Abstract
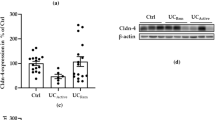
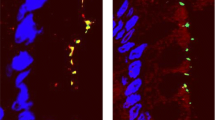
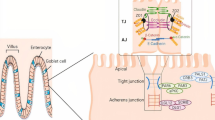
Abnormalities of transmembrane and cytoplasmic proteins of tight junctions (TJ) have been implicated in pathogenesis of both celiac (CeD) and Crohn’s diseases (CD). Since disease pathogenesis in CeD and CD are different, we planned to study if there is any differential expression pattern of TJ marker proteins and ultrastructural changes, respectively, in duodenal villi vs crypts. Endoscopic duodenal biopsies from treatment naïve patients with CeD (n = 24), active CD (n = 28), and functional dyspepsia (as controls, n = 15), both at baseline and 6 months after treatment, were subjected to light microscopic analysis (modified Marsh grading); immune-histochemical staining and Western blot analysis to see the expression of key TJ proteins [trans-membrane proteins (claudin-2, claudin-3, claudin-4, occludin, and JAM) and cytoplasmic protein (ZO-1)]. Transmission electron microscopy and image analysis of the TJs were also performed. There was significant overexpression of claudin-2 (pore-forming) and occludin (protein maintaining cell polarity) with under-expression of claudin-3 and claudin-4 (pore-sealing proteins) in treatment naïve CeD and active CD with simultaneous alteration in ultrastructure of TJs such as loss of penta-laminar structure and TJ dilatation. Normalization of some of these TJ proteins was noted 6 months after treatment. These changes were not disease specific and were not different in duodenal villi and crypts. Overexpression of pore-forming and under-expression of pore-sealing TJ proteins lead to dilatation of TJ. These changes are neither disease specific nor site specific and the end result of mucosal inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turner JR (2000) Show me the pathway! Regulation of paracellular permeability by Na (+)-glucose cotransport. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 41(3):265–281
Zhu A, Kaunitz J (2008) Gastroduodenal mucosal defense. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10(6):548–554
Edelblum KL, Turner JR (2009) The tight junction in inflammatory disease: communication breakdown. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9(6):715–720
Hollander D (1999) Intestinal permeability, leaky gut, and intestinal disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 1(5):410–416
Fanning AS, Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1999) Transmembrane proteins in the tight junction barrier. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(6):1337–1345
D’Incà R, Di Leo V, Corrao G, Martines D et al (1999) Intestinal permeability test as a predictor of clinical course in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 94(10):2956–2960
Rosenthal R, Milatz S, Krug SM, Oelrich B et al (2010) Claudin-2, a component of the tight junction, forms a paracellular water channel. J Cell Sci 123:1913–1921
Van Itallie CM, Holmes J, Bridges A, Anderson JM (2009) Claudin-2-dependent changes in noncharged solute flux are mediated by the extracellular domains and require attachment to the PDZ-scaffold. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:82–87
Milatz S, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Günzel D et al (2010) Claudin-3 acts as a sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798(11):2048–2057
D’Souza T, Agarwal R, Morin PJ (2005) Phosphorylation of claudin-3 at threonine 192 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates tight junction barrier function in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280(28):26233–26240
Litkouhi B, Kwong J, Lo C-M, Smedley JG 3rd et al (2007) Claudin-4 over expression in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with hypomethylation and is a potential target for modulation of tight junction barrier function using a C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Neoplasia 9(4):304–314
Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2001) Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J Clin Invest 107(10):1319–1327
Du D, Xu F, Yu L, Zhang C et al (2010) The tight junction protein, occludin, regulates the directional migration of epithelial cells. Dev Cell 18(1):52–63
Mandell KJ, Parkos CA (2005) The JAM family of proteins. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57(6):857–867
Bazzoni G (2003) The JAM, family of junctional adhesion molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15(5):525–530
Husby S, Koletzko S, Korponay-Szabó IR, Mearin ML et al (2012) European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54(1):136–160
Stange EF, Travis SPL, Vermeire S, Beglinger C et al (2006) European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: definitions and diagnosis. Gut 55(Suppl I):i1–i15
Sostegni R, Daperno M, Scaglione N, Lavagna A, Rocca R, Pera A (2003) Review article: Crohn’s disease: monitoring disease activity. Aliment PharmacolTher 17 (Suppl. 2): 11–17
Marsh MN (1992) Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. A molecular and immunobiologic approach to the spectrum of gluten sensitivity ('celiac sprue'). Gastroenterology 102:330–354
Vilela EG, Torres HOG, Ferrari MLA, Lima AS, Cunha AS (2008) Gut permeability to lactulose and mannitol differs in treated Crohn’s disease and celiac disease patients and healthy subjects. Braz J Med Biol Res 41(12):1105–1109
