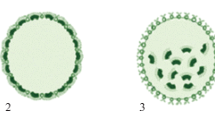
Abstract
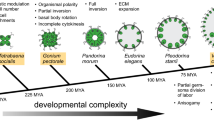
This paper represents an attempt to unify data from various lines of Volvox research: developmental biology, biogeography, and evolution. Several species (such as Volvox carteri and Volvox spermatosphaera) are characterized by rapid divisions of asexual reproductive cells, which may proceed in darkness. By contrast, several other species (such as Volvox aureus, Volvox globator, and Volvox tertius) exhibit slow and light/dependent divisions. The transition from the former pattern of asexual life cycle to the latter one has occurred in three lineages of the genus Volvox. Since V. aureus (unlike V. carteri) is able to complete the life cycle at a short photoperiod (8 h light/16 h dark regime), it is reasonable to suggest that the abovementioned evolutionary transitions might have occurred as adaptations to short winter days in high latitudes under warm climate conditions in the deep past. In the case of the lineage leading to V. tertius + Volvox dissipatrix, the crucial reorganizations of asexual life cycle might have occurred between about 45 and 60 million years ago in relatively high latitudes of Southern Hemisphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron EJ, Sloan JL, Harrison CGA (1980) Potential significance of land–sea distribution and surface albedo variations as a climatic forcing factor; 180 m.y. to the present. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 30:17–40
Chapman VJ, Thompson RH, Segar ECM (1957) Check list of fresh-water algae of New Zealand. Trans Roy Soc N Z 84:695–747
Coleman AW (1996) The Indian connection, crucial to reconstruction of the historical biogeography of freshwater algae: examples among Volvocaceae (Chlorophyta). Nova Hedwigia 112:477–482
DeConto RM, Pollard D, Wilson PA, Pӓlike H, Lear CH, Pagan M (2008) Thresholds for Cenozoic bipolar glaciation. Nature 455:652–656
Desnitski AG (1992) Cellular mechanisms of the evolution of ontogenesis in Volvox. Arch Protistenkd 141:171–178
Desnitski AG (1995) A review on the evolution of development in Volvox—morphological and physiological aspects. Eur J Protistol 31:241–247
Desnitskiy AG (1984) Some features of cell division regulations in Volvox. Tsitologiia 26:269–274
Desnitskiy AG (1996) On the geographical distribution of the species of the genus Volvox (Chlorophyta, Volvocales). Bot J (St Petersburg) 81(3):28–33
Desnitskiy AG (1997) The synopsis of the species of the genus Volvox. Vestnik St Petersburg State University 24:19–29
Desnitskiy AG (2006) Evolutionary reorganizations of ontogenesis in related species of coenobial volvocine algae. Russ J Dev Biol 37:213–223
Desnitskiy AG (2008a) Volvox: evolutionary reorganizations of ontogenesis in related species. St. Petersburg University Press, St. Petersburg
Desnitskiy AG (2008b) On the problem of ecological evolution of Volvox. Russ J Dev Biol 39:122–124
Desnitskiy AG (2009) Volvox (Chlorophyta, Volvocales) as a model organism in developmental biology. Russ J Dev Biol 40:238–241
Desnitskiy AG (2014) Ontogenetic diversity of colonies and intercellular cytoplasmic bridges in the algae of the genus Volvox. Russ J Dev Biol 45:231–234
Eldrett JS, Greenwood DR, Harding IC, Huber M (2009) Increased seasonality through the Eocene to Oligocene transition in northern high latitudes. Nature 459:969–973
Ettl H (1983) Chlorophyta. 1. Phytomonadina. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Gilbert SF (2001) Ecological developmental biology: developmental biology meets the real world. Dev Biol 233:1–12
Gilbert SF (2009) Ecological development biology. In: Encyclopedia of life sciences (ELS). Wiley, Chichester. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0020479
Herman AB, Spicer RA, Kvacek J (2002) Late Cretaceous climate of Eurasia and Alaska: a quantitative palaeobotanical approach. In: Wagreich M (ed) Aspects of Cretaceous stratigraphy and palaeobiogeography. Verlag der Ȍsterreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Wien, pp. 93–108
Herron MD, Michod RE (2008) Evolution of complexity in the volvocine algae: transitions in individuality through Darwin’s eye. Evolution 62:436–451
Herron MD, Hackett JD, Aylward FO, Michod RE (2009) Triassic origin and early radiation of multicellular volvocine algae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:3254–3258
Herron MD, Desnitskiy AG, Michod RE (2010) Evolution of developmental programs in Volvox (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 46:316–324
Isaka N, Kawai-Toyooka H, Matsuzaki R, Nakada T, Nozaki H (2012) Description of two new monoecious species of Volvox sect. Volvox (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) based on comparative morphology and molecular phylogeny of cultured material. J Phycol 48:759–767
Iyengar MOP, Desikachary TV (1981) Volvocales. Indian Council Agriculture Research, New Delhi
Karn RC, Starr RC, Hudock GA (1974) Sexual and asexual differentiation in Volvox obversus (Shaw) Printz, strains WD3 and WD7. Arch Protistenkd 116:142–148
Kirk DL (1998) Volvox: molecular-genetic origins of multicellularity and cellular differentiation. Cambridge University Press, New York
Kirk DL (2005) A twelve-step program for evolving multicellularity and a division of labor. BioEssays 27:299–310
Komarenko LE, Vassilieva II (1978) Freshwater green algae of Yakutia waters. Nauka Press, Moscow, Russia
