Abstract
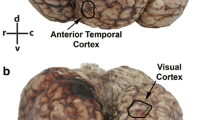
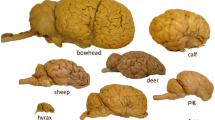
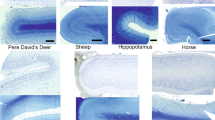
The present quantitative study extends our investigation of cetartiodactyls by exploring the neuronal morphology in the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) neocortex. Here, we investigate giraffe primary visual and motor cortices from perfusion-fixed brains of three subadults stained with a modified rapid Golgi technique. Neurons (n = 244) were quantified on a computer-assisted microscopy system. Qualitatively, the giraffe neocortex contained an array of complex spiny neurons that included both “typical” pyramidal neuron morphology and “atypical” spiny neurons in terms of morphology and/or orientation. In general, the neocortex exhibited a vertical columnar organization of apical dendrites. Although there was no significant quantitative difference in dendritic complexity for pyramidal neurons between primary visual (n = 78) and motor cortices (n = 65), there was a significant difference in dendritic spine density (motor cortex > visual cortex). The morphology of aspiny neurons in giraffes appeared to be similar to that of other eutherian mammals. For cross-species comparison of neuron morphology, giraffe pyramidal neurons were compared to those quantified with the same methodology in African elephants and some cetaceans (e.g., bottlenose dolphin, minke whale, humpback whale). Across species, the giraffe (and cetaceans) exhibited less widely bifurcating apical dendrites compared to elephants. Quantitative dendritic measures revealed that the elephant and humpback whale had more extensive dendrites than giraffes, whereas the minke whale and bottlenose dolphin had less extensive dendritic arbors. Spine measures were highest in the giraffe, perhaps due to the high quality, perfusion fixation. The neuronal morphology in giraffe neocortex is thus generally consistent with what is known about other cetartiodactyls.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson K, Bones B, Robinson B, Hass C, Lee H, Ford K, Roberts T-A, Jacobs B (2009) The morphology of supragranular pyramidal neurons in the human insular cortex: a quantitative Golgi study. Cereb Cortex 19:2131–2144
Badeer HS (1997) Is the flow in the giraffe’s jugular vein a “free” fall? Comp Biochem Physiol A 118:573–576
Badlangana NL, Bhagwandin A, Fuxe K, Manger PR (2007a) Distribution and morphology of putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the medulla oblongata of a sub adult giraffe, Giraffa camelopardalis. J Chem Neuroanat 34:69–79
Badlangana NL, Bhagwandin A, Fuxe K, Manger PR (2007b) Observations on the giraffe central nervous system related to the corticospinal tract, motor cortex and spinal cord: what difference does a long neck make? Neurosci 148:522–534
Badlangana NL, Adams JW, Manger PR (2009) The giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) cervical vertebral column: a heuristic example in understanding evolutionary processes? Zool J Linn Soc 155:736–757
Barasa A (1960) Forma, grandezza e densitá dei neuroni della corteccia cerebrale in mammiferi di grandezza corporea differente. Z Zellforsch 53:69–89
Bashaw MJ (1993) Social behavior and communication in a heard of captive giraffe. Dissertation, Georgia Institute of Technology
Bashaw MJ, Bloomsmith MA, Maple TL, Bercovitch FB (2007) The structure of social relationships among captive female giraffe (Giraffe camelopardalis). J Comp Psychol 121:46–53
