Abstract
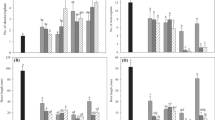
The effect of supplementing either meta-topolin (mT) or N 6-benzyladenine (BA) requiring cultures with roscovitine (6-benzylamino-2-[1(R)-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]amino-9-isopropylpurine), a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) and N-glucosylation inhibitor, and INCYDE (2-chloro-6-(3-methoxyphenyl)aminopurine), an inhibitor of cytokinin (CK) degradation, on the endogenous CK profiles and physiology of banana in vitro was investigated. Growth parameters including multiplication rate and biomass were recorded after 42 days. Endogenous CK levels were quantified using UPLC–MS/MS while the photosynthetic pigment and phenolic contents were evaluated spectrophotometrically. The highest regeneration rate (93 %) was observed in BA + roscovitine while mT + INCYDE plantlets produced most shoots. Treatment with BA + roscovitine had the highest shoot length and biomass. Although not significant, there was a higher proanthocyanidin level in BA + roscovitine treatments compared to the control (BA). The levels of total phenolics and flavonoids were significantly higher in mT + roscovitine treatment than in the mT-treated regenerants. The presence of roscovitine and/or INCYDE had no significant effect on the photosynthetic pigments of the banana plantlets. Forty-seven aromatic and isoprenoid CKs categorized into nine CK-types were detected at varying concentrations. The presence of mT + roscovitine and/or INCYDE increased the levels of O-glucosides while 9-glucosides were higher in the presence of BA. Generally, the underground parts had higher CK levels than the aerial parts; however, the presence of INCYDE increased the level of CK quantified in the aerial parts. From a practical perspective, the use of roscovitine and INCYDE in micropropagation could be crucial in the alleviation of commonly observed in vitro-induced physiological abnormalities.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BA:
-
N 6-Benzyladenine
- BA9G:
-
N 6-Benzyladenine-9-glucoside
- BAR:
-
N 6-Benzyladenosine
- BAR5′MP:
-
N 6-Benzyladenosine-5′-monophosphate
- CCE:
-
Cyanidin chloride equivalents
- CDK:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- CE:
-
Catechin equivalents
- CK:
-
Cytokinin
- CKX:
-
Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase
- cZ:
-
cis-Zeatin
- cZ9G:
-
cis-Zeatin-9-glucoside
- cZOG:
-
cis-Zeatin-O-glucoside
- cZR:
-
cis-Zeatin riboside
- cZR5′MP:
-
cis-Zeatin riboside-5′-monophosphate
- cZROG:
-
cis-Zeatin-O-glucoside riboside
- DHZ:
-
Dihydrozeatin
- DHZ9G:
-
Dihydrozeatin-9-glucoside
- DHZOG:
-
Dihydrozeatin-O-glucoside
- DHZR:
-
Dihydrozeatin riboside
- DHZR5′MP:
-
Dihydrozeatin riboside-5′-monophosphate
- DHZROG:
-
Dihydrozeatin-O-glucoside riboside
- DMRT:
-
Duncan’s multiple range test
- GAE:
-
Gallic acid equivalents
- IAC:
-
Immunoaffinity chromatography
- INCYDE:
-
2-Chloro-6-(3-methoxyphenyl)aminopurine
- iP:
-
N 6-Isopentenyladenine
- iP9G:
-
N 6-Isopentenyladenine-9-glucoside
- iPR:
-
N 6-Isopentenyladenosine
- iPR5′MP:
-
N 6-Isopentenyladenosine-5′-monophosphate
- IPT:
-
Isopentenyltransferase
- Kin:
-
Kinetin
- Kin9G:
-
Kinetin-9-glucoside
- KinR:
-
Kinetin riboside
- KinR5′MP:
-
Kinetin riboside-5′-monophosphate
- MRM:
-
Multiple reaction monitoring
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- mT:
-
meta-Topolin
- mT9G:
-
meta-Topolin-9-glucoside
- mTOG:
-
meta-Topolin-O-glucoside
- mTR:
-
meta-Topolin riboside
- mTR5′MP:
-
meta-Topolin-5′-monophosphate
- mTROG:
-
meta-Topolin-O-glucoside riboside
- oT:
-
ortho-Topolin
- oT9G:
-
ortho-Topolin-9-glucoside
- oTOG:
-
ortho-Topolin-O-glucoside
- oTR:
-
ortho-Topolin riboside
- oTR5′MP:
-
ortho-Topolin-5′-monophosphate
- oTROG:
-
ortho-Topolin-O-glucoside riboside
- PGR:
-
Plant growth regulator
- PPFD:
-
Photosynthetic photon flux density
- pT:
-
para-Topolin
- PTC:
-
Plant tissue culture
- pTOG:
-
para-Topolin-O-glucoside
- pTR:
-
para-Topolin riboside
- pTR5′MP:
-
para-Topolin-5′-monophosphate
- pTROG:
-
para-Topolin-O-glucoside riboside
- tZ:
-
trans-Zeatin
- tZ9G:
-
trans-Zeatin-9-glucoside
- tZOG:
-
trans-Zeatin-O-glucoside
- tZR:
-
trans-Zeatin riboside
- tZR5′MP:
-
trans-Zeatin riboside-5′-monophosphate
- tZROG:
-
trans-Zeatin-O-glucoside riboside
- UPLC:
-
Ultra performance liquid chromatography
References
