Abstract
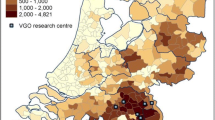
An increase in acute autochthonous hepatitis E virus (HEV) infections has been recorded in Germany. These are suspected to be zoonotically transmitted from wild boar, deer and domestic pig. The latter may represent a major reservoir for HEV. In this study, 537 sera from humans living in Westphalia and Lower Saxony, representing areas of high pig density in Germany, were tested for the presence of HEV-specific antibodies. Among them were 302 individuals with occupational, direct contact to pigs and 235 individuals without direct contact to pigs. Two commercial tests and one in-house assay were applied for the detection of HEV-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. Sera were also tested in an assay that detects all classes of HEV-specific antibodies. Depending on the test used, the seroprevalence ranged from 4.1 to 27.9 %. Exposition to pigs was found to be associated with a significantly higher seroprevalence in subjects with contact to pigs (13.2–32.8 %) compared with that in non-exposed humans (7.7–21.7 %). In particular, individuals younger than 40 years with occupational exposure exhibited a markedly higher HEV seroprevalence compared with non-exposed individuals of that age group. In general, HEV seroprevalence increased with age resulting in a similar prevalence level in the age group of ≥50 years for exposed and non-exposed individuals. Analysis of all sera by a commercial anti-HEV IgM ELISA revealed 35 positive and 25 borderline samples. However, only one positive serum could be confirmed by an IgM line assay. Selected samples from IgM and/or IgG as well as total HEV antibody-positive individuals were also tested for the presence of HEV RNA. In one of the 78 samples, the only IgM ELISA positive and IgM line assay confirmed sample, RNA of HEV genotype 3 was detected. This sequence has high similarity to HEV sequences obtained from wild boars and domestic pigs from Germany and The Netherlands. This study demonstrates that in addition to the consumption of raw or undercooked meat, direct contact to pigs has to be considered as an additional risk factor for HEV infection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batts W, Yun S, Hedrick R, Winton J (2011) A novel member of the family Hepeviridae from cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii). Virus Res 158:116–123
Payne CJ, Ellis TM, Plant SL, Gregory AR, Wilcox GE (1999) Sequence data suggests big liver and spleen disease virus (BLSV) is genetically related to hepatitis E virus. Vet Microbiol 68:119–125
Drexler JF, Seelen A, Corman VM, Tateno AF, Cottontail V, Melim Zerbinati R, Gloza-Rausch F, Klose SM, Adu-Sarkodie Y, Oppong SK, Kalko EK, Osterman A, Rasche A, Adam A, Muller MA, Ulrich RG, Leroy EM, Lukashev AN, Drosten C (2012) Bats worldwide carry hepatitis E virus-related viruses that form a putative novel genus within the family Hepeviridae. J Virol 86:9134–9147
Raj VS, Smits SL, Pas SD, Provacia LB, Moorman-Roest H, Osterhaus AD, Haagmans BL (2012) Novel hepatitis E virus in ferrets, The Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis 18:1369–1370
Johne R, Plenge-Bonig A, Hess M, Ulrich RG, Reetz J, Schielke A (2010) Detection of a novel hepatitis E-like virus in faeces of wild rats using a nested broad-spectrum RT-PCR. J Gen Virol 91:750–758
Johne R, Heckel G, Plenge-Bonig A, Kindler E, Maresch C, Reetz J, Schielke A, Ulrich RG (2010) Novel hepatitis E virus genotype in Norway rats, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis 16:1452–1455
Meng XJ, Anderson DA, Arankalle VA, Emerson SU, Harrison TJ, Jameel S, Okamoto H (2012) Hepeviridae. In: King AMQ, Adams MJ, Carstens EB, Lefkowitz EJ (eds) Virus taxonomy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1021–1028