Bercovitch FB, Berry PSM (2013) Herd composition, kinship and fission-fusion social dynamics among wild giraffe. Afr J Ecol 51:206–216
Bercovitch FB, Bashaw MJ, del Castillo SM (2006) Sociosexual behavior, male mating tactics, and the reproductive cycle of giraffe Giraffa camelopardalis. Horm Behav 50:314–321
Betz W (1874) Anatomischer Nachweis zweier Gehirncentra. Zbl med Wiss 12(578–580):595–599
Bianchi S, Bauernfeind AL, Gupta K, Stimpson CD, Spocter MA, Bonar CJ, Manger PR, Hof PR, Jacobs B, Sherwood CC (2011) Neocortical neuron morphology in Afrotheria: comparing the rock hyrax with the African elephant. Ann NY Acad Sci 1225:37–46
Boddy AM, McGowen MR, Sherwood CC, Grossman LI, Goodman M, Wildman DE (2012) Comparative analysis of encephalization in mammals reveals relaxed constraints on anthropoid primate and cetacean brain scaling. J Evol Biol 25:981–994
Bok ST (1959) Histonomy of the cerebral cortex. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bota M, Swanson LW (2007) The neuron classification problem. Brain Res Rev 56:79–88
Braak H (1978) On magnopyramidal temporal fields in the human brain—probable morphological counterparts of Wernicke’s speech region. Anat Embryol 152:141–169
Braak H, Braak E (1976) The pyramidal cells of Betz within the cingulate and precentral gigantopyramidal field in the human brain: a Golgi and pigmentarchitectonic study. Cell Tiss Res 172:103–119
Braak H, Braak E (1985) Golgi preparations as a tool in neuropathology with particular reference to investigations of the human telencephalic cortex. Prog Neurobiol 25:93–139
Brodmann K (1909) Vergleichende Lokalisationlehre der Grosshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. J. A. Barth, Leipzig
Butti C, Raghanti MA, Sherwood CC, Hof PR (2011) The neocortex of cetaceans: cytoarchitecture and comparison with other aquatic and terrestrial species. Ann NY Acad Sci 1225:47–58
Butti C, Fordyce ER, Raghanti MA, Gu X, Bonar CJ, Wicinski BA, Wong EW, Roman J, Brake A, Eaves E, Spocter MA, Tang CY, Jacobs B, Sherwood CC, Hof PR (2014a) The cerebral cortex of the pygmy hippopotamus, Hexaprotodon liberiensis (Cetartiodactyla, Hippopotamidae): MRI, cytoarchitecture, and neuronal morphology. Anat Rec 297:670–700
Butti C, Janeway CM, Townshend C, Ridgway SH, Manger PR, Sherwood CC, Hof PR, Jacobs B (2014b) Neuronal morphology in cetartiodactyls. I. A comparative Golgi analysis of neuronal morphology in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus), the minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), and the humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae). Brain Struct Funct (submitted)
Bux F, Bhagwandin A, Fuxe K, Manger PR (2010) Organization of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic nuclei in the diencephalon, midbrain and pons of sub-adult male giraffes. J Chem Neuroanat 39:189–203
Carter KD, Seddon JM, Frère CH, Carter JK, Goldizen AW (2012) Fission-fusion dynamics in wild giraffes may be driven by kinship, spatial overlap and individual social preferences. Anim Behav 85:385–394
Changizi MA (2001) Principles underlying mammalian neocortical scaling. Biol Cybern 84:207–215
Chan-Palay V, Palay SL, Billings-Gagliardi SM (1974) Meynert cells in primate visual cortex. J Neurocytol 3:631–658
Clemo HR, Meredith MA (2012) Dendritic spine density in multisensory versus primary sensory cortex. Synapse 66:714–724
Coe MJ (1967) “Necking” behavior in the giraffe. J Zool Lond 151:313–321
Coimbra JP, Hart NS, Collin SP, Manger PR (2013) Scene from above: retinal ganglion cell topography and spatial resolving power in the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis). J Comp Neurol 521:2042–2057