Amoo SO, Finnie JF, Van Staden J (2011) The role of meta-topolins in alleviating micropropagation problems. Plant Growth Regul 63:197–206
Aremu AO, Bairu MW, Finnie JF, Van Staden J (2012a) Stimulatory role of smoke–water and karrikinolide on the photosynthetic pigment and phenolic contents of micropropagated ‘Williams’ bananas. Plant Growth Regul 67:271–279
Aremu AO, Bairu MW, Doležal K, Finnie JF, Van Staden J (2012b) Topolins: a panacea to plant tissue culture challenges? Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 108:1–16
Auer CA (1997) Cytokinin conjugation: recent advances and patterns in plant evolution. Plant Growth Regul 23:17–32
Bairu MW, Stirk WA, Doležal K, Van Staden J (2007) Optimizing the micropropagation protocol for the endangered Aloe polyphylla: can meta-topolin and its derivatives serve as replacement for benzyladenine and zeatin? Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 90:15–23
Bairu MW, Stirk WA, Doležal K, Van Staden J (2008) The role of topolins in micropropagation and somaclonal variation of banana cultivars ‘Williams’ and ‘Grand Naine’ (Musa spp. AAA). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 95:373–379
Bairu MW, Novák O, Doležal K, Van Staden J (2011) Changes in endogenous cytokinin profiles in micropropagated Harpagophytum procumbens in relation to shoot-tip necrosis and cytokinin treatments. Plant Growth Regul 63:105–114
Bajguz A, Piotrowska A (2009) Conjugates of auxin and cytokinin. Phytochemistry 70:957–969
Binarová P, Doležel J, Draber P, Heberle-Bors E, Strnad M, Bögre L (1998) Treatment of Vicia faba root tip cells with specific inhibitors to cyclin-dependent kinases leads to abnormal spindle formation. Plant J 16:697–707
Blagoeva E, Malbeck J, Gaudinová A, Vaněk T, Vaňková R (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, roscovitine, in combination with exogenous cytokinin, N6-benzyladenine, causes increase of cis-cytokinins in immobilized tobacco cells. Biotechnol Lett 25:469–472
Blagoeva E, Dobrev PI, Malbeck J, Motyka V, Gaudinová A, Vaňková R (2004a) Effect of exogenous cytokinins, auxins and adenine on cytokinin N-glucosylation and cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase activity in de-rooted radish seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 44:15–23
Blagoeva E, Dobrev PI, Jí M, Motyka V, Strnad M, Hanuš J, Vaňková R (2004b) Cytokinin N-glucosylation inhibitors suppress deactivation of exogenous cytokinins in radish, but their effect on active endogenous cytokinins is counteracted by other regulatory mechanisms. Physiol Plant 121:215–222
Blakesley D (1991) Uptake and metabolism of 6-benzyladenine in shoot cultures of Musa and Rhododendron. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 25:69–74
Brzobohatý B, Moore I, Palme K (1994) Cytokinin metabolism: implications for regulation of plant growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 26:1483–1497
Buer CS, Imin N, Djordjevic MA (2010) Flavonoids: new roles for old molecules. J Integrat Plant Biol 52:98–111
Carimi F, Zottini M, Formentin E, Terzi M, Lo Schiavo F (2003) Cytokinins: new apoptotic inducers in plants. Planta 216:413–421
Chen C-M (1997) Cytokinin biosynthesis and interconversion. Physiol Plant 101:665–673
Chernyad’ev II (2009) The protective action of cytokinins on the photosynthetic machinery and productivity of plants under stress (review). Appl Biochem Microbiol 45:351–362
Coste A, Vlase L, Halmagyi A, Deliu C, Coldea G (2011) Effects of plant growth regulators and elicitors on production of secondary metabolites in shoot cultures of Hypericum hirsutum and Hypericum maculatum. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 106:279–288
De Azevedo WF, Leclerc S, Meijer L, Havlicek L, Strnad M, Kim S-H (1997) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues. Eur J Biochem 243:518–526
De Klerk G-J, Guan H, Huisman P, Marinova S (2011) Effects of phenolic compounds on adventitious root formation and oxidative decarboxylation of applied indoleacetic acid in Malus ‘Jork 9’. Plant Growth Regul 63:175–185
Dwivedi S, Vanková R, Motyka V, Herrera C, Zizkova E, Auer C (2010) Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana mutant ror-1 (roscovitine-resistant) and its utilization in understanding of the role of cytokinin N-glycosylation pathway in plants. Plant Growth Regul 61:231–242
