Abstract
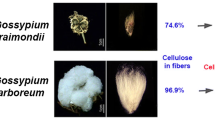
Cotton fiber is an excellent model system of cellulose biosynthesis; however, it has not been widely studied due to the lack of information about the cellulose synthase (CESA) family of genes in cotton. In this study, we initially identified six full-length CESA genes designated as GhCESA5–GhCESA10. Phylogenetic analysis and gene co-expression profiling revealed that CESA1, CESA2, CESA7, and CESA8 were the major isoforms for secondary cell wall biosynthesis, whereas CESA3, CESA5, CESA6, CESA9, and CESA10 should involve in primary cell wall formation for cotton fiber initiation and elongation. Using integrative analysis of gene expression patterns, CESA protein levels, and cellulose biosynthesis in vivo, we detected that CESA8 could play an enhancing role for rapid and massive cellulose accumulation in Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. We found that CESA2 displayed a major expression in non-fiber tissues and that CESA1, a housekeeping gene like, was predominantly expressed in all tissues. Further, a dynamic alteration was observed in cell wall composition and a significant discrepancy was observed between the cotton species during fiber elongation, suggesting that pectin accumulation and xyloglucan reduction might contribute to cell wall transition. In addition, we discussed that callose synthesis might be regulated in vivo for massive cellulose production during active secondary cell wall biosynthesis in cotton fibers.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CalS:
-
Callose synthase
- CESA:
-
Cellulose synthase
- CrI:
-
Crystalline index
- CSC:
-
Cellulose synthase complex
- DP:
-
Degree of polymerization
- EST:
-
Expression sequence tag
- Gb :
-
Gossypium barbadense
- Gh :
-
Gossypium hirsutum
- Kor:
-
Korrigan
- RACE:
-
Rapid-amplification of cDNA ends
- SGT :
-
Sterol glycosyltransferase
- UBQ :
-
Ubiquitin
References
Amor Y, Haigler CH, Johnson S, Wainscott M, Delmer DP (1995) A membrane-associated form of sucrose synthase and its potential role in synthesis of cellulose and callose in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9353–9357
Appenzeller L, Doblin M, Barreiro R, Wang HY, Niu XM, Kollipara K, Carrigan L, Tomes D, Chapman M, Dhugga KS (2004) Cellulose synthesis in maize: isolation and expression analysis of the cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. Cellulose 11:287–299
Arioli T, Peng L, Betzner AS, Burn J, Wittke W, Herth W, Camilleri C, Höfte H, Plazinski J, Birch R, Cork A, Glover J, Redmond J, Williamson RE (1998) Molecular analysis of cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Science 279:717–720
Basra A, Malik CP (1984) Development of the cotton fiber. Int Rev Cytol 89:65–113
Blakeney AB, Harris PJ, Henry RJ, Stone BA (1983) A simple and rapid preparation of alditol acetates for monosaccharide analysis. Carbohydr Res 113:291
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54:484
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burton RA, Shirley NJ, King BJ, Harvey AJ, Fincher GB (2004) The CesA gene family of barley. Quantitative analysis of transcripts reveals two groups of co-expressed genes. Plant Physiol 134:224–236
Carroll A, Somerville C (2009) Cellulosic biofuels. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:165–182
Chaudhary B, Hovav R, Rapp R, Verma N, Udall JA, Wendela JF (2008) Global analysis of gene expression in cotton fibers from wild and domesticated Gossypium barbadense. Evol Dev 10:567–582
Chen F, Duran AL, Blount JW, Sumner LW, Dixon RA (2003) Profiling phenolic metabolites in transgenic alfalfa modified in lignin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 64:1013
Cosgrove DJ (2005) Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:850–861
Cui X, Shin H, Song C, Laosinchai W, Amano Y, Brown RM Jr (2001) A putative plant homolog of the yeast (1 → 3)-β-glucan synthase subunit FKS1 from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) fibers. Planta 213:223–230
Dische Z (1962) Color reactions of carbohydrates. In: Whistler RL, Wolfrom ML (eds) Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 477–512
Djerbi S, Aspeborg H, Nilsson P, Mellerowicz E, Sundberg B, Blomqvist K, Teeri TT (2004) Identification and expression analysis of genes encoding putative cellulose synthases (CesA) in the hybrid aspen, Populus tremula (L.) × P tremuloides (Michx.). Cellulose 11:301–312
Djerbi S, Lindskog M, Arvestad L, Sterky F, Teeri TT (2005) The genome sequence of black cotton wood (Populus trichocarpa) reveals 18 conserved cellulose synthase (CesA) genes. Planta 221:739–746
Doblin MS, De Melis L, Newbigin E, Bacic A, Read SM (2001) Pollen tubes of Nicotiana alata express two genes from different β-glucan synthase families. Plant Physiol 125:2040–2052
Doblin MS, Kurek I, Jacob-Wilk D, Delmer DP (2002) Cellulose biosynthesis in plants: from genes to rosettes. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1407–1420
