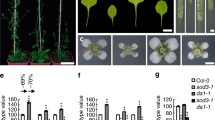
Abstract
The forkhead-associated (FHA) domain is involved in protein–protein interaction by recognizing a phosphothreonine epitope on target proteins. In this study, we investigated in planta functions of the Arabidopsis FHA domain 2. AtFHA2 was mainly localized in the nucleus. Arabidopsis fha2 null mutants grew normally during the vegetative stage, but had severely reduced fertility during reproductive stage. The reduced fertility was mainly caused by defective stamen filament elongation, while female flower parts of the mutants were fertile. Additionally, the mutants had fewer stamens than the wild type and the vegetative organs of the mutants, such as cotyledons and leaves, had increased ploidy. These results suggest that AtFHA2 may play a role in a signaling pathway for the control of plant organ development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi S et al (2011) Programmed induction of endoreduplication by DNA double-strand breaks in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:10004–10009
Ahn J-W, Kim M, Bang JW, Pai H-S (2003) Molecular characteristics and differential expression of two nuclear factors containing the FHA domain in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 165:1023–1032
Alexander MP (1969) Differential staining of aborted and nonaborted pollen. Stain Technol 44:117–122
Barrero JM, Piqueras P, González-Guzmán M, Serrano R, Rodríguez PL, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2005) A mutational analysis of the ABA1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana highlights the involvement of ABA in vegetative development. J Exp Bot 56:2071–2083
Cecchetti V, Altamura MM, Falasca G, Costantino P, Cardarelli M (2008) Auxin regulates Arabidopsis anther dehiscence, pollen maturation, and filament elongation. Plant Cell 20:1760–1774
Cheng Y, Dai X, Zhao Y (2006) Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA flavin monooxygenases controls the formation of floral organs and vascular tissues in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 20:1790–1799
Cheng H, Song S, Xiao L, Soo HM, Cheng Z, Xie D, Peng J (2009) Gibberellin acts through jasmonate to control the expression of MYB21, MYB24, and MYB57 to promote stamen filament growth in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 5:e1000440
Devoto A, Nieto-Rostro M, Xie D, Ellis C, Harmston R, Patrick E, Davis J, Sherratt L, Coleman M, Turner JG (2002) COI1 links jasmonate signalling and fertility to the SCF ubiquitin-ligase complex in Arabidopsis. Plant J 32:457–466
Fletcher JC (2002) Shoot and floral meristem maintenance in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:45–66
Hammet A, Pike BL, McNees CJ, Conlan LA, Tenis N, Heierhorst J (2003) FHA domains as phospho-threonine binding modules in cell signaling. IUBMB Life 55:23–27
Ishiguro S, Kawai-Oda A, Ueda J, Nishida I, Okada K (2001) The DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCIENCE gene encodes a novel phospholipase A1 catalyzing the initial step of jasmonic acid biosynthesis, which synchronizes pollen maturation, anther dehiscence, and flower opening in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2191–2209
Joubès J, Chevalier C (2000) Endoreduplication in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 43:735–745
Kim M, Ahn JW, Song K, Paek KH, Pai H-S (2002) Forkhead-associated domains of the tobacco NtFHA1 transcription activator and the yeast Fhl1 forkhead transcription factor are functionally conserved. J Biol Chem 277:38781–38790
Kim M, Ahn J-W, Jin U-H, Choi D, Paek K-H, Pai H-S (2003) Activation of the programmed cell death pathway by inhibition of proteasome function in plants. J Biol Chem 278:19406–19415
Lee JY, Lee HS, Wi SJ, Park KY, Schmit AC, Pai H-S (2009) Dual functions of Nicotiana benthamiana Rae1 in interphase and mitosis. Plant J 59:278–291
Li J, Smith GP, Walker JC (1999) Kinase interaction domain of kinase-associated protein phosphatase, a phosphoprotein-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7821–7826
Lohmann JU, Hong RL, Hobe M, Busch MA, Parcy F, Simon R, Weigel D (2001) A molecular link between stem cell regulation and floral patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell 105:793–803
Mahajan A, Yuan C, Lee H, Chen ES, Wu PY, Tsai MD (2008) Structure and function of the phosphothreonine-specific FHA domain. Sci Signal 1:re12
Mandaokar A, Browse J (2009) MYB108 acts together with MYB24 to regulate jasmonate-mediated stamen maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149:851–862
Mandaokar A, Thines B, Shin B, Lange BM, Choi G, Koo YJ, Choi YD, Browse J (2006) Transcriptional regulators of stamen development in Arabidopsis by transcriptional profiling. Plant J 46:984–1008
Morris ER, Chevalier D, Walker JC (2006) DAWDLE, a forkhead-associated domain gene, regulates multiple aspects of plant development. Plant Physiol 141:932–941
Nagpal P et al (2005) Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development 132:4107–4118
Preuss D, Rhee SY, Davis RW (1994) Tetrad analysis possible in Arabidopsis with mutation of the QUARTET (QRT) genes. Science 264:1458–1460
Procissi A, de Laissardière S, Férault M, Vezon D, Pelletier G, Bonhomme S (2001) Five gametophytic mutations affecting pollen development and pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 158:1773–1783
Prunet N, Morel P, Negrutiu I, Trehin C (2009) Time to stop: flower meristem termination. Plant Physiol 150:1764–1772
Sanders PM, Bui AQ, Weterings K, McIntire KN, Hsu Y-C, Lee PY, Truong MT, Beals TP, Goldberg RB (1999) Anther developmental defects in Arabidopsis thaliana male-sterile mutants. Sex Plant Reprod 11:297–322
Sanders PM, Lee PY, Biesgen C, Boone JD, Beals TP, Weiler EW, Goldberg RB (2000) The Arabidopsis DELAYED DEHISCENCE1 gene encodes an enzyme in the jasmonic acid synthesis pathway. Plant Cell 12:1041–1061
Stintzi A, Browse J (2000) The Arabidopsis male-sterile mutant, opr3, lacks the 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductase required for jasmonate synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10625–10630
Stone JM, Trotochaud AE, Walker JC, Clark SE (1998) Control of meristem development by CLAVATA1 receptor kinase and kinase-associated protein phosphatase interactions. Plant Physiol 117:1217–1225
Sugimoto-Shirasu K, Roberts K (2003) “Big it up”: endoreduplication and cell-size control in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:544–553
Wilson ZA, Zhang DB (2009) From Arabidopsis to rice: pathways in pollen development. J Exp Bot 60:1479–1492
Yanofsky MF (1995) Floral meristems to floral organs: genes controlling early events in Arabidopsis flower development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:167–188
Yu B et al (2008) The FHA domain proteins DAWDLE in Arabidopsis and SNIP1 in humans act in small RNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10073–10078
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program [PMBC (No. PJ009079) and SSAC (No. PJ008214); RDA] and the Mid-career Researcher Program (No. 2012047824; NRF/MEST) of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
E.-R. Ahn and H.-K. Cho contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, ER., Cho, HK. & Pai, HS. The forkhead-associated domain 2 (FHA2) in Arabidopsis plays a role in plant fertility by regulating stamen development. Planta 237, 1015–1023 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1815-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1815-7