Constantinidis C, Williams GC, Goldman-Rakic PS (2002) A role for inhibition in shaping the temporal flow of information in prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 5:175–180
Cozzi B, Povinelli M, Ballarin C, Granato A (2014) The brain of the horse: weight and cephalization quotients. Brain Behav Evol 83:9–16
Crawford JM, Curtis DR (1966) Pharmacological studies on feline Betz cells. J Physiol 186:121–138
Crile G, Quiring DP (1940) A record of the body weight and certain organ and gland weights of 3690 animals. Ohio J Sci 40:219–259
de Lima AD, Voigt T, Morrison JH (1990) Morphology of the cells within the inferior temporal gyrus that project to the prefrontal cortex in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 296:159–172
Deacon TW (1990) Rethinking mammalian brain evolution. Am Zool 30:629–705
DeFelipe J, Alonso-Nanclares L, Arellano JI (2002) Microstructure of the neocortex: comparative aspects. J Neurocytol 31:299–316
DeFelipe J, López-Cruz PL, Benavides-Piccione R, Bielza C, Larrañaga P, Anderson S, Burkhalter A, Cauli B, Fairén A, Feldmeyer D, Fishell G, Fitzpatrick D, Freund TF, González-Burgos G, Hestrin S, Hill S, Hof PR, Huang J, Jones EG, Kawaguchi Y, Kisvárday Z, Kubota Y, Lewis DA, Marín O, Markram H, McBain CJ, Meyer HS, Monyer H, Nelson SB, Rockland K, Rossier J, Rubenstein JLR, Rudy B, Scanziani M, Shepherd GM, Sherwood CC, Staiger JF, Tamás G, Thomson A, Wang Y, Yuste R, Ascoli GA (2013) New insights into the classification and nomenclature of cortical GABAergic interneurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:202–216
Dell L-H, Patzke N, Bhagwandin A, Bux F, Fuxe K, Barber G, Siegel JM, Manger PR (2012) Organization and number of orexinergic neurons in the hypothalamus of two species of Cetartiodactyla: a comparison of giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) and harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J Chem Neuroanat 44:98–109
Elston GN (2003) Cortex, cognition and the cell: new insights into the pyramidal neuron and prefrontal function. Cereb Cortex 13:1124–1138
Elston GN (2007) Specialization of the neocortical pyramidal cell during primate evolution. In: Kass JH, Preuss TM (eds) Evolution of nervous systems: a comprehensive reference, vol 4. Elsevier, New York, pp 191–242
Elston GN, Manger P (2014) Pyramidal cells in V1 of African rodents are bigger, more branched and more spiny than those in primates. Front Neuroanat 8:4. doi:10.3389/fnana.2014.00004
Elston GN, Rosa MGP (1998a) Complex dendritic fields of pyramidal cells in the frontal eye field of the macaque monkey: comparison with parietal areas 7a and LIP. Neuroreport 9:127–131
Elston GN, Rosa MGP (1998b) Morphological variation of layer III pyramidal neurones in the occipitotemporal pathway of the macaque monkey visual cortex. Cereb Cortex 8:278–294
Elston GN, Benavides-Piccione R, DeFelipe J (2001) The pyramidal cell in cognition: a comparative study in human and monkey. J Neurosci 21:RC163
Elston GN, Benavides-Piccione R, Elston A, Zietsch B, Defelipe J, Manger P, Casagrande V, Kaas JH (2006) Specializations of the granular prefrontal cortex of primates: implications for cognitive processing. Anat Rec 288:26–35
Escobar MI, Pimienta H, Caviness VS Jr, Jacobson M, Crandall JE, Kosik KS (1986) Architecture of apical dendrites in the murine neocortex: dual apical dendritic systems. Neuroscience 17:975–989
