Abstract
Purpose
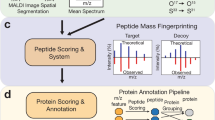
For several decades, conventional histological staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) have been the main tools to visualize and understand tissue morphology and structure. IHC visualizes the spatial distribution of individual protein species directly in tissue. However, a specific antibody is required for each protein, and multiplexing capabilities are extremely limited, rarely visualizing more than two proteins simultaneously. With the recent emergence of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-imaging), it is becoming possible to study more complex proteomic patterns directly in tissue. However, the analysis and interpretation of large and complex MALDI-imaging data requires advanced computational methods. In this paper, we show how the recently introduced method of spatial segmentation can be applied to analysis and interpretation of a larynx carcinoma section and compare the spatial segmentation with the histological annotation of the same tissue section.
Methods
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging is a label-free spatially resolved analytical technique, which allows detection and visualization of hundreds of proteins at once. Spatial segmentation of the MALDI-imaging data by clustering of spectra by their similarity was performed, automatically generating spatial a segmentation map of the tissue section, where regions of similar proteomic patterns were highlighted. The tissue was stained with the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), histopathologically analyzed and annotated. The segmentation map was interpreted after its overlay with the H&E microscopy image.
Results
The automatically generated segmentation map exhibits high correspondence to the detailed histological annotation of the larynx carcinoma tissue section. By superimposing, the segmentation map based on the proteomic profiles with H&E-stained microscopic images, we demonstrate precise localization of complex and histopathologically relevant tissue features in an automated way.
Conclusions
The combination of MALDI-imaging and automatic spatial segmentation is a useful approach in analyzing carcinoma tissue and provides a deeper insight into the functional proteomic organization of the respective tissue.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrethsen J, Bogebo R, Gammeltoft S, Olsen J, Winther B, Raskov H (2005) Upregulated expression of human neutrophil peptides 1, 2 and 3 (HNP 1–3) in colon cancer serum and tumours: a biomarker study. BMC Cancer 5(1):8
Alexandrov T, Kobarg JH (2011) Efficient spatial segmentation of large imaging mass spectrometry datasets with spatially aware clustering. Bioinformatics 27(13):i230–i238. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr246
Alexandrov T, Becker M, Deininger SO, Ernst G, Wehder L, Grasmair M, von Eggeling F, Thiele H, Maass P (2010) Spatial segmentation of imaging mass spectrometry data with edge-preserving image denoising and clustering. J Proteome Res 9(12):6535–6546. doi:10.1021/pr100734z
Alexandrov T, Meding S, Trede D, Kobarg JH, Balluff B, Walch A, Thiele H, Maass P (2011) Super-resolution segmentation of imaging mass spectrometry data: solving the issue of low lateral resolution. J Proteomics. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.08.002
Cazares L, Adam B, Ward M, Nasim S, Schellhammer P, Semmes O, Wright GJ (2002) Normal, benign, preneoplastic, and malignant prostate cells have distinct protein expression profiles resolved by surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Clin Cancer Res 8(8):2541–2552
Cazares LH, Troyer DA, Wang B, Drake RR, Semmes OJ (2011) MALDI tissue imaging: from biomarker discovery to clinical applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(1):17–27. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5003-6
Chaurand P, Sanders ME, Jensen RA, Caprioli RM (2004) Proteomics in diagnostic pathology: profiling and imaging proteins directly in tissue sections. Am J Pathol 165(4):1057–1068
Deininger S, Ebert M, Fütterer A, Gerhard M, Röcken C (2008) MALDI imaging combined with hierarchical clustering as a new tool for the interpretation of complex human cancers. J Proteome Res 7(12):5230–5236
Deutskens F, Yang J, Caprioli RM (2011) High spatial resolution imaging mass spectrometry and classical histology on a single tissue section. J Mass Spectrom 46(6):568–571. doi:10.1002/jms.1926
