zheng J, Bird IM (2004) Functional characterization of HUVEC-CS: Ca2+ signaling, ERK 1/2 activation, mitogenesis and vasodilator production. J Endocrinol 182(3):485–499
Hanagiri T, Fukumoto M, Koyanagi Y, Furutani Y, Tanaka F (2014) Regulatory T-cells and micrometastasis in lymph nodes of stage I NSCLC. Anticancer Res 34(12):7185–7190
Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ (2013) Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 501:346–354
Kusmartsev SA, Li Y, Chen SH (2000) Gr-1+ myeloid cells derived from tumor-bearing mice inhibit primary T cell activation induced through CD3/CD28 costimulation. J Immunol 165(2):779–785
Li Y, Shen G, Nie W, Li Z, Sang Y, Zhang B, Wei Y (2014) Irradiated tumor cells of lipopolysaccharide stimulation elicit an enhanced anti-tumor immunity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140(11):1815–1823
Matejuk A, Leng Q, Chou ST, Mixson AJ (2011) Vaccines targeting the neovasculature of tumors. Vasc Cell 3(1):7
Mulligan JK, Young MR (2010) Tumors induce the formation of suppressor endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59(2):267–277
Nurieva RI, Chung Y (2010) Understanding the development and function of T follicular helper cells. Cell Mol Immunol 7(3):190–197
Okaji Y, Tsuno NH, Saito S, Yoneyama S, Tanaka M, Nagawa H, Takahashi K (2006) Vaccines targeting tumour angiogenesis—a novel strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Eur J Surg Oncol 32(4):363–370
Okaji Y, Tsuno NH, Tanaka M, Yoneyama S, Matsuhashi M, Kitayama J, Saito S, Nagura Y, Tsuchiya T, Yamada J, Tanaka J, Yoshikawa N, Nishikawa T, Shuno Y, Todo T, Saito N, Takahashi K, Nagawa H (2008) Pilot study of anti-angiogenic vaccine using fixed whole endothelium in patients with progressive malignancy after failure of conventional therapy. Eur J Cancer 44(3):383–390
Rossi A, Gabbrielli E, Villano M, Messina M, Ferrara F, Weber E (2010) Human microvascular lymphatic and blood endothelial cells produce fibrillin: deposition patterns and quantitative analysis. J Anat 217(6):705–714
Shibuya M (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: its unique signaling and specific ligand, VEGF-E. Cancer Sci 94:751–756
Sigurdsson V, Fridriksdottir AJ, Kjartansson J, Jonasson JG, Steinarsdottir M, Petersen OW, Ogmundsdottir HM, Gudjonsson T (2006) Human breast microvascular endothelial cells retain phenotypic traits in long-term finite life span culture. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 42(10):332–340
Sun RS, Sui JF, Chen XH, Ran XZ, Yang ZF, Guan WD, Yang T (2011) Detection of CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with chronic autoimmune urticaria. Australas J Dermatol 52(3):15–18
Veitonmaki N, Fuxe J, Hultdin M, Roos G, Pettersson RF, Cao Y (2003) Immortalization of bovine capillary endothelial cells by hTERT alone involves inactivation of endogenous p16INK4A/pRb. FASEB J 17(6):764–766
Vestweber D (2008) VE-cadherin: the major endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and blood vessel formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(2):223–232
Wei YQ, Wang QR, Zhao X, Yang L, Tian L, Lu Y, Kang B, Lu CJ, Huang MJ, Lou YY, Xiao F, He QM, Shu JM, Xie XJ, Mao YQ, Lei S, Luo F, Zhou LQ, Liu CE, Zhou H, Jiang Y, Peng F, Yuan LP, Li Q, Wu Y, Liu JY (2000) Immunotherapy of tumors with xenogeneic endothelial cells as a vaccine. Nat Med 6(10):1160–1166
Wen VW, Wu K, Baksh S, Hinshelwood RA, Lock RB, Clark SJ, Moore MA, Mackenzie KL (2006) Telomere-driven karyotypic complexity concurs with p16INK4a inactivation in TP53-competent immortal endothelial cells. Cancer Res 66(22):10691–10700
Yang J, Chang E, Cherry AM, Bangs CD, Oei Y, Bodnar A, Bronstein A, Chiu CP, Herron GS (1999) Human endothelial cell life extension by telomerase expression. J Biol Chem 274(37):26141–26148
Young AT, Lakey JR, Murray AG, Mullen JC, Moore RB (2003) In vitro senescence occurring in normal human endothelial cells can be rescued by ectopic telomerase activity. Transpl Proc 35(7):2483–2485
Zhang H, Pan KH, Cohen SN (2003) Senescence-specific gene expression fingerprints reveal cell-type-dependent physical clustering of up-regulated chromosomal loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(6):3251–3256
Zhao Z, Yao Y, Ding Z, Chen X, Xie K, Luo Y, Zhang J, Chen X, Wu X, Xu J, Zhao J, Niu T, Liu J, Li Q, Zhang W, Wen Y, Su J, Hu B, Bu H, Wei Y, Wu Y (2011) Antitumour immunity mediated by mannan-modified adenovirus vectors expressing VE-cadherin. Vaccine 29(25):4218–4224
Zhou X, Li J, Wang Z, Chen Z, Qiu J, Zhang Y, Wang W, Ma Y, Huang N, Cui K, Li J, Wei YQ (2013) Cellular immunotherapy for carcinoma using genetically modified EGFR-specific T lymphocytes. Neoplasia 15(5):544–553
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81372246 and 81123003), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2014AA020708 and 2015AA020309), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grants 20120181110029), National Science and Technology Major Projects for “Major New Drugs Innovation and Development” (No. 2009zx09503-020) and the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB529900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, X., Fang, C., Zhou, J. et al. Fusion with human lung cancer cells elongates the life span of human umbilical endothelial cells and enhances the anti-tumor immunity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 111–123 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2002-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2002-6