Abstract
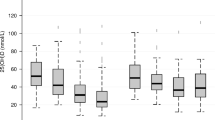
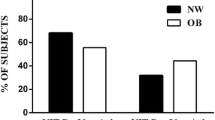
Vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency is common among non-white children; however, little is known about the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency in non-white obese children living in the Netherlands. Therefore, a retrospective analysis was performed on data from multi-ethnic Dutch children and adolescents 6–18 years who visited the obesity outpatient clinic in 2012–2013. We performed anthropometric measurements, oral glucose tolerance test, and measured 25(OH)D and lipid levels. Vitamin D insufficiency was defined as 25(OH)D levels 37.5- <50 nmol/L and vitamin D deficiency as 25(OH)D <37.5 nmol/L. In total, data from 387 children were obtained (mean age 11.6 years, 41.1 % boys, 10.3 % Dutch native, 25.6 % Turkish, 24.5 % Moroccan, 7.5 % African Surinamese, and 7.0 % West African). The median 25(OH)D level was 34 (range 12–105) nmol/L. In total, 17.8 % were vitamin D sufficient, 24.5 % with vitamin D insufficiency, and 57.6 % with vitamin D deficiency. Obese ethnic children showed the highest (87.5 %) and normal weight white children showed the lowest (20.0 %) prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency . Conclusion: Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency is extremely prevalent in treatment-seeking obese ethnic children. However, there was no evidence of an effect of vitamin D status on various components of the metabolic syndrome in our cohort.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 25(OH)D:
-
25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance
- IFG:
-
Impaired fasting glucose
- IGM:
-
Impaired glucose metabolism
- IGT:
-
Impaired glucose tolerance
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- WC:
-
Waist circumference
- Z-BMI:
-
Body Mass Index standard deviation score for age and sex
- Z-WC:
-
Waist circumference standard deviation score for age and sex
References
Alemzadeh R, Kichler J, Babar G, Calhoun M (2008) Hypovitaminosis D in obese children and adolescents: relationship with adiposity, insulin sensitivity, ethnicity, and season. Metabolism 57(2):183–191
Aypak C, Turedi O, Yuce A (2014) The association of vitamin D status with cardiometabolic risk factors, obesity and puberty in children. Eur J Pediatr 173(3):367–373. doi:10.1007/s00431-013-2177-2
Bhan I, Powe CE, Berg AH, Ankers E, Wenger JB, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani RI (2012) Bioavailable vitamin D is more tightly linked to mineral metabolism than total vitamin D in incident hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 82(1):84–89
Brouwers HF, Verburg AD, Looij BJ, Jansen EJ (2010) Rickets in the Benelux. A case report of two Indian immigrants. Acta Orthopaedia Belg 76(6):850–853
Creo AL, Rosen JS, Ariza AJ, Hidaka KM, Binns HJ (2013) Vitamin D levels, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risks in very young obese children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 26(1–2):97–104
De Luca HF (2004) Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr 80(6):1689S–1696S
De Man SA, Andre JL, Bachmann H, Grobbee DE, Ibsen KK, Laaser U, Lippert P, Hofman A (1991) Blood pressure in childhood: pooled findings of six European studies. J Hypertens 9(2):109
Dijksman T, van Doorn K (2011) A girl with bowed legs. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 155(26):A2345
Earthman C, Beckman L, Masodkar K, Sibley S (2012) The link between obesity and low circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations: considerations and implications. Int J Obes 36(3):387–396
Fitzpatrick TB (1988) The validity and practicality of sun-reactive skin types I through VI. Arch Dermatol 124(6):869–871
Fredriks AM, van Buuren S, Fekkes M, Verloove-Vanhorick SP, Wit JM (2005) Are age references for waist circumference, hip circumference and waist-hip ratio in Dutch children useful in clinical practice? Eur J Pediatr 164(4):216–222
Fredriks AM, Van Buuren S, Wit JM, Verloove-Vanhorick SP (2000) Body index measurements in 1996-7 ‚ compared with 1980. Arch Dis Child 82(2):107–112
Gerasimidis K, Shepherd S, Rashid R, Edwards CA, Ahmed F (2014) Group and individual agreement between field and dual x-ray absorptiometry-based body composition techniques in children from standard schools and a sports academy. J Acad Nutr Diet 114(1):91–98
Gonzalez-Gross M, Valtuena J, Breidenassel C, Moreno LA, Ferrari M, Kersting M, De Henauw S, Gottrand F, Azzini E, Widhalm K (2012) Vitamin D status among adolescents in Europe: the healthy lifestyle in Europe by nutrition in adolescence study. Synthesis 15:18
Gonzalez-Molero I, Rojo-Martinez G, Morcillo S, Gutierrez C, Rubio E, Perez-Valero V, Esteva I, de Adana MR, Almaraz M, Colomo N (2013) Hypovitaminosis D and incidence of obesity: a prospective study. Eur J Clin Nutr 67(6):680–682
Hintzpeter B, Scheidt-Nave C, Muller MJ, Schenk L, Mensink GB (2008) Higher prevalence of vitamin D deficiency is associated with immigrant background among children and adolescents in Germany. J Nutr 138(8):1482–1490
Huibers MH, Visser DH, Deckers MM, van Schoor NM, van Furth AM, Wolf BH (2014) Vitamin D deficiency among native Dutch and first- and second-generation non-Western immigrants. Eur J Pediatr 173(5):583–588. doi:10.1007/s00431-013-2198-x
