Abstract
Main conclusion
The plant-specific 4/1 protein interacts, both in yeast two-hybrid system and in vitro, and co-localizes in plant cells with plant BAP-like protein, the orthologue of human protein BAP31.
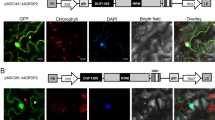
In yeast two-hybrid system, we identified a number of Nicotiana benthamiana protein interactors of Nt-4/1, the protein known to affect systemic transport of potato spindle tuber viroid. For one of these interactors, an orthologue of human B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 (BAP31) termed plant BAP-like protein (PBL), the ability to interact with Nt-4/1 was studied in greater detail. Analyses of purified proteins expressed in bacterial cells carried out in vitro with the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectroscopy revealed that the N. tabacum PBL (NtPBL) was able to interact with Nt-4/1 with high-affinity, and that their complex can form at physiologically relevant concentrations of both proteins. Subcellular localization studies of 4/1-GFP and NtPBL-mRFP transiently co-expressed in plant cells revealed the co-localization of the two fusion proteins in endoplasmic reticulum-associated bodies, suggesting their interaction in vivo. The N-terminal region of the Nt-4/1 protein was found to be required for the specific subcellular targeting of the protein, presumably due to a predicted amphipathic helix mediating association of the Nt-4/1 protein with cell membranes. Additionally, this region was found to contain a trans-activator domain responsible for the Nt-4/1 ability to activate transcription of a reporter gene in yeast.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP31:
-
Human B-cell receptor-associated protein 31
- PBL:
-
Plant BAP-like protein
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- mRFP:
-
Monomeric red fluorescent protein
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
References
Breckenridge DG, Stojanovic M, Marcellus RC, Shore GC (2003) Caspase cleavage product of BAP31 induces mitochondrial fission through endoplasmic reticulum calcium signals, enhancing cytochrome c release to the cytosol. J Cell Biol 160:1115–1127
Chichkova NV, Tuzhikov AI, Taliansky M, Vartapetian AB (2012) Plant phytaspases and animal caspases: structurally unrelated death proteases with a common role and specificity. Physiol Plant 145:77–84
Chou PY, Fasman GD (1974) Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry 13:222–245
Cymer F, von Heijne G, White SH (2015) Mechanisms of integral membrane protein insertion and folding. J Mol Biol 427:999–1022
Ducret A, Nguyen M, Breckenridge DG, Shore GC (2003) The resident endoplasmic reticulum protein, BAP31, associates with gamma-actin and myosin B heavy chain. Eur J Biochem 270:342–349
Ernst WL, Shome K, Wu CC, Gong X, Frizzell RA, Aridor M (2016) VAMP-associated proteins (VAP) as receptors that couple cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteostasis with lipid homeostasis. J Biol Chem 291:5206–5220
Formstecher E, Aresta S, Collura V, Hamburger A, Meil A, Trehin A, Reverdy C et al (2005) Protein interaction mapping: a Drosophila case study. Genome Res 15:376–384
Gautier R, Douguet D, Antonny B, Drin G (2008) HELIQUEST: a web server to screen sequences with specific α-helical properties. Bioinformatics 24:2101–2102
Grigoriev II, Senin II, Tikhomirova NK, Komolov KE, Permyakov SE, Zernii EY, Koch KW, Philippov PP (2012) Synergetic effect of recoverin and calmodulin on regulation of rhodopsin kinase. Front Mol Neurosci 5:28
Heath-Engel HM, Wang B, Shore GC (2012) Bcl2 at the endoplasmic reticulum protects against a Bax/Bak-independent paraptosis-like cell death pathway initiated via p20Bap31. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:335–347