Fernández MA, Vrba ES (2005) A complete estimate of the phylogenetic relationships in Ruminantia: a dated species-level supertree of the extant ruminants. Biol Rev 80:269–302
Ferrer I (1987) The basic structure of the neocortex in insectivorous bats (Miniopterus sthreibersi and Pipistrellus pipistrellus). J Hirnforsch 28:237–243
Ferrer I (1989) The basic structure of the neocortex of the bat. Neurosci Res 6:573–580
Ferrer I, Perera M (1988) Structure and nerve organization in the cerebral cortex of the dolphin Stenella coeruleoalba a Golgi study: with special attention to the primary auditory area. Anat Embryol 178:161–173
Ferrer I, Fábrigues I, Condom E (1986a) A Golgi study of the sixth layer of the cerebral cortex I. The lissencephalic brain of Rodentia, Lagomorpha. Insectivora and Chiroptera. J Anat 145:217–234
Ferrer I, Fábrigues I, Condom E (1986b) A Golgi study of the sixth layer of the cerebral cortex II. The gyrencephalic brain of Carnivora. Artiodactyla and primates. J Anat 146:87–104
Friant M (1968) Développement et morphologie du cerveau des giraffidae (Okapi et Girafe) [The development and morphology of the brain of giraffidae (okapi and giraffe)]. Acta Neurol Belg 68:483–498
Garey LJ, Winkllemann E, Brauer K (1985) Golgi and Nissl studies of the visual cortex of the bottlenose dolphin. J Comp Neurol 240:305–321
Germroth P, Schwerdtfeger WK, Buhl EH (1989) Morphology of identified entorhinal neurons projecting to the hippocampus. A light microscopical study combining retrograde tracing and intracellular injection. Neuroscience 30:683–691
Glezer II, Morgane PJ (1990) Ultrastructure of synapses and Golgi analysis of neurons in neocortex of the lateral gyrus (visual cortex) of the dolphin and pilot hale. Brain Res Bull 24:401–427
Graur D, Higgins DG (1994) Molecular evidence for the inclusion of cetaceans within the order Artiodactyla. Mol Biol Evol 11:357–364
Harrison KH, Hof PR, Wang SS-H (2002) Scaling laws in the mammalian neocortex: does form provide clues to function? J Neurocytol 31:289–298
Hassanin A, Douzery EJP (2003) Molecular and morphological phylogenies of Ruminantia and the alternative position of the Moschidae. Syst Biol 52:206–228
Hassiotis M, Ashwell KWS (2003) Neuronal classes in the isocortex of a monotreme, the Australian echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus). Brain Behav Evol 61:6–27
Haug H (1987) Brain sizes, surfaces, and neuronal sizes of the cortex cerebri: a stereological investigation of man and his variability and a comparison with some mammals (primates, whales, marsupials, insectivores, and one elephant). Am J Anat 180:126–142
Hawkins DM, Kass GV (1982) Automatic interaction detection. In: Hawkins D (ed) Topics in applied multivariate analysis. University of Cambridge Press, Cambridge, pp 269–302
Hayes TL, Lewis DA (1995) Anatomical specialization of the anterior motor speech area: hemispheric differences in magnopyramidal neurons. Brain Lang 49:289–308
Hof PR, Sherwood CC (2005) Morphomolecular neuronal phenotypes in the neocortex reflect phylogenetic relationships among certain mammalian orders. Anat Rec 287:1153–1163
Hof PR, Sherwood CC (2007) The evolution of neuron classes in the neocortex of mammals. In: Krubitzer LA, Kaas H (eds) The evolution of nervous systems in mammals. Evolution of nervous systems, vol 3. Academic Press, Oxford pp 113–124
Hof PR, Van der Gucht E (2007) Structure of the cerebral cortex of the humpback whale, Megaptera novaeangliae (Cetacea, Mysticeti, Balaenopteridae). Anat Rec 290:1–31