Zhao C, Ma Z, Harrison TJ, Feng R, Zhang C, Qiao Z, Fan J, Ma H, Li M, Song A, Wang Y (2009) A novel genotype of hepatitis E virus prevalent among farmed rabbits in China. J Med Virol 81:1371–1379
Aggarwal R, Jameel S (2011) Hepatitis E. Hepatology 54:2218–2226
Smith DB, Purdy MA, Simmonds P (2013) Genetic variability and the classification of hepatitis E virus. J Virol 87:4161–4169
Aggarwal R (2011) Hepatitis E: historical, contemporary and future perspectives. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(Suppl 1):72–82
Meng XJ (2011) From barnyard to food table: the omnipresence of hepatitis E virus and risk for zoonotic infection and food safety. Virus Res 161:23–30
Aggarwal R (2013) Diagnosis of hepatitis E. Nat Rev Gastroenterol hepatol 10:24–33
Wedemeyer H, Pischke S, Manns MP (2012) Pathogenesis and treatment of hepatitis E virus infection. Gastroenterology 142:1388–1397 e1381
Kamar N, Rostaing L, Izopet J (2013) Hepatitis E virus infection in immunosuppressed patients: natural history and therapy. Semin Liver Dis 33:62–70
Arankalle VA, Lole KS, Deshmukh TM, Chobe LP, Gandhe SS (2007) Evaluation of human (genotype 1) and swine (genotype 4)-ORF2-based ELISAs for anti-HEV IgM and IgG detection in an endemic country and search for type 4 human HEV infections. J Viral Hepat 14:435–445
Dremsek P, Wenzel JJ, Johne R, Ziller M, Hofmann J, Groschup MH, Werdermann S, Mohn U, Dorn S, Motz M, Mertens M, Jilg W, Ulrich RG (2012) Seroprevalence study in forestry workers from eastern Germany using novel genotype 3- and rat hepatitis E virus-specific immunoglobulin G ELISAs. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:189–200
Meng XJ, Wiseman B, Elvinger F, Guenette DK, Toth TE, Engle RE, Emerson SU, Purcell RH (2002) Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis E virus in veterinarians working with swine and in normal blood donors in the United States and other countries. J Clin Microbiol 40:117–122
Obriadina A, Meng JH, Ulanova T, Trinta K, Burkov A, Fields HA, Khudyakov YE (2002) A new enzyme immunoassay for the detection of antibody to hepatitis E virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17(Suppl 3):S360–S364
Peralta B, Casas M, de Deus N, Martin M, Ortuno A, Perez-Martin E, Pina S, Mateu E (2009) Anti-HEV antibodies in domestic animal species and rodents from Spain using a genotype 3-based ELISA. Vet Microbiol 137:66–73
Khudyakov Y, Kamili S (2011) Serological diagnostics of hepatitis E virus infection. Virus Res 161:84–92
Aggarwal R (2013) Hepatitis E: clinical presentation in disease-endemic areas and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis 33:30–40
Johne R, Dremsek P, Kindler E, Schielke A, Plenge-Bonig A, Gregersen H, Wessels U, Schmidt K, Rietschel W, Groschup MH, Guenther S, Heckel G, Ulrich RG (2012) Rat hepatitis E virus: geographical clustering within Germany and serological detection in wild Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Infect Genet Evol 12:947–956
Wilhelm BJ, Rajic A, Greig J, Waddell L, Trottier G, Houde A, Harris J, Borden LN, Price C (2011) A systematic review/meta-analysis of primary research investigating swine, pork or pork products as a source of zoonotic hepatitis E virus. Epidemiol Infect 139:1127–1144
Vollmer T, Diekmann J, Johne R, Eberhardt M, Knabbe C, Dreier J (2012) Novel approach for detection of hepatitis E virus infection in German blood donors. J Clin Microbiol 50:2708–2713
Carpentier A, Chaussade H, Rigaud E, Rodriguez J, Berthault C, Boue F, Tognon M, Touze A, Garcia-Bonnet N, Choutet P, Coursaget P (2012) High hepatitis E virus seroprevalence in forestry workers and in wild boars in France. J Clin Microbiol 50:2888–2893
