Abstract
Main conclusion
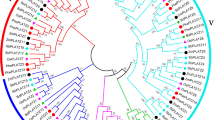
29 Moso bamboo VQ proteins were genome-wide identified for the first time, and bioinformatics analysis was performed to investigate phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary divergence. The qRT-PCR data show that PeVQ genes response to different stress treatments.
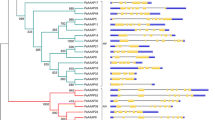
Accumulating evidence suggests that VQ motif-containing proteins in rice (Oryza sativa), Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and maize (Zea mays) play fundamental roles in response to various biotic and abiotic stresses. However, little is known about the functions of VQ family proteins in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). In this study, we performed a genome-wide bioinformatic analysis and expression profiling of PeVQ genes. A total of 29 VQ genes was identified and divided into seven subgroups (I–VII) based on phylogenetic analysis. Gene structure and conserved motif analysis revealed that 25 of 29 VQ genes contained no introns. Multiple sequence alignment showed that Moso bamboo VQ motif-containing proteins contained five variations of the conserved motif. The time of duplication and divergence of Moso bamboo from rice and maize was calculated using K s analysis. A heat map was generated using microarray data from 29 Moso bamboo VQ genes suggesting that these genes were expressed in different tissues or developmental stages. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and promoter analysis indicated that PeVQ genes were differentially regulated following treatment with polyethylene glycol, abscisic acid and salicylic acid. Our results provide a solid foundation for further research of the specific functions of VQ motif-containing proteins in Moso bamboo.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- K a :
-
Number of non-synonymous substitutions per non-synonymous site
- K s :
-
Number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site
- MYA:
-
Million years ago
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SIB1(2):
-
Sigma factor binding protein 1(2)
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman JD (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. NAR J 25(17):3389–3402
Andreasson E, Jenkins T, Brodersen P, Thorgrimsen S, Petersen NH, Zhu S, Qiu JL, Micheelsen P, Rocher A, Petersen M (2005) The MAP kinase substrate MKS1 is a regulator of plant defense responses. EMBO J 24(14):2579–2589. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600737
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren JY, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp335
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004) Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16(7):1667–1678
Bryfczynski S (2009) GraphPad: a CS2/CS7 tool for graph creation. In: Proceedings of the fourth annual southeast regional conference, 2009, Clemson, pp 1–3. doi:10.1145/1566445.1566517
Cao J, Huang J, Yang Y, Hu X (2011) Analyses of the oligopeptide transporter gene family in poplar and grape. BMC Genomics 12(1):459–464. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-465
Chen R, Li X, Song W, Liang G, Zhang P, Lin R, Zong W, Chen C, Fung H (2003) Chromosome atlas of major economic plants genome in China, Tomus IV: chromosome atlas of various bamboo species. Science Press, Beijing. ISBN 7030108353
Cheng Y, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Chi YJ, Zhou J, Chen JY, Wang F, Fan B, Shi K, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Chen Z (2012) Structural and functional analysis of VQ motif-containing proteins in Arabidopsis as interacting proteins of WRKY transcription factors. Plant Physiol 159(2):810–825. doi:10.1104/pp.112.196816
Fan C, Ma J, Guo Q, Li X, Wang H, Lu M (2013) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS One 8:e56573. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056573
Finn RD, Penelope Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC et al (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44(database issue):D279–D285. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43(1):205–227. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.135923
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC (2007) GSDS:a gene structure display server. Hereditas 29(8):1023–1026. doi:10.1360/yc-007-1023
Hu R, Qi G, Kong Y, Kong D, Qian G, Zhou G (2010) Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol 10(10):1–23. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-145
Hu Y, Chen L, Wang H, Zhang L, Wang F, Yu D (2013) Arabidopsis transcription factor WRKY8 functions antagonistically with its interacting partner VQ9 to modulate salinity stress tolerance. Plant J 74:730–745. doi:10.1111/tpj.12159
Jing Y, Lin R (2015) The VQ motif-containing protein family of plant-specific transcriptional regulators. Plant Physiol 169(1):371–378. doi:10.1104/pp.15.00788
Journotcatalino N, Somssich IE, Roby D, Kroj T (2006) The transcription factors WRKY11 and WRKY17 act as negative regulators of basal resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 18(11):3289–3302. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.044149