Hof PR, Bogaert YE, Rosenthal RE, Fiskum G (1996) Distribution of neuronal populations containing neurofilament protein and calcium-binding proteins in the canine neocortex: regional analysis and cell typology. J Chem Neuroanat 11:81–98
Hof PR, Glezer II, Condé F, Flagg RA, Rubin MB, Nimchinsky EA, Vogt Weisenhorn DM (1999) Cellular distribution of the calcium-binding proteins parvalbumin, calbindin, and calretinin in the neocortex of mammals: phylogenetic and developmental patterns. J Chem Neuroanat 16:77–116
Hof PR, Nimchinsky EA, Young WG, Morrison JH (2000) Numbers of meynert and layer IVB cells in area V1: a stereologic analysis in young and aged macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol 420:113–126
Hof PR, Chanis R, Marino L (2005) Cortical complexity in cetacean brains. Anat Rec 287A:1142–1152
Horner CH, Arbuthnott E (1991) Methods of estimation of spine density—are spines evenly distributed throughout the dendritic field? J Anat 177:179–184
Innis AC (1958) The behavior of the giraffe, Giraffa camelopardalis, in the eastern Transvaal. Proc Zool Soc Lond 131:245–278
Innocenti GM, Vercelli A (2010) Dendritic bundles, minicolumns, columns, and cortical output units. Front Neuroanat 4:11. doi:10.3389/neuro.05.011.2010
Jacobs B, Scheibel AB (1993) A quantitative dendritic analysis of Wernicke’s area in humans I. Lifespan changes. J Comp Neurol 327:83–96
Jacobs B, Scheibel AB (2002) Regional dendritic variation in primate cortical pyramidal cells. In: Schuz A, Miller R (eds) Cortical areas: unity and diversity (conceptual advances in brain research series). Taylor & Francis, London, pp 111–131
Jacobs B, Schall M, Scheibel AB (1993) A quantitative dendritic analysis of Wernicke’s area in humans II. Gender, hemispheric, and environmental factors. J Comp Neurol 327:97–111
Jacobs B, Driscoll L, Schall M (1997) Life-span dendritic and spine changes in areas 10 and 18 of human cortex: a quantitative Golgi study. J Comp Neurol 386:661–680
Jacobs B, Schall M, Prather M, Kapler E, Driscoll L, Baca S (2001) Regional dendritic and spine variation in human cerebral cortex: a quantitative Golgi study. Cereb Cortex 11:558–571
Jacobs B, Lubs J, Hannan M, Anderson K, Butti C, Sherwood CC, Hof PR, Manger PR (2011) Neuronal morphology in the African elephant (Loxodonta africana) neocortex. Brain Struct Funct 215:273–298
Jacobs B, Johnson N, Wahl D, Schall M, Maseko BC, Lewandowski A, Raghanti MA, Wicinski B, Butti C, Hipkins WD, Bertelsen MF, Reep RL, Hof PR, Sherwood CC, Manger PR (2014) Comparative neuronal morphology of cerebellar cortex in afrotherians (African elephant, Florida manatee), primates (human, common chimpanzee), cetartiodactyls (humpback whale, giraffe), and carnivores (Siberian tiger, clouded leopard). Front Neuroanat 8:24. doi:10.3389/fnana.2011.00024
Kaas JH (2000) Why is brain size so important: design problems and solutions as neocortex gets bigger or smaller. Brain Mind 1:7–23
Kaiserman-Abramof IR, Peters A (1972) Some aspects of the morphology of Betz cells in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Brain Res 43:527–546
Kawaguchi Y (1995) Physiological subgroups of nonpyramidal cells with specific morphological characteristics in layer II/III of rat frontal cortex. J Neurosci 15:2638–2665
Kisvárday ZF, Cowey A, Somogyi P (1986) Synaptic relationships of a type of GABA-immunoreactive neuron (clutch cell), spiny stellate cells and lateral geniculate nucleus afferents in layers IVC of the monkey striate cortex. Neurosci 19:741–761
Kisvárday ZF, Gulyas A, Beroukas D, North JB, Chub IW, Somogyi P (1990) Synapses, axonal and dendritic patterns of GABA-immunoreactive neurons in human cerebral cortex. Brain 113:793–812