Krumbholz A, Mohn U, Lange J, Motz M, Wenzel JJ, Jilg W, Walther M, Straube E, Wutzler P, Zell R (2012) Prevalence of hepatitis E virus-specific antibodies in humans with occupational exposure to pigs. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:239–244
Miyamura T (2011) Hepatitis E virus infection in developed countries. Virus Res 161:40–46
Bouwknegt M, Engel B, Herremans MM, Widdowson MA, Worm HC, Koopmans MP, Frankena K, de Roda Husman AM, De Jong MC, Van Der Poel WH (2008) Bayesian estimation of hepatitis E virus seroprevalence for populations with different exposure levels to swine in The Netherlands. Epidemiol Infect 136:567–576
Galiana C, Fernandez-Barredo S, Garcia A, Gomez MT, Perez-Gracia MT (2008) Occupational exposure to hepatitis E virus (HEV) in swine workers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 78:1012–1015
Drobeniuc J, Favorov MO, Shapiro CN, Bell BP, Mast EE, Dadu A, Culver D, Iarovoi P, Robertson BH, Margolis HS (2001) Hepatitis E virus antibody prevalence among persons who work with swine. J Infect Dis 184:1594–1597
Geng J, Wang L, Wang X, Fu H, Bu Q, Liu P, Zhu Y, Wang M, Sui Y, Zhuang H (2011) Potential risk of zoonotic transmission from young swine to human: seroepidemiological and genetic characterization of hepatitis E virus in human and various animals in Beijing, China. J Viral Hepat 18:e583–e590
Pourpongporn P, Samransurp K, Rojanasang P, Wiwattanakul S, Srisurapanon S (2009) The prevalence of anti-hepatitis E in occupational risk groups. J Med Assoc Thai 92(Suppl 3):S38–S42
Meng XJ (2010) Hepatitis E virus: animal reservoirs and zoonotic risk. Vet Microbiol 140:256–265
Chaussade H, Rigaud E, Allix A, Carpentier A, Touze A, Delzescaux D, Choutet P, Garcia-Bonnet N, Coursaget P (2013) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence and risk factors for individuals in working contact with animals. J Clin Virol 58:504–508
Anonymous (2014) Übermittelte Hepatitis E-Fälle nach Meldekategorie, Deutschland, Fälle entsprechend der Referenzdefinition des RKI. Robert Koch-Institut, Datenstand, 19 March 2014
Faber MS, Wenzel JJ, Jilg W, Thamm M, Hohle M, Stark K (2012) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence among adults, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis 18:1654–1657
Kaci S, Nockler K, Johne R (2008) Detection of hepatitis E virus in archived German wild boar serum samples. Vet Microbiol 128:380–385
Adlhoch C, Wolf A, Meisel H, Kaiser M, Ellerbrok H, Pauli G (2009) High HEV presence in four different wild boar populations in East and West Germany. Vet Microbiol 139:270–278
Schielke A, Sachs K, Lierz M, Appel B, Jansen A, Johne R (2009) Detection of hepatitis E virus in wild boars of rural and urban regions in Germany and whole genome characterization of an endemic strain. Virol J 6:58
Wenzel JJ, Preiss J, Schemmerer M, Huber B, Plentz A, Jilg W (2011) Detection of hepatitis E virus (HEV) from porcine livers in Southeastern Germany and high sequence homology to human HEV isolates. J Clin Virol 52:50–54
Baechlein C, Seehusen F, Nathues H, Beilage E, Baumgartner W, Grummer B (2013) Molecular detection of hepatitis E virus in German domestic pigs. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 126:25–31
Baechlein C, Schielke A, Johne R, Ulrich RG, Baumgaertner W, Grummer B (2010) Prevalence of hepatitis E virus-specific antibodies in sera of German domestic pigs estimated by using different assays. Vet Microbiol 144:187–191
Dremsek P, Joel S, Baechlein C, Pavio N, Schielke A, Ziller M, Durrwald R, Renner C, Groschup MH, Johne R, Krumbholz A, Ulrich RG (2013) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence of domestic pigs in Germany determined by a novel in-house and two reference ELISAs. J Virol Methods 190:11–16
Krumbholz A, Joel S, Neubert A, Dremsek P, Durrwald R, Johne R, Hlinak A, Walther M, Lange J, Wutzler P, Sauerbrei A, Ulrich RG, Zell R (2013) Age-related and regional differences in the prevalence of hepatitis E virus-specific antibodies in pigs in Germany. Vet Microbiol 167:394–402
