Abstract
Introduction
It has been reported that the R497K polymorphism of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene has attenuated functions in ligand binding, tyrosine kinase activation, and growth stimulation. On other hand, EGFR gene mutations at kinase domain in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been examined for their ability to predict sensitivity to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Materials and methods
We investigated the EGFR mutations and/or R497K polymorphism statuses in 225 surgically treated NSCLC cases. 192 adenocarcinoma cases were included. The presence or absence of EGFR polymorphism of exon 13 was analyzed by PCR–RFLP method.
Results
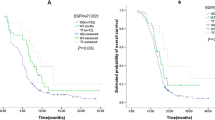
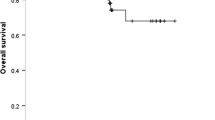
EGFR mutations at kinase domain were found from 95 of 225 lung cancer patients. In 86.2% of patients, homo- or heterozygous Lys497 allele was present. No correlation existed between R497K EGFR genotype and clinico-pathological features, such as gender, smoking status, and pathological subtypes.
Conclusions
EGFR mutation status was not correlated with R497KEGFR genotype of lung cancers. In node-negative patients, R497KEGFR genotype was not correlated with disease outcome. In node-positive patients, however, R497K EGFR was significantly associated with better overall survival. This association was attributable to neo-adjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy. In 46 total gefitinib treated NSCLC patients, the prognosis was not different between the EGFR wild type (GG) patients and AG+AA patients. R497KEGFR polymorphism might be associated with favorable prognosis of advanced lung cancers and correlated with chemosensitivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandres E, Brarricarte R, Cantero C, Honorato B, Malumbres R, Zarate R, Alcalde J, Garcia-Foncillas J (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) polymorphisms and survival in head and neck cancer patients. Oral Oncol 43:713–719
Brandt B, Meyer-Staeckling S, Schmidt H, Agelopoulos K, Buerger H (2006) Mechanisms of egfr gene transcription modulation: relationship to cancer risk and therapy response. Clin Cancer Res 12:7252–7260
Dubey S, Stephenson P, Levy DE, Miller JA, Keller SM, Schiller JH, Johnson DH, Kolesar JM (2006) EGFR dinucleotide repeat polymorphism as a prognostic indicator in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 1:406–412
Dumontet C, Isaac S, Souquet PJ, Bejui-Thivolet F, Pacheco Y, Peloux N, Frankfurter A, Luduena R, Perol M (2005) Expression of class III beta tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with resistance to taxane chemotherapy. Bull Cancer 92:E25–E30
Endo K, Konishi A, Sasaki H, Takada M, Tanaka H, Okumura M, Kawahara M, Sugiura H, Kuwabara Y, Fukai I, Matsumura A, Yano M, Kobayashi Y, Mizuno K, Haneda H, Suzuki E, Iuchi K, Fujii Y (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in non-small cell lung cancer using highly sensitive and fast TaqMan PCR assay. Lung Cancer 50:375–384
Fukushima T, Favereaux F, Huang H, Shimizu T, Yonezawa Y, Nakazato Y, Ohagki H (2006) Genetic alterations in primary glioblastomas in Japan. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:12–18
Ginsberg RJ, Kris K, Armstrong G (1993) Cancer of the lung. In: Principles and practice of oncology. Lippincott 1993; Fourth Edition, Philadelphia 673–682
Kang D, Gridley G, Huang WY, Engel LS, Winn DM, Brown LM, Bravo-Otero E, Wu T, Diehl SR, Hayes RB (2005) Microsatellite polymorphisms in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene and the transforming growth factor-alpha (TGFA) gene and risk of oral cancer in Puerto Rico. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15:343–347
Keller SM, Adak S, Wagner H, Herskovic A, Komaki R, Brooks BJ, Perry MC, Livingston RB, Johnson DH (2000) A randomized trial of postoperative adjuvant therapy in patients with completely resected stage II or IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 343:1217–1222
Liu G, Gurubhagavatula S, Zhou W, Wang Z, Yeap BY, Asomaning K, Su L, Heist R, Lynch TJ, Christiani DC (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor polymorphisms and clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. Pharmacogenomics J 8:129–138
Liu W, Wu X, Zhang W, Montenegro RC, Fackenthal DL, Spitz JA, Huff LM, Innocenti F, Das S, Cook EH Jr, Cox NJ, Bates SE, Ratain MJ (2007) Relationship of EGFR mutations, expression, amplification, and polymorphisms to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in the NCI60 cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 13:6788–6795
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. New Eng J Med 350:2129–2139
Moriai T, Kobrin MS, Hope C, Speck L, Korc M (1994) A variant epidermal growth factor receptor exhibits altered type a transforming growth factor binding and transmembrane signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:10217–10221
Nicolson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME (2001) EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37:S9–S15
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, Brambilla E, Andre F, Haddad Y, Taranchon E, Filipits M, Pirker R, Popper JH, Stahel R, Sabatier L, Pignon JP, Tursz T, Le Chevalier T, Soria JC (2006) DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 355:983–991
Onn A, Correa AM, Gilcrease M, Isobe T, Massarelli E, Bucane CD, O’Reilly MS, Hong WK, Fidler IJ, Putnum JB, Herbst RS (2004) Synchronous overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2-neu protein is a predictor of poor outcome in patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:136–143
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Seller WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Diherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singth B, Heelman R, Rusch V, Fulton L, Mardis E, Kupfer D, Wilson R, Kri M, Varmus H (2004) EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never smokers’’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and elrotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13306–13311
Sasaki H, Endo K, Takada M, Kawahara M, Kitahara H, Tanaka H, Okumura M, Matsumura A, Iuchi K, Kawaguchi T, Kawano O, Yukiue H, Yokoyama T, Yano M, Fujii Y (2007) EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation in Japanese lung cancer. Lung Cancer 58:324–328
Shintani S, Matsuo K, Crohin CC, McBride J, Tsuji T, Donoff RB, Posner M, Todd R, Wong DT (1999) Intragenic mutation analysis of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene in malignant human oral keratinocytes. Cancer Res 59:4142–4147
Wang WS, Chen PM, Chiou TJ, Liu JH, Lin JK, Lin TC et al (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor R497K polymorphism is a favorable prognostic factor for patients with colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:3597–3603
Zhang W, Park DJ, Lu B, Yang DY, Gordon M, Groshen S, Yun J, Press OA, Vallbohmer D, Rhodes K, Lenz HJ (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene polymorphisms predict pelvic recurrence in patients with rectal cancer treated with chemoradiation. Clin Cancer Res 11:600–605
Zhang W, Stabile LP, Keohavong P, Romkes M, Grandis JR, Traynor AM, Siegfried JM (2006) Mutation and polymorphism in the EGFR-TK domain associated with lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 1:635–647
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Emi Sugiyama for his excellent technical assistances. This work was supported by AstraZeneca Research Grant 2004, Grand-in-Aid for Research in Nagoya City University (2006), and Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (Nos, 19390367, 18390381,18659407).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, H., Okuda, K., Shimizu, S. et al. EGFR R497K polymorphism is a favorable prognostic factor for advanced lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135, 313–318 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0464-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0464-5