Fagard M, Desnos T, Desprez T, Goubet F, Refregier G, Mouille G, McCann M, Rayon C, Vernhettes S, Höfte H (2000) PROCUSTE1 encodes a cellulose synthase required for normal cell elongation specifically in roots and dark-grown hypocotyls of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2409–2423
Frohman MA, Dushand MK, Martin GR (1988) Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligo nucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8998–9002
Fry SC (1988) The growing plant cell wall: chemical and metabolic analysis. Longman, London
Ghazi YA, Bourot S, Arioli T, Dennis ES, Llewellyn DJ (2009) Transcript profiling during fiber development identifies pathways in secondary metabolism and cell wall structure that may contribute to cotton fiber quality. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1364–1381
Goldberg R, Morvan C, Jauneau A, Jarvis MC (1996) Methyl-esterification, de-esterification and gelation of pectins in the primary cell wall. In: Visser J, Voragen AFG (eds) Pectins and pectinases. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 151–172
Grover CE, Kim HR, Wing RA, Paterson AH, Wendel JF (2004) Incongruent patterns of local and global genome size evolution in cotton. Genome Res 14:1474–1482
Haigler CH, Zhang DS, Wilkerson CG (2005) Biotechnological improvement of cotton fibre maturity. Physiol Plant 124:285–294
Hayashi T (1989) Xyloglucans in the primary cell wall. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40:139–168
Hayashi T, Delmer DP (1988) Xyloglucan in the cell walls of cotton fiber. Carbohydr Res 181:273–277
Holland N, Holland D, Helentjaris T, Dhugga KS, Xoconostle-Cazares B, Delmer DP (2000) A comparative analysis of the plant cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. Plant Physiol 123:1313–1323
Hong Z, Delauney AJ, Verma DPS (2001) A cell plate-specific callose synthase and its interaction with phragmoplastin. Plant Cell 13:755–768
Hu XP, Hsieh YL (1997) Crystalline structure of developing cotton fibers. J Polym Sci Pol Phys 34:1451–1459
Ji SJ, Lu YC, Feng JX, Wei G, Li J, Shi YH, Fu Q, Liu D, Luo JC, Zhu YX (2003) Isolation and analyses of genes preferentially expressed during early cotton fiber development by subtractive PCR and cDNA array. Nucleic Acids Res 31:2534–2543
Kim HJ, Triplett BA (2001) Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro: models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol 127:1361–1366
Kim HJ, Triplett BA, Zhang HB, Lee MK, Hinchliffe DJ, Li P, Fang DD (2012) Cloning and characterization of homeologous cellulose synthase catalytic subunit 2 genes from allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Gene 494:181–189
Kudlicka K, Brown RM Jr (1997) Cellulose and callose biosynthesis in higher plants. Solubilization and separation of (1 → 3)- and (1 → 4)-beta-glucan synthase activities from mung bean. Plant Physiol 115:643–656
Lane DR, Wiedemeier A, Peng LC, Höfte H, Vernhettes S, Desprez T, Hocart CH, Birch RJ, Baskin TI, Burn JE, Arioli T, Betzner AS, Williamson RE (2001) Temperature-sensitive alleles of RSW2 link the KORRIGAN endo-1,4-β-glucanase to cellulose synthesis and cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:278–288
Laosinchai W, Cui X, Brown RM Jr (2000) A full length cDNA of cotton cellulose synthase has high homology with the Arabidopsis rsw1 gene and the cotton Cel1 gene. Plant Physiol 122:291
Lee JJ, Woodward AW, Jeffery CZ (2007) Gene expression changes and early events in cotton fibre development. Ann Bot-Lond 100:1391–1401
Lee J, Burns TH, Light G, Sun Y, Fokar M, Kasukabe Y, Fujisawa K, Maekawa Y, Allen RD (2010) Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase genes in cotton and their role in fiber elongation. Planta 232:1191–1205
Lin ZX, Wang Y, Zhang XL, Zhang JF (2012) Functional markers for cellulose synthase and their comparison to SSRs in cotton. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:1270–1275
Maltby D, Carpita NC, Montezinos D, Kulow C, Delmer DP (1979) β-1, 3-Glucan in developing cotton fibers. Plant Physiol 63:1158–1164
Meinert MC, Delmer DP (1977) Changes in biochemical composition of the cell wall in cotton fiber during development. Plant Physiol 59:1088–1097
Mutwil M, Obro J, Willats WG, Persson S (2008) Gene CAT—novel web tools that combine BLAST and co-expression analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Web server Issue):W320–W326
Pagant S, Bichet A, Sugimoto K, Lerouxel O, Desprez T, McCann M, Lerouge P, Vernhettes S, Höfte H (2002) KOBITO1 encodes a novel plasma membrane protein necessary for normal synthesis of cellulose during cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:2001–2013
Pang CY, Wang H, Pang Y, Xu C, Jiao Y, Qin YM, Western TL, Yu SX, Zhu YX (2010) Comparative proteomics indicates that biosynthesis of pectic precursors is important for cotton fiber and Arabidopsis root hair elongation. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:2019–2033