Wright NA (2005) Morson and Dawson’s Gastrointestinal Pathology, 4th edn. Gut 54(4):568–568
Yu AS (2000) Paracellular solute transport: more than just a leak? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 9(5):513–515
Szakál DN, Gyorffy H, Arató A, Cseh A et al (2010) Mucosal expression of claudins 2, 3 and 4 in proximal and distal part of duodenum in children with coeliac disease. Virchows Arch 456(3):245–250
Schumann M, Gunzel D, Buergel N, Richter JF et al (2012) Cell polarity-determining proteins Par-3 and PP-1 are involved in epithelial tight junction defects in coeliac disease. Gut 61(2):220–228
Schumann M, Kamel S, Pahlitzsch ML, Lebenheim L et al (2012) Defective tight junctions in refractory celiac disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1258:43–51
Veres G, Gyorffy H, Szakall DN, Szabo E et al (2007) Claudins expression in the proximal and distal parts of duodenum in patients with celiac disease. Z Gastroenterol 45:45–A117
Sapone A, Lammers KM, Casolaro V, Cammarota M et al (2011) Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med 9:23
Zeissig S, Bürgel N, Günzel D, Richter J et al (2007) Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 56(1):61–72
Weber CR, Nalle SC, Tretiakova M, Rubin DT, Turner JR (2008) Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic transformation. Lab Investig 88(10):1110–1120
Suzuki T, Yoshinaga N, Tanabe S (2011) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem 286:31263–31271
Vogelsang H, Schwarzenhofer M, Oberhuber G (1998) Changes in gastrointestinal permeability in celiac disease. Dig Dis 16(6):333–336
Ma TY, Boivin MA, Ye D, Pedram A, Said HM (2005) Mechanism of TNF-{alpha} modulation of Caco-2 intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier: role of myosin light-chain kinase protein expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288(3):G422–G430
Montalto M, Cuoco L, Ricci R, Maggiano N, Vecchio FM, Gasbarrini G (2002) Immunohistochemical analysis of ZO-1 in the duodenal mucosa of patients with untreated and treated celiac disease. Digestion 65(4):227–233
Pizzuti D, Bortolami M, Mazzon E, Buda A et al (2004) Transcriptional downregulation of tight junction protein ZO-1 in active coeliac disease is reversed after a gluten-free diet. Dig Liver Dis 36(5):337–341
Drago S, El Asmar R, Di Pierro M, Grazia Clemente M et al (2006) Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: Effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Scand J Gastroenterol 41(4):408–419
Sadi RA, Khatib K, Guo S, Ye D, Youssef M, Ma T (2011) Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Physiol 300(6):G1054–G1064
Vetrano S, Resciqno M, Cera MR, Correale C et al (2008) Unique role of junctional adhesion molecule-a in maintaining mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 135(1):173–184
Söderholm JD, Olaison G, Peterson KH, Franzén LE et al (2002) Augmented increase in tight junction permeability by luminal stimuli in the non-inflamed ileum of Crohn’s disease. Gut 50(3):307–313
Benjamin J, Makharia GK, Ahuja V, Kalaivani M, Joshi YK (2008) Intestinal permeability and its association with the patient and disease characteristics in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 14(9):1399–1405
Bjarnason I, Peters TJ, Veall N (1983) Intestinal permeability defect in coeliac disease. Lancet 1(8336):1284–1285
Lameris AL, Huybers S, Kaukinen K, Mäkelä TH et al (2013) Expression profiling of claudins in the human gastrointestinal tract in health and during inflammatory bowel disease. Scandinavian J Gastroenterol 68:58–59. doi:10.3109/00365521.2012.741616
Das P, Goswami P, Das TK, Nag T et al (2012) Comparative tight junction protein expressions in colonic Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and tuberculosis: a new perspective. Virchows Arch 460(3):261–270
Fasano A, Uzzau S, Fiore C, Margaretten K (1997) The enterotoxic effect on zonula occludens toxin on rabbit small intestine involves the paracellular pathway. Gastroenterology 112:839–846
Lammers KM, Lu R, Brownley J, Thomas K et al (2008) Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 135:194–204
Paterson BM, Lammers KM, Arrieta MC, Fasano A, Meddings JB (2007) The safety, tolerance, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of single doses of AT-1001 in coeliac disease subjects: a proof of concept study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26:757–766
Kelly CP, Green PHR, Murray JA, Di Marino A et al (2009) Effect of larazotide acetate on the prevention of signs and symptoms of coeliac disease in patients undergoing a gluten challenge: a randomised placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology 136:M2048
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for providing grant for this study. We also express our gratitude to all the patients who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goswami, P., Das, P., Verma, A.K. et al. Are alterations of tight junctions at molecular and ultrastructural level different in duodenal biopsies of patients with celiac disease and Crohn's disease?. Virchows Arch 465, 521–530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1651-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1651-1