Abstract
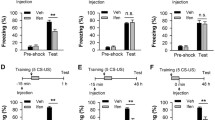
Epileptic seizures negatively affect cognition. However, the mechanisms that contribute to cognitive impairments after seizures are largely unknown. Here, we examined the effects of long-term kindling (i.e., 99 stimulations) of limbic (basolateral amygdala, dorsal hippocampus) and non-limbic (caudate nucleus) brain sites on conditioned fear and hippocampal plasticity. We first showed that kindling had no effect on acquisition of a hippocampal-dependent trace fear-conditioning task but limbic kindling impaired the retrieval of these fear memories. To determine the relationship between memory and hippocampal neuronal activity, we examined the expression of Fos protein 90 min after memory retrieval (i.e., 4 days after the last kindling stimulation). We found that limbic kindling, but not non-limbic kindling, decreased Fos expression in the granule cell layer, hilus, CA3 pyramidal cell layer, and CA1 pyramidal cell layer. Next, to investigate a mechanism that could contribute to dampen hippocampal neuronal activity in limbic-kindled rats, we focused on the endogenous anticonvulsant neuropeptide Y (NPY), which is expressed in a subset of GABAergic interneurons and can prevent glutamate release through interactions with its Y2 receptor. We found that limbic kindling significantly decreased the number of NPY-immunoreactive cells in several hippocampal subfields despite minimal staining of the neurodegenerative marker Fluoro-Jade B. However, we also noted that limbic kindling enhanced NPY immunoreactivity throughout the mossy fiber pathway. In these same regions, we observed limbic kindling-induced de novo expression of the NPY Y2 receptor. These novel findings demonstrate the site-specific effects of kindling on cognition and NPY plasticity, and they provide evidence that altered hippocampal NPY after limbic seizures coincides with dampened neural activity and cognitive impairments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baraban SC, Hollopeter G, Erickson JC, Schwartzkroin PA, Palmiter RD (1997) Knock-out mice reveal a critical antiepileptic role for neuropeptide Y. J Neurosci 17:8927–8936
Botterill JJ, Fournier NM, Guskjolen AJ, Lussier AL, Marks WN, Kalynchuk LE (2014) Amygdala kindling disrupts trace and delay fear conditioning with parallel changes in Fos protein expression throughout the limbic brain. Neuroscience 265:158–171
Cardoso A, Freitas-da-Costa P, Carvalho LS, Lukoyanov NV (2010) Seizure-induced changes in neuropeptide Y-containing cortical neurons: potential role for seizure threshold and epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Behav 19:559–567
Cassel JC, Cassel S, Galani R, Kelche C, Will B, Jarrard L (1998) Fimbria-fornix vs selective hippocampal lesions in rats: effects on locomotor activity and spatial learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 69:22–45
Colmers WF, El BB (2003) Neuropeptide Y and Epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr 3:53–58
de Lanerolle NC, Kim JH, Robbins RJ, Spencer DD (1989) Hippocampal interneuron loss and plasticity in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res 495:387–395
Fournier NM, Darnbrough AL, Wintink AJ, Kalynchuk LE (2009) Altered synapsin I immunoreactivity and fear behavior in male and female rats subjected to long-term amygdala kindling. Behav Brain Res 196:106–115
Fournier NM, Andersen DR, Botterill JJ, Sterner EY, Lussier AL, Caruncho HJ, Kalynchuk LE (2010) The effect of amygdala kindling on hippocampal neurogenesis coincides with decreased reelin and DISC1 expression in the adult dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 20:659–671
Fournier NM, Botterill JJ, Marks WN, Guskjolen AJ, Kalynchuk LE (2013) Impaired recruitment of seizure-generated neurons into functional memory networks of the adult dentate gyrus following long-term amygdala kindling. Exp Neurol 244:96–104
Furtinger S, Pirker S, Czech T, Baumgartner C, Ransmayr G, Sperk G (2001) Plasticity of Y1 and Y2 receptors and neuropeptide Y fibers in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 21:5804–5812
Giorgi FS, Blandini F, Cantafora E, Biagioni F, Armentero MT, Pasquali L, Orzi F, Murri L, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008) Activation of brain metabolism and fos during limbic seizures: the role of locus coeruleus. Neurobiol Dis 30:388–399
Gobbi M, Gariboldi M, Piwko C, Hoyer D, Sperk G, Vezzani A (1998) Distinct changes in peptide YY binding to, and mRNA levels of, Y1 and Y2 receptors in the rat hippocampus associated with kindling epileptogenesis. J Neurochem 70:1615–1622
Goddard GV, McIntyre DC, Leech CK (1969) A permanent change in brain function resulting from daily electrical stimulation. Exp Neurol 25:295–330