Kawahara Y, Oono Y, Kanamori H, Matsumoto T, Itoh T, Minami E (2012) Simultaneous RNA-Seq analysis of a mixed transcriptome of rice and blast fungus interaction. PLoS One 7(11):e49423. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049423
Kim DY, Kwon SI, Choi C, Lee H, Ahn I, Park SR, Bae SC, Lee SC, Hwang DJ (2013) Expression analysis of rice VQ genes in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Gene 529(2):208–214. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.023
Lai ZB, Li Y, Wang F, Cheng Y, Fan BF, Yu JQ, Chen ZX (2011) Arabidopsis sigma factor binding proteins are activators of the WRKY33 transcription factor in plant defense. Plant Cell 23(10):3824–3841. doi:10.1105/tpc.111.090571
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Rese 40(database issue):302–305. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr931
Lewis PO, Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M, Lewis PO (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Li N, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S (2014a) Comprehensive analysis of VQ motif-containing gene expression in rice defense responses to three pathogens. Plant Cell Rep 33(9):1493–1505. doi:10.1007/s00299-014-1633-4
Li Y, Jing Y, Xu G, Li J, Lin R (2014b) Arabidopsis VQ MOTIF-CONTAINING PROTEIN29 represses seedling de-etiolation by interacting with PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1. Plant Physiol 164(4):2068–2080. doi:10.1104/pp.113.234492
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187
Liu X, Wang X, Pang Y, Liang J, Liu S, Sun X, Tang K (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel WRKY gene from Brassica chinensis. Mol Biol 40(5):816–824. doi:10.1134/s0026893306050074
Liu Q, Wang H, Zhang Z, Wu J, Ying F, Zhu Z (2009) Divergence in function and expression of the NOD26-like intrinsic proteins in plants. BMC Genomics 10(1):313
Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luo M, Dennis ES, Berger F, Peacock WJ, Chaudhury A (2005) MINISEED3 (MINI3), a WRKY family gene, and HAIKU2 (IKU2), a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) KINASE gene, are regulators of seed size in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(48):17531–17536. doi:10.1073/pnas.05084218102
Maher C, Stein L, Ware D (2006) Evolution of Arabidopsis microRNA families through duplication events. Genome Res 16(4):510–519. doi:10.1101/gr.4680506
Marchler-Bauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, De Weese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LW, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczycki CJ et al (2011) CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39(1):D225–D229. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq769
Pecher P, Lennart E, Siska H, Katja K, Kai N, Gerit B, Joachim U, Martin W, Dierk S, Justin L (2014) The Arabidopsis thaliana mitogen-activated protein kinases MPK3 and MPK6 target a subclass of ‘VQ-motif’-containing proteins to regulate immune responses. New Phytol 203(2):592–606. doi:10.1111/nph.12817
Peng ZH, Lu TT, Li LB, Liu XH, Gao ZM, Hu T, Yang XW, Feng Q, Guan JP, Weng QJ, Fan DL, Zhu CR, Lu Y, Han B, Jiang ZH (2010) Genome-wide characterization of the biggest grass, bamboo, based on 10,608 putative full-length cDNA sequences. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):1–13. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-116
Peng ZH, Lu Y, Li LB, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Gao ZM, Lu HY, Hu T, Yao N, Liu KY, Li Y, Fan DL, Guo YL, Li WJ, Lu YQ (2013) The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat Genet 45(4):1–2. doi:10.1038/ng.2569
Perruc E, Charpenteau M, Ramirez BC, Jauneau A, Galaud JP, Ranjeva R, Ranty B (2004) A novel calmodulin-binding protein functions as a negative regulator of osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant J 38(3):410–420. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02062.x
Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2002) Targets of AtWRKY6 regulation during plant senescence and pathogen defense. Genes Dev 16(9):1139–1149. doi:10.1101/gad.222702
Ross AF (1961) Systemic acquired resistance induced by localized virus infections in plants. Virology 14(3):340–358. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(61)90319-1
Rozas J (2009) DNA sequence polymorphism analysis using DnaSP. Methods Mol Biol 537(537):337–350. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-251-9_17
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Shang Y, Yan L, Liu ZQ, Cao Z, Mei C, Xin Q, Wu FQ, Wang XF, Du SY, Jiang T, Zhang XF, Zhao R, Sun HL, Liu H, Yu YT, Zhang DP (2010) The Mg-chelatase H subunit of Arabidopsis antagonizes a group of WRKY transcription repressors to relieve ABA-responsive genes of inhibition. Plant Cell 22(6):1909–1935. doi:10.1105/tpc.110.073874
Song W, Zhao H, Zhang X, Lei L, Lai J (2016) Genome-wide identification of VQ motif-containing proteins and their expression profiles under abiotic stresses in maize. Front Plant Sci 6(281):1177. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.01177