Anonymous (2013) Statistische Ämter des Bundes und der Länder, Regionaldatenbank Deutschland, Schweine je 100 ha landwirtschaftl. genutz. Fläche. https://www.regionalstatistik.de/genesis/online/logon. Daten für den Regionalatlas ab dem 8 April 2013
Schnegg A, Burgisser P, Andre C, Kenfak-Foguena A, Canellini G, Moradpour D, Abravanel F, Izopet J, Cavassini M, Darling KE (2013) An analysis of the benefit of using HEV genotype 3 antigens in detecting anti-HEV IgG in a European population. PLoS One 8:e62980
Anonymous (2005) Pigs density map matching FAOSTAT 2005 (modelled). http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/resources/en/glw/Modelled_maps/pigs_modelled-2005.jpg
Krumbholz A, Lange J, Durrwald R, Walther M, Muller TH, Kuhnel D, Wutzler P, Sauerbrei A, Zell R (2014) Prevalence of antibodies to European porcine influenza viruses in humans living in high pig density areas of Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol 203:13–24
Sauerbrei A, Langenhan T, Brandstadt A, Schmidt-Ott R, Krumbholz A, Girschick, Huppertz H, Kaiser P, Liese J, Streng A, Niehues T, Peters J, Sauerbrey A, Schroten H, Tenenbaum T, Wirth S, Wutzler P (2014) Prevalence of antibodies against influenza A and B viruses in children in Germany, 2008 to 2010. Euro surveillance: bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin 19
Krumbholz A, Neubert A, Girschick H, Huppertz HI, Kaiser P, Liese J, Streng A, Niehues T, Peters J, Sauerbrey A, Schroten H, Tenenbaum T, Wirth S, Sauerbrei A (2013) Prevalence of antibodies against hepatitis A virus among children and adolescents in Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol 202:417–424
Kaufmann A, Kenfak-Foguena A, Andre C, Canellini G, Burgisser P, Moradpour D, Darling KE, Cavassini M (2011) Hepatitis E virus seroprevalence among blood donors in southwest Switzerland. PLoS One 6:e21150
Meader E, Thomas D, Salmon R, Sillis M (2010) Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in the UK farming population. Zoonoses Public Health 57:504–509
Myint KS, Endy TP, Gibbons RV, Laras K, Mammen MP Jr, Sedyaningsih ER, Seriwatana J, Glass JS, Narupiti S, Corwin AL (2006) Evaluation of diagnostic assays for hepatitis E virus in outbreak settings. J Clin Microbiol 44:1581–1583
Jothikumar N, Cromeans TL, Robertson BH, Meng XJ, Hill VR (2006) A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J Virol Methods 131:65–71
Herremans M, Vennema H, Bakker J, van der Veer B, Duizer E, Benne CA, Waar K, Hendrixks B, Schneeberger P, Blaauw G, Kooiman M, Koopmans MP (2007) Swine-like hepatitis E viruses are a cause of unexplained hepatitis in the Netherlands. J Viral Hepat 14:140–146
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 33:363–374
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Abdi H (2007) Bonferroni and Sidak corrections for multiple comparisons. In: Salkind NJ (ed) Encyclopedia of measurement and statistics. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Pas SD, Streefkerk RH, Pronk M, de Man RA, Beersma MF, Osterhaus AD, van der Eijk AA (2013) Diagnostic performance of selected commercial HEV IgM and IgG ELISAs for immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. J Clin Virol 58:629–634
Reinheimer C, Allwinn R, Berger A (2012) Hepatitis E: are psychiatric patients on special risk? Med Microbiol Immunol 201:171–175
Juhl D, Baylis SA, Blumel J, Gorg S, Hennig H (2014) Seroprevalence and incidence of hepatitis E virus infection in German blood donors. Transfusion 54:49–56
Krumbholz A, Neubert A, Joel S, Girschick H, Huppertz HI, Kaiser P, Liese J, Streng A, Niehues T, Peters J, Sauerbrey A, Schroten H, Tenenbaum T, Wirth S, Zell R, Sauerbrei A (2014) Prevalence of hepatitis E virus antibodies in children in Germany. Pediatr Infect Dis J 33:258–262
