Abstract
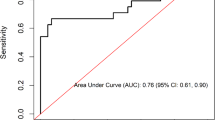
The main objective of the study was to evaluate whether in vitro QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT) assay antigen-specific IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-12 (p40) production is associated with active TB. In a cohort of 77 pulmonary TB patients (PTB), 67 healthy household contacts (HHC) and 83 healthy control subjects (HCS), the antigen-specific cytokines levels were determined in supernatants generated from QFT-GIT tubes. Antigen-specific IL-1β levels were significantly higher in PTB than HHC and HCS. At a fixed cutoff point (1,108 pg/ml), IL-1β showed positivity of 62.33 % in PTB, 22.38 % in HHC and 22.89 % in HCS. Moreover, antigen-specific IL-1β assay can differentiate PTB and HHC (believed to be latently infected) (p < 0.0001). Like IL-1β, significantly higher levels of antigen-specific TNF-α were associated with PTB and displayed 43.63 % positivity in PTB. The antigen-specific IL-2 levels were associated both with PTB (54.54 %) and HHC (48.14 %). Other cytokines levels did not differ among the groups. Our results suggest that antigen-specific IL-1β can be used as a biomarker for active TB diagnosis as well as for differential diagnosis of PTB and LTBI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (WHO) Global tuberculosis control—surveillance, planning, financing. WHO Report, Geneva 2013 (WHO/HTM/TB/2013.11)
Pai M, Kalantri S, Dheda K (2006) New tools and emerging technologies for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: part II. Active tuberculosis and drug resistance. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 6:423–432
Brock I, Weldingh K, Lillebaek T, Follmann F, Andersen P (2004) Comparison of tuberculin skin test and new specific blood test in tuberculosis contacts. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:65–69
Hill PC, Brookes RH, Adetifa IM, Fox A, Jackson-Sillah D et al (2006) Comparison of enzyme-linked immunospot assay and tuberculin skin test in healthy children exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Pediatrics 117(5):1542–1548
Pai M, Kalantri S, Dheda K (2006) New tools and emerging technologies for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: part I latent tuberculosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 6(3):413–422
Pai M, Kalantri S, Menzies D (2006) Discordance between tuberculin skin test and interferon-gamma assays. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 10(8):942–943
Menzies D, Pai M, Comstock G (2007) Meta-analysis: new tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: areas of uncertainty and recommendations for research. Ann Intern Med 146(5):340–354
Soborg B, Andersen AB, Larsen HK, Weldingh K, Andersen P, Kofoed K et al (2007) Detecting a low prevalence of latent tuberculosis among health care workers in Denmark detected by M. tuberculosis specific IFN-γ whole-blood test. Scand J Infect Dis 39(6–7):554–559
Bartu V, Havelkova M, Kopecka E (2008) QuantiFERON-TB Gold in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis. J Int Med Res 36(3):434–437
Chee CB, Gan SH, Khinmar KW, Barkham TM, Koh CK et al (2008) Comparison of sensitivities of two commercial gamma interferon release assays for pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 46(6):1935–1940
Kabeer BSA, Raman B, Thomas A, Perumal V, Raja A (2010) Role of QuantiFERON-TB gold, interferon gamma inducible protein-10 and tuberculin skin test in active tuberculosis diagnosis. PLoS One 5(2):e9051
Kabeer BSA, Sikhamani R, Swaminathan S, Perumal V, Paramasivam P, Raja A (2009) Role of interferon gamma release assay in active TB diagnosis among HIV infected individuals. PLoS One 4(5):e5718
Goletti D, Raja A, Ahamed Kabeer BS, Rodrigues C, Sodha A, Butera O et al (2010) IFN-γ, but not IP-10, MCP-2 or IL-2 response to RD1 selected peptides associates to active tuberculosis. J Infect 61(2):133–143
Sutherland JS, de Jong BC, Jeffries DJ, Adetifa IM, Ota MO (2010) Production of TNF-α, IL-12(p40) and IL-17 can discriminate between active TB disease and latent infection in a West African Cohort. PLoS One 5(8):e12365
Kellar KL, Gehrke J, Weis SE, Mahmutovic-Mayhew A, Davila B, Zajdowicz MJ et al (2011) Multiple cytokines are released when blood from patients with tuberculosis is stimulated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens. PLoS One 6(11):e26545
Kasahara K, Kobayashi K, Shikama Y, Yoneya I, Soezima K, Ide H et al (1988) Direct evidence for granuloma inducing activity of interleukin-1: induction of experimental pulmonary granuloma formation in mice by interleukin-1-coupled beads. Am J Pathol 130(3):629–638
Stenger S (2005) Immunological control of tuberculosis: role of tumour necrosis factor and more. Ann Rheum Dis 64(4):24–28
Raja A (2004) Immunology of tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 120(4):213–232
Larsen CG, Thomsen MK, Gesser B, Thomsen PD, Deleuran BW, Nowak J, Skødt V, Thomsen HK, Deleuran M, Thestrup-Pedersen K et al (1995) The delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction is dependent on IL-8. Inhibition of a tuberculin skin reaction by an anti-IL-8 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol 155(4):2151–2157
Ameixa C, Friedland JS (2002) Interleukin-8 secretion from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected monocytes is regulated by protein tyrosine kinases but not by ERK1/2 or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Infect Immun 70(8):4743–4746
Law K, Weiden M, Harkin T, Tchou-Wong K, Chi C, Rom WN (1996) Increased release of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor–α by bronchoalveolar cells lavaged from involved sites in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153(2):799–804
Juffermans NP, Florquin S, Camoglio L, Verbon A, Kolk AH, Speelman P, van Deventer SJ et al (2000) Interleukin-1 signaling is essential for host defense during murine pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect Dis 182(3):902–908