Guzowski JF, Timlin JA, Roysam B, McNaughton BL, Worley PF, Barnes CA (2005) Mapping behaviorally relevant neural circuits with immediate-early gene expression. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:599–606
Hale MW, Hay-Schmidt A, Mikkelsen JD, Poulsen B, Shekhar A, Lowry CA (2008) Exposure to an open-field arena increases c-Fos expression in a distributed anxiety-related system projecting to the basolateral amygdaloid complex. Neuroscience 155:659–672
Hannesson DK, Howland J, Pollock M, Mohapel P, Wallace AE, Corcoran ME (2001) Dorsal hippocampal kindling produces a selective and enduring disruption of hippocampally mediated behavior. J Neurosci 21:4443–4450
Hannesson DK, Pollock MS, Howland JG, Mohapel P, Wallace AE, Corcoran ME (2008) Amygdaloid kindling is anxiogenic but fails to alter object recognition or spatial working memory in rats. Epilepsy Behav 13:52–61
Helfer V, Deransart C, Marescaux C, Depaulis A (1996) Amygdala kindling in the rat: anxiogenic-like consequences. Neuroscience 73:971–978
Hokfelt T (1991) Neuropeptides in perspective: the last ten years. Neuron 7:867–879
Huusko N, Romer C, Ndode-Ekane XE, Lukasiuk K, Pitkanen A (2013) Loss of hippocampal interneurons and epileptogenesis: a comparison of two animal models of acquired epilepsy. Brain Struct Funct doi:10.1007/s00429-013-0644-1
Kalynchuk LE (2000) Long-term amygdala kindling in rats as a model for the study of interictal emotionality in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:691–704
Kalynchuk LE, Pinel JP, Treit D, Kippin TE (1997) Changes in emotional behavior produced by long-term amygdala kindling in rats. Biol Psychiatry 41:438–451
Kalynchuk LE, Pinel JP, Treit D (1998) Long-term kindling and interictal emotionality in rats: effect of stimulation site. Brain Res 779:149–157
Kalynchuk LE, Pinel JP, Treit D (1999) Characterization of the defensive nautre of kindling-induced emotionality in rats. Beh Neurosci 113:766–775
Kee N, Teixeira CM, Wang AH, Frankland PW (2007) Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 10:355–362
Knapska E, Maren S (2009) Reciprocal patterns of c-Fos expression in the medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala after extinction and renewal of conditioned fear. Learn Mem 16:486–493
Kuruba R, Hattiangady B, Parihar VK, Shuai B, Shetty AK (2011) Differential susceptibility of interneurons expressing neuropeptide Y or parvalbumin in the aged hippocampus to acute seizure activity. PLoS One 6:e24493
Levenson J, Weeber E, Selcher JC, Kategaya LS, Sweatt JD, Eskin A (2002) Long-term potentiation and contextual fear conditioning increase neuronal glutamate uptake. Nat Neurosci 5:155–161
Long L, Xiao B, Feng L, Yi F, Li G, Li S, Mutasem MA, Chen S, Bi F, Li Y (2011) Selective loss and axonal sprouting of GABAergic interneurons in the sclerotic hippocampus induced by LiCl-pilocarpine. Int J Neurosci 121:69–85
Lurton D, Cavalheiro EA (1997) Neuropeptide-Y immunoreactivity in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Brain Res 116:186–190
Nadler JV, Tu B, Timofeeva O, Jiao Y, Herzog H (2007) Neuropeptide Y in the recurrent mossy fiber pathway. Peptides 28:357–364
Nieminen SA, Sirvio J, Teittinen K, Pitkanen A, Airaksinen MM, Riekkinen P (1992) Amygdala kindling increased fear-response, but did not impair spatial memory in rats. Physiol Behav 51:845–849
Noe F, Vaghi V, Balducci C, Fitzsimons H, Bland R, Zardoni D, Sperk G, Carli M, During MJ, Vezzani A (2010) Anticonvulsant effects and behavioural outcomes of rAAV serotype 1 vector-mediated neuropeptide Y overexpression in rat hippocampus. Gene Ther 17:643–652
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Pinel JP, Rovner LI (1978) Experimental epileptogenesis: kindling-induced epilepsy in rats. Exp Neurol 58:190–202
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation I. After-discharge threshold. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:269–279
Ramamoorthy P, Whim MD (2008) Trafficking and fusion of neuropeptide Y-containing dense-core granules in astrocytes. J Neurosci 28:13815–13827
Redrobe JP, Dumont Y, St-Pierre JA, Quirion R (1999) Multiple receptors for neuropeptide Y in the hippocampus: putative roles in seizures and cognition. Brain Res 848:153–166
Richter-Levin G, Canevari L, Bliss TV (1995) Long-term potentiation and glutamate release in the dentate gyrus: links to spatial learning. Behav Brain Res 66:37–40
Rizzi M, Monno A, Samanin R, Sperk G, Vezzani A (1993) Electrical kindling of the hippocampus is associated with functional activation of neuropeptide Y-containing neurons. Eur J Neurosci 5:1534–1538
Scharfman HE, McCloskey DP (2009) Postnatal neurogenesis as a therapeutic target in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 85:150–161
Scharfman HE, Goodman JH, Sollas AL, Croll SD (2002) Spontaneous limbic seizures after intrahippocampal infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Exp Neurol 174:201–214