Frébort I, Kowalska M, Hluska T, Frébortová J, Galuszka P (2011) Evolution of cytokinin biosynthesis and degradation. J Exp Bot 62:2431–2452
Gajdošová S, Spíchal L, Kamínek M, Hoyerová K, Novák O, Dobrev PI, Galuszka P, Klíma P, Gaudinová A, Žižková E, Hanuš J, Dančák M, Trávníček B, Pešek B, Krupička M, Vaňková R, Strnad M, Motyka V (2011) Distribution, biological activities, metabolism, and the conceivable function of cis-zeatin-type cytokinins in plants. J Exp Bot 62:2827–2840
George EF (1993) Plant propagation by tissue culture, part 1: the technology. Exegetics Ltd, London
Haberer G, Kieber JJ (2002) Cytokinins. New insights into a classic phytohormone. Plant Physiol 128:354–362
Havlíček L, Hanuš J, Veselý J, Leclerc S, Meijer L, Shaw G, Strnad M (1997) Cytokinin-derived cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: synthesis and cdc2 inhibitory activity of Olomoucine and related compounds. J Med Chem 40:408–412
Holub J, Hanuš J, Hanke DE, Strnad M (1998) Biological activity of cytokinins derived from ortho- and meta-hydroxybenzyladenine. Plant Growth Regul 26:109–115
Ivanova M, Novák O, Strnad M, Van Staden J (2006) Endogenous cytokinins in shoots of Aloe polyphylla cultured in vitro in relation to hyperhydricity, exogenous cytokinins and gelling agents. Plant Growth Regul 50:219–230
Kamínek M, Vaněk T, Motyka V (1987) Cytokinin activities of N6-benzyladenosine derivatives hydroxylated on the side-chain phenyl ring. J Plant Growth Regul 6:113–120
Kamínek M, Motyka V, Vaková R (1997) Regulation of cytokinin content in plant cells. Physiol Plant 101:689–700
Kamínek M, Březinov A, Gaudinová A, Motyka V, Vaňková R, Zaăímalová E (2000) Purine cytokinins: a proposal of abbreviations. Plant Growth Regul 32:253–256
Krikorian AD (1995) Hormones in tissue culture and micropropagation. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones: physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 774–796
Letham DS, Palni LMS (1983) The biosynthesis and metabolism of cytokinins. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 34:163–197
Letham DS, Parker CW, Duke CC, Summons RE, MaCleod JK (1977) O-glucosylzeatin and related compounds—a new group of cytokinin metabolites. Ann Bot 41:261–263
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In: Douce R, Packer L (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 148. Academic Press, New York, pp 350–382
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JPJ, Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros J-G, Moulinoux J-P (1997) Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem 243:527–536
Mok DWS, Mok MC (2001) Cytokinin metabolism and action. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:89–118
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Novák O, Tarkowski P, Tarkowská D, Dolezal K, Lenobel R, Strnad M (2003) Quantitative analysis of cytokinins in plants by liquid chromatography-single-quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 480:207–218
Novák O, Hauserová E, Amakorová P, Doležal K, Strnad M (2008) Cytokinin profiling in plant tissues using ultra-performance liquid chromatography—electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 69:2214–2224
Ördög V, Stirk WA, Van Staden J, Novák O, Strnad M (2004) Endogenous cytokinins in three genera of microalgae from the Chlorophyta. J Phycol 40:88–95
Pasternak T, Miskolczi P, Ayaydin F, Mészáros T, Dudits D, Fehér A (2000) Exogenous auxin and cytokinin dependent activation of CDKs and cell division in leaf protoplast-derived cells of alfalfa. Plant Growth Regul 32:129–141
Planchais S, Glab N, Tréhin C, Perennes C, Bureau J-M, Meijer L, Bergounioux C (1997) Roscovitine, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, characterizes restriction point and G2/M transition in tobacco BY-2 cell suspension. Plant J 12:191–202
Planchais S, Glab N, Inzé D, Bergounioux C (2000) Chemical inhibitors: a tool for plant cell cycle studies. FEBS Lett 476:78–83
Ramachandra Rao S, Ravishankar GA (2002) Plant cell cultures: chemical factories of secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 20:101–153
Sakakibara H (2006) Cytokinins: activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:431–449
Schmülling T (2004) Cytokinin. In: Lennarz WJ, Lane MD (eds) Encyclopedia of biological chemistry. Academic Press/Elsevier Science, New York, pp 1–6