Kraus C, Pilleri G (1969a) Zur Feinstruktur der groβen Pyramidenzellen in der V. Cortexschicht der Cetacean (Delphinus delphins und Balaenoptera borealis). Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 80:89–99
Kraus C, Pilleri G (1969b) Zur Histologie der Grosshirnrinde von Balaenoptera borealis (Cetacea, Mysticeti) Invest Cetacea 1:151–170
le Gros Clark WE (1942) The cells of Meynert in the visual cortex of the monkey. J Anat 76:369–376
Lu D, He L, Xiang W, Ai W-M, Cao Y, Wang X-S, Pan A, Luo X-G, Li Z, Yan X–X (2013) Somal and dendritic development of human CA3 pyramidal neurons from midgestation to middle childhood: a quantitative Golgi study. Anat Rec 296:123–132
Lübke J, Egger V, Sakmann B, Feldmeyer D (2000) Columnar organization of dendrites and axons of single and synaptically coupled excitatory spiny neurons in layer 4 of the rat barrel cortex. J Neurosci 10:5300–5311
Lund JS, Lewis DA (1993) Local circuit neurons of the developing mature macaque prefrontal cortex: Golgi and immunocytochemical characteristics. J Comp Neurol 328:282–312
Manger PR, Cort J, Ebrahim N, Goodman A, Henning J, Karolia M, Rodrigues S-L, Strkalj G (2008) Is 21st century neuroscience too focused on the rat/mouse model of the brain function and dysfunction? Front Neuroanat 2:5. doi:10.3389/neuro.05.005.2008
Manger PR, Pillay P, Maseko BC, Bhagwandin A, Gravett N, Moon D-J, Jillani N, Hemingway J (2009) Acquisition of brains from the African elephant (Loxodonta africana): perfusion-fixation and dissection. J Neurosci Methods 179:16–21
Marino L, Connor RC, Fordyce RE, Herman LM, Hof PR, Lefebvre L, Lusseau D, McCowan B, Nimchinsky EA, Pack AA, Rendell L, Reidenberg JS, Reiss D, Uhen MD, Van der Gucht E, Whitehead H (2007) Cetaceans have complex brains for complex cognition. PLoS Biol 5:966–972
Masland RH (2004) Neuronal cell types. Curr Biol 14:R497–R500
Meyer G (1987) Forms and spatial arrangement of neurons in the primary motor cortex of man. J Comp Neurol 262:402–428
Meynert T (1867) Der Bau der Gross-Hirnrinde und seiner örtlichen Verschiedenheiten, nebst einen pathologisch-anatomisch Corollarium. Vierteljahrsschr Psychiatr 1(77–93):125–217
Miller MW (1988) Maturation of rat visual cortex: IV. The generation, migration, morphogenesis and connectivity of atypical oriented pyramidal cells. J Comp Neurol 274:387–405
Mitchell G, Bobbitt JP, Devries S (2008) Cerebral perfusion pressure in giraffe: modeling the effects of head-raising and -lowering. J Theor Biol 252:98–108
Morest DK, Morest RR (2005) Perfusion-fixation of the brain with chrome-osmium solutions for the rapid Golgi method. Am J Anat 118:811–831
Morgane PJ, Jacobs MS, Galaburda A (1985) Conservative features of neocortical evolution in dolphin brain. Brain Behav Evol 26:176–184
Morgane PJ, Glezer LI, Jacobs MS (1988) Visual cortex of the dolphin: an image analysis study. J Comp Neurol 273:3–25
Mountcastle VB (1997) The columnar organization of the neocortex. Brain 120:701–722
Murphy WJ, Pevzner PA, O’Brien SJ (2004) Mammalian phylogenomics comes of age. Trends Genet 20:631–639
Nelson SB, Sugino K, Hempel CM (2006) The problem of neuronal cell types: a physiological genomics approach. Trends Neurosci 29:339–345
Ngowyang G (1932) Beschreibung einer Art von Specialzellen in der Inselrinde. J Psychol Neurol 44:671–674
Nikaido M, Rooney AP, Okada N (1999) Phylogenetic relationships among cetartiodactyls based on insertions of short and long interspersed elements: hippopotamuses are the closest extant relatives of whales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10261–10266