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874:123–130
Schwarzer C, Williamson JM, Lothman EW, Vezzani A, Sperk G (1995) Somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, neurokinin B and cholecystokinin immunoreactivity in two chronic models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 69:831–845
Schwarzer C, Sperk G, Samanin R, Rizzi M, Gariboldi M, Vezzani A (1996) Neuropeptides-immunoreactivity and their mRNA expression in kindling: functional implications for limbic epileptogenesis. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 22:27–50
Schwarzer C, Kofler N, Sperk G (1998) Up-regulation of neuropeptide Y-Y2 receptors in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Mol Pharmacol 53:6–13
Sherafat MA, Ronaghi A, Ahmad-Molaei L, Nejadhoseynian M, Ghasemi R, Hosseini A, Naderi N, Motamedi F (2013) Kindling-induced learning deficiency and possible cellular and molecular involved mechanisms. Neurol Sci 34:883–890
Silva AP, Pinheiro PS, Carvalho AP, Carvalho CM, Jakobsen B, Zimmer J, Malva JO (2003) Activation of neuropeptide Y receptors is neuroprotective against excitotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. FASEB J 17:1118–1120
Sloviter RS, Zappone CA, Harvey BD, Bumanglag AV, Bender RA, Frotscher M (2003) “Dormant basket cell” hypothesis revisited: relative vulnerabilities of dentate gyrus mossy cells and inhibitory interneurons after hippocampal status epilepticus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 459:44–76
Snyder JS, Choe JS, Clifford MA, Jeurling SI, Hurley P, Brown A, Kamhi JF, Cameron HA (2009) Adult-born hippocampal neurons are more numerous, faster maturing, and more involved in behavior in rats than in mice. J Neurosci 29:14484–14495
Sorensen AT, Kanter-Schlifke I, Carli M, Balducci C, Noe F, During MJ, Vezzani A, Kokaia M (2008) NPY gene transfer in the hippocampus attenuates synaptic plasticity and learning. Hippocampus 18:564–574
Sperk G, Marksteiner J, Gruber B, Bellmann R, Mahata M, Ortler M (1992) Functional changes in neuropeptide Y- and somatostatin-containing neurons induced by limbic seizures in the rat. Neuroscience 50:831–846
Stadlbauer U, Langhans W, Meyer U (2013) Administration of the Y2 receptor agonist PYY3-36 in mice induces multiple behavioral changes relevant to schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:2446–2455
Stanic D, Brumovsky P, Fetissov S, Shuster S, Herzog H, Hokfelt T (2006) Characterization of neuropeptide Y2 receptor protein expression in the mouse brain. I. Distribution in cell bodies and nerve terminals. J Comp Neurol 499:357–390
Sun C, Mtchedlishvili Z, Bertram EH, Erisir A, Kapur J (2007) Selective loss of dentate hilar interneurons contributes to reduced synaptic inhibition of granule cells in an electrical stimulation-based animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Comp Neurol 500:876–893
Tu B, Timofeeva O, Jiao Y, Nadler JV (2005) Spontaneous release of neuropeptide Y tonically inhibits recurrent mossy fiber synaptic transmission in epileptic brain. J Neurosci 25:1718–1729
Turski WA, Czuczwar SJ, Kleinrok Z, Turski L (1983) Cholinomimetics produce seizures and brain damage in rats. Experientia 39:1408–1411
Vezzani A, Sperk G (2004) Overexpression of NPY and Y2 receptors in epileptic brain tissue: an endogenous neuroprotective mechanism in temporal lobe epilepsy? Neuropeptides 38:245–252
Vezzani A, Civenni G, Rizzi M, Monno A, Messali S, Samanin R (1994) Enhanced neuropeptide Y release in the hippocampus is associated with chronic seizure susceptibility in kainic acid treated rats. Brain Res 660:138–143
Vezzani A, Sperk G, Colmers WF (1999) Neuropeptide Y: emerging evidence for a functional role in seizure modulation. Trends Neurosci 22:25–30
Whittaker E, Vereker E, Lynch MA (1999) Neuropeptide Y inhibits glutamate release and long-term potentiation in rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res 827:229–233
Woldbye DP, Angehagen M, Gotzsche CR, Elbrond-Bek H, Sorensen AT, Christiansen SH, Olesen MV, Nikitidou L, Hansen TV, Kanter-Schlifke I, Kokaia M (2010) Adeno-associated viral vector-induced overexpression of neuropeptide Y Y2 receptors in the hippocampus suppresses seizures. Brain 133:2778–2788
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) to LEK. LEK holds a CIHR-Canada Research Chair in Behavioral Neuroscience. JJB is supported by an NSERC postgraduate scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Botterill, J.J., Guskjolen, A.J., Marks, W.N. et al. Limbic but not non-limbic kindling impairs conditioned fear and promotes plasticity of NPY and its Y2 receptor. Brain Struct Funct 220, 3641–3655 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0880-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0880-z