Wenzel JJ, Preiss J, Schemmerer M, Huber B, Jilg W (2013) Test performance characteristics of Anti-HEV IgG assays strongly influence hepatitis E seroprevalence estimates. J Infect Dis 207:497–500
Bendall R, Ellis V, Ijaz S, Ali R, Dalton H (2010) A comparison of two commercially available anti-HEV IgG kits and a re-evaluation of anti-HEV IgG seroprevalence data in developed countries. J Med Virol 82:799–805
Pischke S, Heim A, Bremer B, Raupach R, Horn-Wichmann R, Ganzenmueller T, Klose B, Goudeva L, Wagner F, Oehme A, Manns MP, Wedemeyer H (2011) Hepatitis E: an emerging infectious disease in Germany? Z Gastroenterol 49:1255–1257
Anonymous (2013) Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2012, Robert Koch-Institut, Berlin
Veitt R, Reichardt M, Wenzel J, Jilg W (2011) Autochthonous hepatitis E-virus infection as cause of acute hepatitis in Germany—a case report. Z Gastroenterol 49:42–46
Christensen PB, Engle RE, Hjort C, Homburg KM, Vach W, Georgsen J, Purcell RH (2008) Time trend of the prevalence of hepatitis E antibodies among farmers and blood donors: a potential zoonosis in Denmark. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am 47:1026–1031
Renou C, Moreau X, Pariente A, Cadranel JF, Maringe E, Morin T, Causse X, Payen JL, Izopet J, Nicand E, Bourliere M, Penaranda G, Hardwigsen J, Gerolami R, Peron JM, Pavio N (2008) A national survey of acute hepatitis E in France. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27:1086–1093
Mansuy JM, Bendall R, Legrand-Abravanel F, Saune K, Miedouge M, Ellis V, Rech H, Destruel F, Kamar N, Dalton HR, Izopet J (2011) Hepatitis E virus antibodies in blood donors, France. Emerg Infect Dis 17:2309–2312
Slot E, Hogema BM, Riezebos-Brilman A, Kok TM, Molier M, Zaaijer HL (2013) Silent hepatitis E virus infection in Dutch blood donors, 2011 to 2012, Euro surveillance : bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin 18
Zhang S, Tian D, Zhang Z, Xiong J, Yuan Q, Ge S, Zhang J, Xia N (2009) Clinical significance of anti-HEV IgA in diagnosis of acute genotype 4 hepatitis E virus infection negative for anti-HEV IgM. Dig Dis Sci 54:2512–2518
Tian DY, Chen Y, Xia NS (2006) Significance of serum IgA in patients with acute hepatitis E virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 12:3919–3923
Acknowledgments
Mikrogen GmbH and Diasorin S.p.A. have supported this study by free delivery of assays A and B. The authors would like to thank all members of the German Red Cross Blood Donation Centres, Münster and Springe for excellent cooperation as well as all subjects for delivery of blood samples. The authors are indebted to Martina Müller, Christa Rothmann, Dörte Kaufmann and Ute Polster-Brylla for their technical assistance. The support of Silvia Dorn and Michael Dawideit is also cordially acknowledged. This study was supported by a grant of the Foundation of the Paul-Ehrlich-Society for Chemotherapy awarded to A.K.
Conflict of interest
Mikrogen and Diasorin had no influence on testing of samples and interpretation of data as well as on writing of the manuscript. Results of this study have been presented at meetings of the Society of Virology and of the German Research Platform for Zoonoses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Andi Krumbholz and Sebastian Joel have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krumbholz, A., Joel, S., Dremsek, P. et al. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus (HEV) in humans living in high pig density areas of Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol 203, 273–282 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0336-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-014-0336-3