Pear JR, Kawagoe Y, Schreckengost WE, Delmer DP, Stalker DM (1996) Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12637–12642
Peng LC, Hocart CH, Redmond JW, Williamson RE (2000) Fractionation of carbohydrates in Arabidopsis root cell walls shows that three radial swelling loci are specifically involved in cellulose production. Planta 211:406–414
Peng LC, Kawagoe Y, Hogan P, Delmer DP (2002) Sitosterol-β-glucoside as primer for cellulose synthesis in plants. Science 295:147–150
Persson S, Paredez A, Carroll A, Palsdottir H, Doblin M, Poindexter P, Khitrov N, Auer M, Somerville CR (2007) Genetic evidence for three unique components in primary cell wall cellulose synthase complexes in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15566–15571
Roudier F, Fernandez AG, Fujita M, Himmelspach R, Borner GHH, Schindelman G, Song S, Baskin TI, Dupree P, Wasteneys GO, Benfeya PN (2005) COBRA, an Arabidopsis extracellular glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol-anchored protein, specifically controls highly anisotropic expansion through its involvement in cellulose microfibril orientation. Plant Cell 17:1749–1763
Ruan YL, Chourey PS (1998) A fiberless seed mutation in cotton is associated with lack of fiber cell initiation in ovule epidermis and alterations in sucrose synthase expression and carbon partitioning in developing seeds. Plant Physiol 118:399–406
Ryser U (1985) Cell wall biosynthesis in differentiating cotton fibres. Eur J Cell Biol 39:236–256
Scheller HV, Ulvskov P (2010) Hemicelluloses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:263–289
Somerville C (2006) Cellulose synthesis in higher plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:53–78
Song DL, Shen JH, Li LG (2010) Characterization of cellulose synthase complexes in Populus xylem differentiation. New Phytol 187:777–790
Tanaka K, Murata K, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Hirochika H (2003) Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol 133:73–83
Taylor NG, Scheible WR, Cutler S, Somerville CR, Turner SR (1999) The irregular xylem3 locus of Arabidopsis encodes a cellulose synthase required for secondary cell wall synthesis. Plant Cell 11:769–780
Taylor NG, Laurie S, Turner SR (2000) Multiple cellulose synthase catalytic subunits are required for cellulose synthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2529–2540
Taylor NG, Howells RM, Huttly AK, Vickers K, Turner SR (2003) Interactions among three distinct CesA proteins essential for cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1450–1455
Timpa JD, Triplett BA (1993) Analysis of cell-wall polymers during cotton fiber development. Planta 189:101–108
Triplett BA, Kim HJ (2006) Using cotton fiber development to discover how plant cells grow. In: Hayashi T (ed) The science and lore of the plant cell wall. Florida, Boca Raton, p 367
Vaughn KC, Turley RB (1999) The primary walls of cotton fibers contain an ensheathing pectin layer. Protoplasma 209:226–237
Wang LQ, Guo K, Li Y, Tu YY, Hu HZ, Wang BR, Cui XC, Peng LC (2010) Expression profiling and integrative analysis of the CESA/CSL superfamily in rice. BMC Plant Biol 10:282–297
Wu YT, Liu JY (2004) A modified hot borate method for efficient isolation of total RNA from different cotton tissues. Cotton Sci 16:67–71
Xie GS, Yang B, Xu ZD, Li FC, Guo K, Zhang ML, Wang LQ, Zou WH, Wang YT, Peng LC (2013) Global identification of multiple OsGH9 family members and their involvement in cellulose crystallinity modification in rice. PLoS One 8:e50171
Xu N, Zhang W, Ren SF, Liu F, Zhao CQ, Liao HF, Xu ZD, Huang JF, Li Q, Tu YY, Yu B, Wang YT, Jiang JX, Qin JP, Peng LC (2012) Hemicelluloses negatively affect lignocellulose crystallinity for high biomass digestibility under NaOH and H2SO4 pretreatments in Miscanthus. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:58
Zhu HY, Han XY, Lv JH, Zhao L, Xu XY, Zhang TZ, Guo WZ (2011) Structure, expression differentiation and evolution of duplicated fiber developmental genes in Gossypium barbadense and G. hirsutum. BMC Plant Biol 11:40–54
Acknowledgments
We thank Professors Guozheng Yang and Xianda Yi for kindly providing cotton seeds. This work was supported in part by grants from the 973 Specific Pre-project (2010CB134401), the 973 project (2012CB114500), the National Transgenic Project (2009ZX08009-119B) and the 111 Project (B08032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Li and T. Xia contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, A., Xia, T., Xu, W. et al. An integrative analysis of four CESA isoforms specific for fiber cellulose production between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense . Planta 237, 1585–1597 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1868-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1868-2