Nilsson O, Bööj S, Dahlström A, Hargens AR, Millard RW, Pettersson KS (1988) Sympathetic innervation of the cardiovascular system in the giraffe. Blood Vessels 25:299–307
Oelschläger HA (2008) The dolphin brain—a challenge for synthetic neurobiology. Brain Res Bull 75:450–459
Pérez-Barbería FJ, Gordon IJ (2005) Gregariousness increases brain size in ungulates. Oecologia 145:41–52
Peters A, Regidor J (1981) A reassessment of the forms of nonpyramidal neurons in area 17 of cat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 203:685–716
Phillis JW, Limacher JJ (1974) Substance P excitation of cerebral cortical Betz cells. Brain Res 69:158–163
Povysheva NV, Zaitsev AV, Kröner S, Krimer OA, Rotaru DC, González-Burgos G, Lewis DA, Krimer LS (2007) Electrophysiological differences between neurogliaform cells from monkey and rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 97:1030–1039
Price SA, Bininda-Edmonds ORP, Gittleman JL (2005) A complete phylogeny of whales, dolphins and even-toed hoofed mammals (cetartiodactyls). Biol Rev 80:445–473
Purves D (1988) Body and brain: a trophic theory of neural connections. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Radinsky L (1981) Brain evolution in extinct South American ungulates. Brain Behav Evol 18:169–187
Ramón y Cajal S (1922) Studien über die Sehrinde der Katze. J Psychol Neurol 29:161–181
Rivara C, Sherwood C, Bouras C, Hof PR (2003) Stereological characterization and spatial distribution patterns of Betz cells in the human primary motor cortex. Anat Record 270:137–148
Roitman MF, Na E, Anderson G, Jones TA, Bernstein IL (2002) Induction of a salt appetite alters dendritic morphology in nucleus accumbens and sensitizes rats to amphetamine. J Neurosci 22:RC225 (1–5)
Sanides F, Sanides D (1972) The “extraverted neurons” of the mammalian cerebral cortex. Z Anat Entwickl-Gesch 136:272–293
Sasaki S, Iwata M (2001) Ultrastuctural study of Betz cells in the primary motor cortex of human brain. J Anat 199:699–708
Scheibel ME, Scheibel AB (1978a) The dendritic structure of the human Betz cell. In: Brazier MAB, Pets H (eds) Architectonics of the cerebral cortex. Raven Press, New York, pp 43–57
Scheibel ME, Scheibel AB (1978b) The methods of Golgi. In: Robertson RT (ed) Neuroanatomical research techniques. Academic Press, New York, pp 89–114
Sherwood CC, Lee PWH, Rivara CB, Holloway RL, Gilissen EPE, Simmons RMT, Hakeem A, Allman JM, Erwin JM, Hof PR (2003) Evolution of specialized pyramidal neurons in primate visual and motor cortex. Brain Behav Evol 61:28–44
Sherwood CC, Stimpson CD, Butti C, Bonar CJ, Newton AL, Allman JM, Hof PR (2009) Neocortical neuron types in Xenarthra and Afrotheria: implications for brain evolution in mammals. Brain Struct Funct 213:301–328
Shimamura M, Yasue H, Ohshima K, Abe H, Kato H, Kishiro T, Goto M, Munechika I, Okada N (1997) Molecular evidence from retroposons that whales form a clade within even-toed ungulates. Nature 388:666–671
Sholl DA (1953) Dendritic organization of the neurons of the visual and motor cortices of the cat. J Anat 87:387–406
Shultz S, Dunbar RIM (2006) Both social and ecological factors predict ungulate brain size. Proc R Soc B 273:207–215
Solounias N (1999) The remarkable anatomy of the giraffe’s neck. J Zool (London) 247:257–268
Somogyi P, Kisvárday ZF, Martin KAC, Whitteridge D (1983) Synaptic connections of morphologically characterized large basket cells in the striate cortex of cat. Neuroscience 10:261–294