Driemel O, Murzik U, Escher N, Melle C, Bleul A, Dahse R, Reichert TE, Ernst G, von Eggeling F (2007) Protein profiling of oral brush biopsies: S100A8 and S100A9 can differentiate between normal, premalignant and tumor cells. Proteomics Clin Appl 1:486–493
Driemel O, Escher N, Ernst G, Melle C, von Eggeling F (2010) S100A8 cellular distribution in normal epithelium, hyperplasia, dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma and its concentration in serum. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 32(4):219–224
Escher N, Spies-Weisshart B, Kaatz M, Melle C, Bleul A, Driesch D, Wollina U, von Eggeling F (2006) Identification of HNP3 as a tumour marker in CD4+ and CD4-lymphocytes of patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Eur J Cancer 42(2):249–255
Hermani A, Hess J, De SB, Medunjanin S, Grobholz R, Trojan L, Angel P, Mayer D (2005) Calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 as novel diagnostic markers in human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(14):5146–5152
Hermani A, De SB, Medunjanin S, Tessier PA, Mayer D (2006) S100A8 and S100A9 activate MAP kinase and NF-kappaB signaling pathways and trigger translocation of RAGE in human prostate cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 312(2):184–197
Holle A, Haase A, Kayser M, Hohndorf J (2006) Optimizing UV laser focus profiles for improved MALDI performance. J Mass Spectrom 41(6):705–716. doi:10.1002/jms.1041
Jr G, Cazares L, Leung S, Nasim S, Adam B, Yip T, Schellhammer P, Gong L, Vlahou A (1999) Proteinchip(R) surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization (SELDI) mass spectrometry: a novel protein biochip technology for detection of prostate cancer biomarkers in complex protein mixtures. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2(5/6):264–276. doi:10.1038/sj.pcan.4500384
Jurchen JC, Rubakhin SS, Sweedler JV (2005) MALDI-MS imaging of features smaller than the size of the laser beam. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16(10):1654–1659. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2005.06.006
Lagarrigue M, Becker M, Lavigne R, Deininger SO, Walch A, Aubry F, Suckau D, Pineau C (2011) Revisiting rat spermatogenesis with MALDI imaging at 20-microm resolution. Mol Cell Proteomics 10(3):M110 005991. doi:10.1074/mcp.M110.005991
Lundy FT, Orr DF, Gallagher JR, Maxwell P, Shaw C, Napier SS, Gerald CC, Lamey PJ, Marley JJ (2004) Identification and overexpression of human neutrophil alpha-defensins (human neutrophil peptides 1, 2 and 3) in squamous cell carcinomas of the human tongue. Oral Oncol 40(2):139–144
Melle C, Ernst G, Schimmel B, Bleul A, Koscielny S, Wiesner A, Bogumil R, Möller U, Osterloh D, Halbhuber K, von Eggeling F (2004) A technical triade for proteomic identification and characterization of cancer biomarkers. Cancer Res 64(12):4099–4104. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3807
Melle C, Ernst G, Schimmel B, Bleul A, Thieme H, Kaufmann R, Mothes H, Settmacher U, Claussen U, Halbhuber KJ, von Eggeling F (2005) Discovery and identification of alpha-defensins as low abundant, tumor-derived serum markers in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 129(1):66–73
Moog-Lutz C, Bouillet P, Regnier CH, Tomasetto C, Mattei MG, Chenard MP, Anglard P, Rio MC, Basset P (1995) Comparative expression of the psoriasin (S100A7) and S100C genes in breast carcinoma and co-localization to human chromosome 1q21-q22. Int J Cancer 63(2):297–303
Muller CA, Markovic-Lipkovski J, Klatt T, Gamper J, Schwarz G, Beck H, Deeg M, Kalbacher H, Widmann S, Wessels JT, Becker V, Muller GA, Flad T (2002) Human alpha-defensins HNPs-1, -2, and -3 in renal cell carcinoma: influences on tumor cell proliferation. Am J Pathol 160(4):1311–1324
Opitz F, Melle C, Schenke-Layland K, Degenkolbe I, Martin DP, von Eggeling F, Wahlers T, Stock UA (2004) Protein chip system technology: a powerful tool to analyze expression differences in tissue-engineered blood vessels. Tissue Eng 10(3–4):611–620
Paradis V, Degos F, Dargere D, Pham N, Belghiti J, Degott C, Janeau JL, Bezeaud A, Delforge D, Cubizolles M, Laurendeau I, Bedossa P (2005) Identification of a new marker of hepatocellular carcinoma by serum protein profiling of patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatology 41(1):40–47
Rauser S, Marquardt C, Balluff B, Deininger S-O, Albers C, Belau E, Hartmer R, Suckau D, Specht K, Ebert MP, Schmitt M, Aubele M, Hofler H, Walch A (2010) Classification of HER2 receptor status in breast cancer tissues by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 9(4):1854–1863