Harari A, Rozot V, Enders FB, Perreau M, Stalder JM, Nicod LP et al (2011) Dominant TNF-α+ Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD4+ T cell responses discriminate between latent infection and active disease. Nat Med 17(3):372–376
Frahm M, Goswami ND, Owzar K, Hecker E, Mosher A, Cadogan E et al (2011) Discriminating between latent and active tuberculosis with multiple biomarker responses. Tuberculosis 91(3):250–256
Wang S, Diao N, Lu C, Wu J, Gao Y, Chen J et al (2012) Evaluation of the diagnostic potential of IP-10 and IL-2 as biomarkers for the diagnosis of active and latent tuberculosis in a BCG-vaccinated population. PLoS One 7(12):e51338
El-Ahmady O, Mansour M, Zoeir H, Mansour O (1997) Elevated concentrations of interleukins and leukotriene in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Ann Clin Biochem 34(pt2):160–164
Friedland JS, Hartley JC, Hartley CG, Shattock RJ, Griffin GE (1995) Inhibition of ex vivo proinflammatory cytokine secretion in fatal Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Clin Exp Immunol 100(2):233–238
D’Andrea A, Rengaraju M, Valiante NM, Chehimi J, Kubin M, Aste M et al (1992) Production of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12) by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Exp Med 176(5):1387–1398
Cooper AM, Magram J, Ferrante J, Orme IM (1997) Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is crucial to the development of protective immunity in mice intravenously infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Exp Med 186(1):39–45
Central TB Division, Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (1998) Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme manual for laboratory technicians. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, New Delhi. http://www.tbcindia.org/LABMANUAL.pdf
Chadha VK, Jagannatha PS, Vaidyanathan PS, Jagota P (2003) PPD RT23 for tuberculin surveys in India. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 7(2):172–179
Raby E, Moyo M, Devendra A, Banda J, De Haas P, Ayles H et al (2008) The effects of HIV on the sensitivity of a whole blood IFN-gamma release assay in Zambian adults with active tuberculosis. PLoS One 3:e2489
Metcalfe JZ, Everett CK, Steingart KR, Cattamanchi A, Huang L, Hopewell PC et al (2011) Interferon-gamma release assays for active pulmonary TB diagnosis in adults in low and middle-income countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect Dis 204(Suppl 4):S1120–S1129
Sester M, Sotgiu G, Lange C, Giehl C, Girardi E, Migliori GB et al (2011) Interferon-{γ} release assays for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 37(1):100–111
Pinto LM, Grenier J, Schumacher SG, Denkinger CM, Steingart KR, Pai M (2012) Immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: state of the art. Med Princ Pract 21(1):4–13
Roach TI, Barton CH, Chatterjee D, Blackwell JM (1993) Macrophage activation: lipoarabinomannan from avirulent and virulent strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis differentially induces the early genes c-fos, KC, JE, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol 150(5):1886–1896
Dahl KE, Shiratsuchi H, Hamilton BD, Ellner JJ, Toossi Z (1996) Selective induction of transforming growth factor beta in human monocytes by lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun 64(2):399–405
Schauf V, Rom WN, Smith KA, Sampaio EP, Meyn PA et al (1993) Cytokine gene activation and modified responsiveness to interleukin-2 in the blood of tuberculosis patients. J Infect Dis 168(4):1056–1059
Tsukaguchi K, Yoneda T, Yoshikawa M, Tokuyama T, Fu A, Tomoda K et al (1992) Case study of interleukin-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 production peripheral blood monocytes in patients with diabetes mellitus complicated by pulmonary tuberculosis. Kekkaku 67(12):755–760
Su WL, Perng WC, Huang CH, Yang CY, Wu CP, Chen JH (2010) Association of reduced tumor necrosis factor alpha, gamma interferon, and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) but increased IL-10 expression with improved chest radiography in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 17(2):223–231
Chegou NN, Black GF, Kidd M, van Helden PD, Walzl G (2009) Host markers in Quantiferon supernatants differentiate active TB from latent TB infection: preliminary report. BMC Pulm Med 9:21
Jones GJ, Pirson C, Hewinson RG, Vordermeier HM (2010) Simultaneous measurement of antigen-stimulated interleukin-1β and gamma interferon production enhances test sensitivity for the detection of Mycobacterium bovis infection in Cattle. Clin Vaccine Immunol 17(12):1946–1951
Syed Ahamed Kabeer B, Paramasivam P, Raja A (2012) Interferon gamma and interferon gamma inducible protein-10 in detecting tuberculosis infection. J Infect 64(6):573–579
Wu HP, Hua CC, Chuang DY (2007) Decreased in vitro interferon-gamma production in patients with cavitary tuberculosis on chest radiography. Respir Med 101(1):48–52
Bermudez LE, Young LS (1988) Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol 140(9):3006–3013
Bermudez LE, Stevens P, Kolonoski P, Wu M, Young LS (1989) Treatment of experimental disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in mice with recombinant IL-2 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol 143(9):2996–3000
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all the patients participated in this study. Authors also thank the clinicians, social workers and health visitors who helped to collect samples from study patients. Ms. Maddineni Prabhavathi expresses her gratitude to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, for providing senior research fellowship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhavathi, M., Kabeer, B.S.A., Deenadayalan, A. et al. Role of QuantiFERON-TB Gold antigen-specific IL-1β in diagnosis of active tuberculosis. Med Microbiol Immunol 204, 567–574 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0382-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0382-x