Tarou LR, Bashaw MJ, Maple TL (2000) Social attachment in giraffe: response to social separation. Zoo Biol 19:41–51
The Petilla Interneuron Nomenclature Group (PING) (2008) Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:557–568
Thompson AM, Bannister AP (2003) Interlaminar connections in the neocortex. Cereb Cortex 13:5–14
Tyler CJ, Dunlop SA, Lund RD, Harman AM, Dann JF, Beazley LD (1998) Anatomical comparison of the macaque and marsupial visual cortex: common features that may reflect retention of essential cortical elements. J Comp Neurol 400:449–468
Ursing BM, Arnason U (1998) Analyses of mitochondrial genomes strongly support a hippopotamus-whale clade. Proc R Soc Lond B265:2251–2255
Uylings HBM, Ruiz-Marcos A, van Pelt J (1986) The metric analysis of three-dimensional dendritic tree patterns: a methodological review. J Neurosci Methods 18:127–151
Valverde F (1971) Short axon neuronal subsystems in the visual cortex of the monkey. Int J Neurosci 1:181–197
van Brederode JFM, Foehring RC, Spain WJ (2000) Morphological and electrophysiological properties of atypically oriented layer 2 pyramidal cells of the juvenile rat neocortex. Neuroscience 101:851–861
Van der Jeugd HP, Prins HP (2000) Movements and group structure of giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) in Lake Manyara National Park, Tanzania. J Zool 251:15–21
von Bonin G (1938) Studies of the size of the cells in the cerebral cortex. II. The motor area of man, cebus and cat. J Comp Neurol 69:381–390
Walshe FM (1942) The giant cells of Betz, the motor cortex and the pyramidal tract: a critical review. Brain 65:409–461
White EL, Rock MP (1980) Three-dimensional aspects and synaptic relationships of a Golgi-impregnated spiny stellate cell reconstructed from serial thin sections. J Neurocytol 9:615–636
Williams RS, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VS Jr (1978) The Golgi rapid method in clinical neuropathology: the morphologic consequences of suboptimal fixation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 37:13–33
Wittenberg GM, Wang SS-H (2007) Evolution and scaling of dendrites. In: Stuart G, Spruston N, Hausser M (eds) Dendrites. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 43–67
Zeng H, Shen EH, Hohman JG, Oh SW, Bernard A, Royall JJ, Glattfelder KJ, Sunkin SM, Morris JA, Guillozet-Bongaarts AL, Smith KA, Ebbert AJ, Swanson B, Kuan L, Page DT, Overly CC, Lein ES, Hawrylyca MJ, Hof PR, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Jones AR (2012) Large-scale cellular-resolution gene profiling in human neocortex reveals species-specific molecular signatures. Cell 149:483–496
Acknowledgments
Partial support for this work was provided by Colorado College’s divisional research funds (B.J.), the James S. McDonnell Foundation (Grant 22002078, to C.C.S., P.R.H.; Grant 220020293 to C.C.S.), National Science Foundation (BCS-0515484, BCS-0824531 to C.C.S.), and the South African National Research Foundation (P.R.M.; FA2005033100004). We would also like to thank the Danish Cardiovascular Research Program, especially Emil Toft-Brøndum, for allowing us to obtain the specimens of giraffe brains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobs, B., Harland, T., Kennedy, D. et al. The neocortex of cetartiodactyls. II. Neuronal morphology of the visual and motor cortices in the giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis). Brain Struct Funct 220, 2851–2872 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0830-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0830-9