Schmülling T, Werner T, Riefler M, Krupková E, Bartrina y Manns I (2003) Structure and function of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase genes of maize, rice, Arabidopsis and other species. J Plant Res 116:241–252
Schnablová R, Synková H, Vicánková A, Burketová L, Eder J, Cvikrová M (2006) Transgenic ipt tobacco overproducing cytokinins overaccumulates phenolic compounds during in vitro growth. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:526–534
Spíchal L, Kryštof V, Paprskářová M, Lenobel R, Stýskala J, Binarová P, Cenklová V, De Veylder L, Inzé D, Kontopidis G, Fischer PM, Schmülling T, Strnad M (2007) Classical anticytokinins do not interact with cytokinin receptors but inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases. J Biol Chem 282:14356–14363
Stoynova-Bakalova E, Petrov P (2009) Modulating zucchini cotyledon plate meristem activity by interactions between the cycline-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine and cytokinins. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 97:263–269
Strnad M (1997) The aromatic cytokinins. Physiol Plant 101:674–688
Strnad M, Hanus J, Vanek T, Kamínek M, Ballantine JA, Fussell B, Hanke DE (1997) Meta-topolin, a highly active aromatic cytokinin from poplar leaves (Populus × canadensis Moench., cv. Robusta). Phytochemistry 45:213–218
Tao G-Q, Letham DS, Hocart CH, Summons RE (1991) Inhibitors of cytokinin metabolism III. The inhibition of cytokinin N-glucosylation in radish cotyledons. J Plant Growth Regul 10:179–185
Tréhin C, Planchais S, Glab N, Perennes C, Tregear J, Bergounioux C (1998) Cell cycle regulation by plant growth regulators: involvement of auxin and cytokinin in the re-entry of Petunia protoplasts into the cell cycle. Planta 206:215–224
Upfold SJ, Van Staden J (1990) Cytokinins in cut carnation flowers. VII. The effect of zeatin and dihydrozeatin derivatives on flower longevity. Plant Growth Regul 9:77–81
Valero-Aracama C, Kane M, Wilson S, Philman N (2010) Substitution of benzyladenine with meta-topolin during shoot multiplication increases acclimatization of difficult- and easy-to-acclimatize sea oats (Uniola paniculata L.) genotypes. Plant Growth Regul 60:43–49
Van Staden J, Crouch NR (1996) Benzyladenine and derivatives—their significance and interconversion in plants. Plant Growth Regul 19:153–175
Vuylsteke DR (1998) Shoot-tip culture for the propagation, conservation, and distribution of Musa germplasm. International Institute of Tropical Agriculture, Ibadan
Werbrouck SPO, Van der Jeugt B, Dewitte W, Prinsen E, Van Onckelen HA, Debergh PC (1995) The metabolism of benzyladenine in Spathiphyllum floribundum ‘Schott Petite’ in relation to acclimatisation problems. Plant Cell Rep 14:662–665
Werbrouck SPO, Strnad M, Van Onckelen HA, Debergh PC (1996) Meta-topolin, an alternative to benzyladenine in tissue culture? Physiol Plant 98:291–297
Werner T, Motyka V, Strnad M, Schmülling T (2001) Regulation of plant growth by cytokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10487–10492
Zaffari GR, Peres LEP, Kerbauy GB (1998) Endogenous levels of cytokinins, indoleacetic acid, abscisic acid, and pigments in variegated somaclones of micropropagated banana leaves. J Plant Growth Regul 17:59–61
Zalabák D, Pospíšilová H, Šmehilová M, Mrízová K, Frébort I, Galuszka P (2012) Genetic engineering of cytokinin metabolism: prospective way to improve agricultural traits of crop plants. Biotechnol Adv. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.1012.1003
Zatloukal M, Gemrotová M, Dolezal K, Havlícek L, Spíchal L, Strnad M (2008) Novel potent inhibitors of A. thaliana cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase. Bioorg Med Chem 16:9268–9275
Acknowledgments
The University of KwaZulu-Natal (Pietermaritzburg), South Africa and Centre of the Region Haná for Biotechnological and Agricultural Research, Palacký University (Olomouc), Czech Republic for providing financial support (Grant No. ED0007/01/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aremu, A.O., Bairu, M.W., Novák, O. et al. Physiological responses and endogenous cytokinin profiles of tissue-cultured ‘Williams’ bananas in relation to roscovitine and an inhibitor of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (INCYDE) treatments. Planta 236, 1775–1790 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1721-z