Hemsley PA (2015) The importance of lipid modified proteins in plants. New Phytol 205:476–489
Kazakov AS, Sokolov AS, Vologzhannikova AA, Permyakova ME, Khorn PA, Ismailov RG, Denessiouk KA, Denesyuk AI, Rastrygina VA, Baksheeva VE, Zernii EY, Zinchenko DV, Glazatov VV, Uversky VN, Mirzabekov TA, Permyakov EA, Permyakov SE (2016) Interleukin-11 binds specific EF-hand proteins via their conserved structural motifs. J Biomol Struct Dyn 8:1–14
Kim KM, Adachi T, Nielsen PJ, Terashima M, Lamers MC, Köhler G, Reth M (1994) Two new proteins preferentially associated with membrane immunoglobulin D. EMBO J 13:3793–3800
Kim WT, Seo Choi H, Min Lee H, Jang YJ, Ryu CJ (2014) B-cell receptor-associated protein 31 regulates human embryonic stem cell adhesion, stemness, and survival via control of epithelial cell adhesion molecule. Stem Cells 32:2626–2641
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Lazareva EA, Lezzhov AA, Komarova TV, Morozov SY, Heinlein M, Solovyev AG (2016) A novel block of plant virus movement genes. Mol Plant Pathol. doi:10.1111/mpp.12418
Lupas A, Van Dyke M, Stock J (1991) Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science 252:1162–1164
Makarova SS, Minina EA, Makarov VV, Semenyuk PI, Kopertekh L, Schiemann J, Serebryakova MV, Erokhina TN, Solovyev AG, Morozov SY (2011) Orthologues of a plant-specific At-4/1 gene in the genus Nicotiana and the structural properties of bacterially expressed 4/1 protein. Biochimie 93:1770–1778
Makarova SS, Solovyev AG, Morozov SY (2014) RNA-binding properties of the plant protein Nt-4/1. Biochemistry (Mosc) 79:717–726
Minina EA, Erokhina TN, Garushyants SK, Solovyev AG, Morozov SY (2009) Subcellular localization of the new plant protein 4/1 and analysis of heterologous protein-protein interactions indicate its ability for nuclear-cytoplasmic transport. Dokl Biochem Biophys 429:296–300
Morozov SY, Makarova SS, Erokhina TN, Kopertekh L, Schiemann J, Owens RA, Solovyev AG (2014) Plant 4/1 protein: potential player in intracellular, cell-to-cell and long-distance signaling. Front Plant Sci 5:26
Morozov SY, Milyutina IA, Bobrova VK, Ryazantsev DY, Erokhina TN, Zavriev SK, Agranovsky AA, Solovyev AG, Troitsky AV (2015a) Structural evolution of the 4/1 genes and proteins in non-vascular and lower vascular plants. Biochimie 119:125–136
Morozov SY, Solovyev AG, Troitsky AV (2015b) Phylogeny of the plant 4/1 proteins. Data Brief 6:8–11
Namba T, Tian F, Chu K, Hwang SY, Yoon KW, Byun S, Hiraki M, Mandinova A, Lee SW (2013) CDIP1-BAP31 complex transduces apoptotic signals from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria under endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Rep 5:331–339
Ng FW, Nguyen M, Kwan T, Branton PE, Nicholson DW, Cromlish JA, Shore GC (1997) p28 Bap31, a Bcl-2/Bcl-XL- and procaspase-8-associated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 139:327–338
Orgel JP (2006) Surface-active helices in transmembrane proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 7:553–560
Paape M, Solovyev AG, Erokhina TN, Minina EA, Schepetilnikov MV, Lesemann DE, Schiemann J, Morozov SY, Kellmann JW (2006) At-4/1, an interactor of the Tomato spotted wilt virus movement protein, belongs to a new family of plant proteins capable of directed intra- and intercellular trafficking. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:874–883
Paquet ME, Cohen-Doyle M, Shore GC, Williams DB (2004) Bap29/31 influences the intracellular traffic of MHC class I molecules. J Immunol 172:7548–7555
Piskacek S, Gregor M, Nemethova M, Grabner M, Kovarik P, Piskacek M (2007) Nine-amino-acid transactivation domain: establishment and prediction utilities. Genomics 89:756–768