Leliaert F, Verbruggen H, Vanormelingen P, Steen F, López-Bautista JM, Zuccarello GC, De Clerck O (2014) DNA-based species delimitation in algae. Eur J Phycol 49:179–196
Nozaki H (1988) Morphology, sexual reproduction and taxonomy of Volvox carteri f. kawasakiensis f. nov. (Chlorophyta) from Japan. Phycologia 27:209–220
Nozaki H (2003) Origin and evolution of the genera Pleodorina and Volvox. Biologia 58:425–431
Nozaki H, Coleman AW (2011) A new species of Volvox sect. Merrillosphaera (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) from Texas. J Phycol 47:673–679
Nozaki H, Matsuzaki R, Yamamoto K, Kawachi M, Takahashi F (2015a) Delineating a new heterothallic species of Volvox (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) using new strains of “Volvox africanus”. PLoS One 10(11):e0142632. doi:101371/journal.pone.0142632
Nozaki H, Ueki N, Misumi O, Yamamoto K, Yamashita S, Herron MD, Rozenzweig F (2015b) Morphology and reproduction of Volvox capensis (Volvocales, Chlorophyceae) from Montana, USA. Phycologia 54:316–320
Pancost RD, Taylor KWR, Inglis GN, Kennedy EM, Handley L, Hollis CJ, et al. (2013) Early Paleogene evolution of terrestrial climate in the SW Pacific, southern New Zealand. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 14:5413–5429
Pappas V, Miller SM (2009) Functional analysis of the Volvox carteri asymmetric division protein GlsA. Mech Dev 126:842–851
Parra OO, Gonzales M, Dellarossa V (1983) Manual taxonomico del fitoplancton de aguas continentales. V. Chlorophyceae. Parte 1. Editorial Universidad de Concepcion, Concepcion
Poole I, Cantrill D, Utescher T (2005) A multi-proxy approach to determine Antarctic terrestrial palaeoclimate during the Late Cretaceous and Early Tertiary. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 222:95–121
Prescott GW (1955) Algae of the Panama Canal and its tributaries. 1. Flagellated organisms. Ohio J Sci 55:99–121
Prochnik SE, Umen J, Nedelcu AM, Hallmann A, Miller SM, Nishii I, et al. (2010) Genomic analysis of organismal complexity in the multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Science 329:223–226
Pross J, Contreras L, Bijl PK, Greenwood DR, Bohaty SM, Schouten S, et al. (2012) Persistent near-tropical warmth on the Antarctic continent during the early Eocene epoch. Nature 488:73–77
Schmitt R, Fabry S, Kirk DL (1992) In search of molecular origins of cellular differentiation in Volvox and its relatives. Int Rev Cytol 139:189–265
Scotese CR (2001) Atlas of earth history. Vol. 1. Paleogeography. PALEOMAP Project, Arlington, Texas
Senft WH, Hunchberger RA, Roberts KE (1981) Temperature dependence of growth and phosphorus uptake in two species of Volvox (Volvocales, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 17:323–329
Sheath RG, Hellebust JA (1978) Comparison of algae in the euplankton, tychoplankton, and periphyton of a tundra pond. Can J Bot 56:1472–1483
Sheath RG, Steinman AD (1982) A checklist of freshwater algae of the Northwest Territories, Canada. Can J Bot 60:1964–1997
Sleigh MA (1989) Protozoa and other protists. Edward Arnold, New York
Smith GM (1944) A comparative study of the species of Volvox. Trans Am Microsc Soc 63:265–310
Starr RC (1968) Cellular differentiation in Volvox. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 59:1082–1088
Starr RC (1970) Control of differentiation in Volvox. Dev Biol 4(suppl):59–100
Starr RC (1972) Sexual reproduction in Volvox dissipatrix. Brit Phycol J 7:284
Starr RC, O’Neil RM, Miller CE (1980) L-glutamic acid as a mediator of sexual morphogenesis in Volvox capensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:1025–1028
Stein JR, Borden CA (1979) Checklist of freshwater algae of British Columbia. Syesis 12:3–39
Talling JF, Sinada F, Taha OE, Sobhy EMH (2009) Phytoplankton: composition, development and productivity. In: Dumont HJ (ed) The Nile: origin, environments, limnology and human use. Springer, The Hague, pp. 431–462
Talling JF, Prowse GA (2010) Selective recruitment and resurgence of tropical river phytoplankton: evidence from the Nile system of lakes, rivers, reservoirs and ponds. Hydrobiologia 637:187–195
Ueki N, Matsunaga S, Inouye I, Hallmann A (2010) How 5000 independent rowers coordinate their strokes in order to row into the sunlight: phototaxis in the multicellular green alga Volvox. BMC Biol 8:103. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-103
Vande Berg WJ, Starr RC (1971) Structure, reproduction and differentiation in Volvox gigas and Volvox powersii. Arch Protistenkd 113:195–219
Veevers JJ, Powell CMA, Roots SR (1991) Review of seafloor spreading around Australia. I. Synthesis of the patterns of spreading. Aust J Earth Sci 38:373–389
Whitford LA (1950) Some fresh-water algae from Mississippi. Castanea 15:117–123
Whitford LA (1956) Additions to the fresh-water algae in North Carolina I. Trans Am Microsc Soc 75:196–203
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Matthew Herron (University of Montana, Missoula) for helpful discussion on Volvox phylogeny and comments on an early draft of this paper. My sincere thanks go to an anonymous reviewer who made valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Angelika Stollewerk
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desnitskiy, A.G. Major ontogenetic transitions during Volvox (Chlorophyta) evolution: when and where might they have occurred?. Dev Genes Evol 226, 349–354 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-016-0557-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-016-0557-0