Lenders CM, Feldman HA, Von Scheven E, Merewood A, Sweeney C, Wilson DM, Lee PD, Abrams SH, Gitelman SE, Wertz MS (2009) Relation of body fat indexes to vitamin D status and deficiency among obese adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr 90(3):459–467
Liel Y, Ulmer E, Shary J, Hollis BW, Bell NH (1988) Low circulating vitamin D in obesity. Calcif Tissue Int 43(4):199–201
Loomis WF (1967) Skin-pigment regulation of vitamin-D biosynthesis in man variation in solar ultraviolet at different latitudes may have caused racial differentiation in man. Science 157(3788):501–506
Matthews D, Hosker J, Rudenski A, Naylor B, Treacher D, Turner R (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and B-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
McKinney K, Breitkopf CR, Berenson AB (2008) Association of race, body fat and season with vitamin D status among young women: a cross-sectional study. Clin Endocrinol 69(4):535–541
Meulmeester J, Van den Berg H, Wedel M, Boshuis P, Hulshof K, Luyken R (1990) Vitamin D status, parathyroid hormone and sunlight in Turkish, Moroccan and Caucasian children in The Netherlands. Eur J Clin Nutr 44(6):461–470
Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, Collett-Solberg PF, Kappy M (2008) Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics 122(2):398–417
NGHS Coordinating Center (1998) NHLBI Growth and Health Study (NGHS) data monitoring report. Maryland Medical Research, Baltimore
Olson ML, Maalouf NM, Oden JD, White PC, Hutchison MR (2011) Vitamin D deficiency in obese children and its relationship to glucose homeostasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(1):279–285
Pettifor JM (2004) Nutritional rickets: deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or both? Am J Clin Nutr 80(6):1725S–1729S
Powe CE, Ricciardi C, Berg AH, Erdenesanaa D, Collerone G, Ankers E, Wenger J, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R, Bhan I (2011) Vitamin D-binding protein modifies the vitamin D-bone mineral density relationship. J Bone Miner Res 26(7):1609–1616
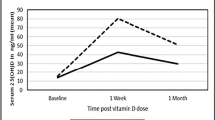
Radhakishun NNE, van Vliet M, Poland DCW, Weijer O, Beijnen JH, Brandjes DPM, Diamant M, von Rosenstiel IA (2014) Efficacy and tolerability of a high loading dose (25000 IU weekly) vitamin D3 supplementation in vitamin D deficient obese children
Rajakumar K, de Las Heras J, Chen TC, Lee S, Holick MF, Arslanian SA (2011) Vitamin D status, adiposity, and lipids in black American and Caucasian children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(5):1560–1567
Reis JP, von Muhlen D, Miller ER, Michos ED, Appel LJ (2009) Vitamin D status and cardiometabolic risk factors in the United States adolescent population. Pediatrics 124(3):e371–e379
Sartorio A, Del Col A, Agosti F, Mazzilli G, Bellentani S, Tiribelli C, Bedogni G (2006) Predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Eur J Clin Nutr 61(7):877–883
Schulpen TW (1982) Once again, rickets in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 126(14):610–613
Schwartz JB, Lai J, Lizaola B, Kane L, Markova S, Weyland P, Terrault NA, Stotland N, Bikle D (2014) A comparison of measured and calculated free 25(OH) vitamin D levels in clinical populations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(5):1631–1637
Sluyter JD, Schaaf D, Scragg RK, Plank LD (2010) Prediction of fatness by standing 8-electrode bioimpedance: a multiethnic adolescent population. Obesity 18(1):183–189
Stanley T, Bredella MA, Pierce L, Misra M (2013) The ratio of parathyroid hormone to vitamin D Is a determinant of cardiovascular risk and insulin sensitivity in adolescent girls. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 11(1):56–62
Tanner T (1962) Growth at adolescence: with a general consideration of the effects of hereditary and environmental factors upon growth and maturation from birth to maturity, 2nd edn. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Van der Meer I, Middelkoop B, Boeke A, Lips P (2011) Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Turkish, Moroccan, Indian and sub-Sahara African populations in Europe and their countries of origin: an overview. Osteoporos Int 22(4):1009–1021
Wang L, Song Y, Manson JE, Pilz S, Marz W, Michaelsson K, Lundqvist A, Jassal SK, Barrett-Connor E, Zhang C (2012) Circulating 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular disease a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 5(6):819–829
Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW, Allen K, Lopes M, Savoye M, Morrison J (2004) Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med 350(23):2362–2374
Williams DM, Fraser A, Lawlor DA (2011) Associations of vitamin D, parathyroid hormone and calcium with cardiovascular risk factors in US adolescents. Heart 97(4):315–320
World Health Organization (1987) Measuring obesity: classification and description of anthropometric data. Report on a WHO consultation of the epidemiology of obesity. Warsaw 21–23 October 1987. Copenhagen: WHO, 1989. Nutrition Unit document, EUR/ICP /NUT 123
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Michaela Diamant passed away during the preparation of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhakishun, N., van Vliet, M., von Rosenstiel, I. et al. High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency in Dutch multi-ethnic obese children. Eur J Pediatr 174, 183–190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2378-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-014-2378-3