Quistgaard EM, Low C, Moberg P, Guettou F, Maddi K, Nordlund P (2013) Structural and biophysical characterization of the cytoplasmic domains of human BAP29 and BAP31. PLoS One 8:e71111
Solovyev AG, Makarova SS, Remizowa MV, Lim HS, Hammond J, Owens RA, Kopertekh L, Schiemann J, Morozov SY (2013a) Possible role of the Nt-4/1 protein in macromolecular transport in vascular tissue. Plant Signal Behav 8:e25784
Solovyev AG, Minina EA, Makarova SS, Erokhina TN, Makarov VV, Kaplan IB, Kopertekh L, Schiemann J, Richert-Pöggeler KR, Morozov SY (2013b) Subcellular localization and self-interaction of plant-specific Nt-4/1 protein. Biochimie 95:1360–1370
Spiliotis ET, Manley H, Osorio M, Zúñiga MC, Edidin M (2000) Selective export of MHC class I molecules from the ER after their dissociation from TAP. Immunity 13:841–851
Stojanovic M, Germain M, Nguyen M, Shore GC (2005) BAP31 and its caspase cleavage product regulate cell surface expression of tetraspanins and integrinmediated cell survival. J Biol Chem 280:30018–30024
von Bargen S, Salchert K, Paape M, Piechulla B, Kellmann J-W (2001) Interactions between the tomato spotted wilt virus movement protein and plant proteins showing homologies to myosin, kinesin and DnaJ-like chaperones. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:1083–1093
von Heijne G (2007) Formation of transmembrane helices in vivo—is hydrophobicity all that matters? J Gen Physiol 129:353–356
Wakana Y, Takai S, Nakajima K, Tani K, Yamamoto A, Watson P, Stephens DJ, Hauri HP, Tagaya M (2008) Bap31 is an itinerant protein that moves between the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and a juxtanuclear compartment related to ER-associated degradation. Mol Biol Cell 19:1825–1836
Wang B, Heath-Engel H, Zhang D, Nguyen N, Thomas DY, Hanrahan JW, Shore GC (2008) BAP31 interacts with Sec61 translocons and promotes retrotranslocation of CFTRDeltaF508 via the derlin-1 complex. Cell 133:1080–1092
Wilson JD, Barlowe C (2010) Yet1p and Yet3p, the yeast homologs of BAP29 and BAP31, interact with the endoplasmic reticulum translocation apparatus and are required for inositol prototrophy. J Biol Chem 285:18252–18261
Zamyatnin AA Jr, Solovyev AG, Sablina AA, Agranovsky AA, Katul L, Vetten HJ, Schiemann J, Hinkkanen AE, Lehto K, Morozov SY (2002) Dual-colour imaging of membrane protein targeting directed by poa semilatent virus movement protein TGBp3 in plant and mammalian cells. J Gen Virol 83:651–662
Zen K, Utech M, Liu Y, Soto I, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2004) Association of BAP31 with CD11b/CD18. Potential role in intracellular trafficking of CD11b/CD18 in neutrophils. J Biol Chem 279:44924–44930
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. S. S. Makarova for the help with subcellular fractionation experiments. The work of A. Pankratenko, A. Atabekova, E. Lazareva, V. Baksheeva, E. Zernii, A. Solovyev and S. Morozov was performed at Moscow State University with financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (Grant 14-14-00053). The work of O. Zhironkina was performed at Moscow State University with financial support of the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant 15-54-78077). The confocal laser scanning microscopy and surface plasmon resonance facilities in Belozersky Institute were funded by Moscow State University Development Program (PNR 5.13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Robert A. Owens retired from Molecular Plant Pathology Laboratory, USDA-ARS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pankratenko, A.V., Atabekova, A.K., Lazareva, E.A. et al. Plant-specific 4/1 polypeptide interacts with an endoplasmic reticulum protein related to human BAP31. Planta 245, 193–205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2601-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2601-8