Rezende TM, de Souza Freire M, Franco OL (2010) Head and neck cancer: proteomic advances and biomarker achievements. Cancer 116(21):4914–4925. doi:10.1002/cncr.25245
Rompp A, Guenther S, Schober Y, Schulz O, Takats Z, Kummer W, Spengler B (2010) Histology by mass spectrometry: label-free tissue characterization obtained from high-accuracy bioanalytical imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(22):3834–3838. doi:10.1002/anie.200905559
Rompp A, Guenther S, Takats Z, Spengler B (2011) Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space (HR(2) MSI) for reliable investigation of drug compound distributions on the cellular level. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(1):65–73. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4990-7
Seeley E, Caprioli R (2008) Molecular imaging of proteins in tissues by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(47):18126–18131. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801374105
Semmes O, Feng Z, Adam B, Banez L, Bigbee W, Campos D, Cazares L, Chan D, Grizzle W, Izbicka E, Kagan J, Malik G, McLerran D, Moul J, Partin A, Prasanna P, Rosenzweig J, Sokoll L, Srivastava S, Thompson I, Welsh M, White N, Winget M, Yasui Y, Zhang Z, Zhu L (2005) Evaluation of serum protein profiling by surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the detection of prostate cancer: I. Assessment of platform reproducibility. Clin Chem 51(1):102–112. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.038950
Sobin LGM, Wittekind C (2009) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours (UICC International Union Against Cancer), 7th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford
Stulik J, Osterreicher J, Koupilova K, Knizek J, Macela A, Bures J, Jandik P, Langr F, Dedic K, Jungblut PR (1999) The analysis of S100A9 and S100A8 expression in matched sets of macroscopically normal colon mucosa and colorectal carcinoma: the S100A9 and S100A8 positive cells underlie and invade tumor mass. Electrophoresis 20(4–5):1047–1054
van Remoortere A, van Zeijl RJ, van den Oever N, Franck J, Longuespee R, Wisztorski M, Salzet M, Deelder AM, Fournier I, McDonnell LA (2010) MALDI imaging and profiling MS of higher mass proteins from tissue. J Am Soc Mass Spectr 21(11):1922–1929
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N, Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA, Nacken W, Foell D, van der Poll T, Sorg C, Roth J (2007) Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med 13(9):1042–1049
von Eggeling F, Davies H, Lomas L, Fiedler W, Junker K, Claussen U, Ernst G (2000) Tissue-specific microdissection coupled with protein chip array technologies: applications in cancer research. Biotechniques 29(5):1066–1070
von Eggeling F, Junker K, Fiedle W, Wollscheid V, Dürst M, Claussen U, Ernst G (2001) Mass spectrometry meets chip technology: a new proteomic tool in cancer research? Electrophoresis 22(14):2898–2902. doi:10.1002/1522-2683(200108)22:14<2898:AID-ELPS2898>3.0.CO;2-A
von Eggeling F, Melle C, Ernst G (2007) Microdissecting the proteome. Proteomics 7(16):2729–2737
Walch A, Rauser S, Deininger SO, Hofler H (2008) MALDI imaging mass spectrometry for direct tissue analysis: a new frontier for molecular histology. Histochem Cell Biol 130(3):421–434. doi:10.1007/s00418-008-0469-9
Ward DG, Suggett N, Cheng Y, Wei W, Johnson H, Billingham LJ, Ismail T, Wakelam MJ, Johnson PJ, Martin A (2006) Identification of serum biomarkers for colon cancer by proteomic analysis. BrJ Cancer 94(12):1898–1905
Wehder L, Ernst G, Crecelius AC, Guntinas-Lichius O, Melle C, Schubert US, von Eggeling F (2010) Depicting the spatial distribution of proteins in human tumor tissue combining SELDI and MALDI imaging and immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 58(10):929–937
Yong HY, Moon A (2007) Roles of calcium-binding proteins, S100A8 and S100A9, in invasive phenotype of human gastric cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res 30(1):75–81
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandrov, T., Becker, M., Guntinas-Lichius, O. et al. MALDI-imaging segmentation is a powerful tool for spatial functional proteomic analysis of human larynx carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 85–95 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1303-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1303-2