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(25):4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Toufighi K, Brady SM, Austin R, Ly E, Provart NJ (2005) The botany array resource: e-northerns, expression angling, and promoter analyses. Plant J 43(1):153–163. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02437.x
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim DW, Kelley DR et al (2012) Corrigendum: differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7(3):562–578. doi:10.1038/nprot1014-2513a
Wang AH, Garcia D, Zhang HY, Feng K, Chaudhury A, Berger F, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Luo M (2010) The VQ motif protein IKU1 regulates endosperm growth and seed size in Arabidopsis. Plant J 63(4):670–679. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04271.x
Wang X, Zhang H, Sun G, Jin Y, Qiu LJ (2014) Identification of active VQ motif-containing genes and the expression patterns under low nitrogen treatment in soybean. Gene 543(2):237–243. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.04.012
Wang M, Vannozzi A, Wang G, Zhong Y, Corso M, Cavallini E, Cheng ZM (2015) A comprehensive survey of the grapevine VQ gene family and its transcriptional correlation with WRKY proteins. Front Plant Sci 6(417):417. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00417
Wu H, Lv H, Li L, Liu J, Mu S, Li X, Gao J (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factors family and the expression patterns of DREB genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS One 10(5):e0126657
Wu M, Li Y, Chen D, Liu H, Zhu D, Yan X (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the IQD gene family in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Sci Rep 6:24520. doi:10.1038/srep24520
Xie YD, Li W, Guo D, Dong J, Zhang Q, Fu Y, Ren D, Peng M, Xia Y (2010) The Arabidopsis gene SIGMA FACTOR-BINDING PROTEIN 1 plays a role in the salicylate- and jasmonate-mediated defence responses. Plant Cell Environ 33(5):828–839. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02109.x
Zhang YJ, Ma PF, Li DZ (2011) High-throughput sequencing of six bamboo chloroplast genomes: phylogenetic implications for temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS One 6(5):e20596. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020596
Zhang M, Sun H, Fei Z, Zhan F, Gong X, Gao S (2014) Fastq_clean: An optimized pipeline to clean the Illumina sequencing data with quality control. In: IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine, Belfast, pp 44–48
Zhang GY, Wang FD, Li JJ, Ding Q, Zhang YH, Li HY, Zhang JN, Gao JW (2015) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the VQ motif-containing protein family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. Pekinensis). Int J Mol Sci 16(12):28683–28704. doi:10.3390/ijms161226127
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Laboratory of Modern Biotechnology for their assistance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Funding
The national natural science foundation of China (31670672) and National Science and Technology Support Program (2015BAD04B03).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
425_2017_2693_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 Expression patterns of 29 VQ genes in Moso bamboo following PEG treatment as determined by qRT-PCR. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) were obtained from three biological and three technical replicates. The error bars indicate standard deviation. * indicates that the level of expression is significantly different from the value of the control (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) (TIFF 188 kb)
425_2017_2693_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig. S2 Expression patterns of 29 VQ genes in Moso bamboo following ABA treatment as determined by qRT-PCR. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) were obtained from three biological and three technical replicates. The error bars indicate standard deviation. * indicates that the level of expression is significantly different from the value of the control (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) (TIFF 200 kb)
425_2017_2693_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Fig. S3 Expression patterns of 29 PeVQ genes in response to SA treatment as determined by qRT-PCR. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) were obtained from three biological and three technical replicates. The error bars indicate standard deviation. * indicates that the level of expression is significantly different from the value of the control (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) (TIFF 202 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liu, H., Zhu, D. et al. Genome-wide analysis of VQ motif-containing proteins in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Planta 246, 165–181 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2693-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2693-9