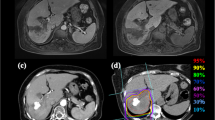
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of our study was to evaluate the feasibility and treatment outcomes of recombinant adenovirus-p53 (rAd-p53, trademarked as Gendicine) combined with fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (fSRT) in treatment of primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
We randomly enrolled 40 patients with HCC treated by fSRT alone (fSRT group) or rAd-p53 combined with fSRT (combined group). Tumor size was 2–5.2 cm (average 3.2 cm). We prescribed 50 Gy in 10 fractions at the 50%–80% isodose line of the planning target volume for 2 weeks in two groups. The combined group was treated with two intratumoral injections of rAd-p53 on day 1 and 8 while fSRT started on day 3. Tumor response was assessed after treatment using modified WHO criteria. The follow-up period was 11–44 months (median 35 months).
Results
The overall response rate of fSRT group was 70%, with 4 patients showing complete response (20%), 10 partial response (50%) and 6 stable disease (30%). Correspondingly the overall response rate of combined group was 85%, with 7 patients showing complete response (35%), 10 partial response (50%) and 3 stable disease (15%). The 1-year survival rates of fSRT group and combined group were 70.0% and 90.0%, respectively. The 1-year disease-free survival rates of fSRT group and combined group were 65% and 85%, respectively. These treatments were well tolerated, because grade 3 or 4 toxicity was not observed.
Conclusion
These results suggest that rAd-p53 combined with fSRT is a relatively safe and effective method for treating primary hepatocellular carcinoma compared with only fSRT. Thus, rAd-p53 combined with fractionated SRT may be preferred as a choice of local treatment for primary HCC when the patients are inoperable or when the patients refuse operation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourdon JC (2007) p53 Family isoforms. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 8(6):332–336. doi:10.2174/138920107783018444
Cook GC, Moosa B (1985) Hepatocellular carcinoma: one of the world’s most common malignancies. Am J Med 233:705–708
Frank DK (2002) Gene therapy for head and neck cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 100:708–726
Krishnan S, Dawson LA, Seong J et al (2008) Radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 15(4):1015–1024. doi:10.1245/s10434-007-9729-5
Méndez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: a single institution phase I-II study. Acta Oncol 45(7):831–837. doi:10.1080/02841860600897934
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Taki K et al (2006) Extrahepatic blood supply to hepatocellular carcinoma: angiographic demonstration and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29(1):39–48. doi:10.1007/s00270-004-0287-y
Neyns B, Noppen M (2003) Intratumoral gene therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current status and future directions. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 59(4):287–295
Senan S, De Ruysscher D, Giraud P et al (2004) Literature-based recommendations for treatment planning and execution in high-dose radiotherapy for lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 71(2):139–146. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2003.09.007
Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM, Suh CO (2001) Determination of optimal dose in external radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 34(Suppl. 1):102a
Shinoura N, Yamamoto N, Asai A (2000) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of Fas ligand gene augments radiation-induced apoptosis in U-373MG glioma cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 91(10):1044–1050
Spandidos DA (2007) Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes as paradigms in oncogenesis. J BUON 12(Suppl 1):S9–S12
Takeda A, Takahashi M, Kunieda E (2008) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with and without transarterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinoma not eligible for other ablation therapies: preliminary results for efficacy and toxicity. Hepatol Res 38(1):60–69. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00084.x
Thottassery JV, Zambetti GP, Arimori K et al (1997) p53-Dependent regulation of MDR1 gene expression causes selective resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(20):11037–11042. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.20.11037
Timiryasova TM, Gridley DS, Chen B (2003) Radiation enhances the anti-tumor effects of vaccinia-p53 gene therapy in glioma. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2(3):223–235
Trodella L, Ciresa M, D’Angelillo R et al (2003) Lymphatic drainage, CTV and molecular imaging in non-small cell lung cancer. Rays 28(3):299–302
Tse RV, Hawkins M, Lockwood G et al (2008) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26(4):657–664. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.3529
Wulf J, Guckenberger M, Haedinger U (2006) Stereotactic radiotherapy of primary liver cancer and hepatic metastases. Acta Oncol 45(7):838–847. doi:10.1080/02841860600904821
Yu YQ, Xu DB, Zhou XD, Lu JZ, Tang ZY, Mack P (1993) Experience with liver resection after hepatic arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 71:62–65. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19930101)71:1<62::AID-CNCR2820710111>3.0.CO;2-8
Zhou ZH, Liu LM, Chen WW et al (2007) Combined therapy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol 80(951):194–201. doi:10.1259/bjr/33521596
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Zhen-zhou Yang, Dr. Feng Jin, Dr. Zhao-yang Zhong and Dr. Meng-xia Li for their kind and excellent technical assistance. Financial Support: National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30872975) for Prof. Dong Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Zx., Wang, D., Wang, G. et al. Clinical study of recombinant adenovirus-p53 combined with fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 625–630 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0701-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-009-0701-6