Abstract
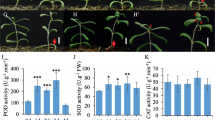
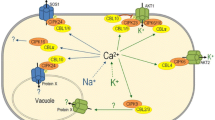
Different plant organelles have high internal stores of Ca2+ compared to the cytoplasm and could play independent roles in stress responses or signal transduction. We used a GFP fusion with the C-domain of calreticulin, which shows low-affinity, high capacity Ca2+ binding in the ER, as a calcium-binding peptide (CBP) to specifically increase stores in the ER and nucleus. Despite the presence of a signal sequence and KDEL retention sequence, our work and previous studies (Brandizzi et al. Plant Journal 34:269–281, 2003) demonstrated both ER and nuclear localization of GFP-CBP. Under normal conditions, GFP-CBP-expressing lines had ~25% more total Ca2+ and higher levels of chlorophyll and seed yield than wild type and GFP controls. CBP-expressing plants also had better survival under intermittent drought or high salt treatments and increased root growth. One member of the CIPK (calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase) gene family, CIPK6, was up-regulated in CBP-expressing plants, even under non-stress conditions. A null mutation in cipk6 abolished the increased stress tolerance of CBP-transgenic plants, as well as the CBP-mediated induction of two stress-associated genes, DREB1A and RD29A, under non-stress conditions. Although this suggested that it was the induction of CIPK6, rather than localized changes in Ca2+, that resulted in increased survival under adverse conditions, CIPK6 induction still required Ca2+. This work demonstrates that ER (or nuclear) Ca2+ can directly participate in signal transduction to alter gene expression. The discovery of a method for increasing Ca2+ levels without deleterious effects on plant growth may have practical applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ca2+ :
-
Calcium
- CBL:
-
Calcineurin B-like
- CIPK:
-
CBL interacting protein kinase
- CBP:
-
Calcium-binding peptide
- CRT:
-
Calreticulin
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- SOS:
-
Salt overly sensitive
References
Akesson A, Persson S, Love J, Boss WF, Widell S, Sommarin M (2005) Overexpression of the Ca2+-binding protein calreticulin in the endoplasmic reticulum improves growth of tobacco cell suspensions (Nicotiana tabacum) in high-Ca2+ medium. Physiol Plantarum 123:92–99
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Ausubel FM (1992) Short protocols in molecular biology: a compendium of methods from Current protocols in molecular biology, 2nd edn edn. Brooklyn, New York
Baksh S, Michalak M (1991) Expression of calreticulin in Escherichia coli and identification of its Ca2+ binding domains. J Biol Chem 266:21458–21465
Bastianutto C, Clementi E, Codazzi F, Podini P, Degiorgi F, Rizzuto R, Meldolesi J, Pozzan T (1995) Overexpression of calreticulin increases the Ca2+ capacity of rapidly exchanging Ca2+ stores and reveals aspects of their lumenal microenvironment and function. J Cell Biol 130:847–855
Batelli G, Verslues PE, Agius F, Qiu Q, Fujii H, Pan S, Schumaker KS, Grillo S, Zhu J (2007) SOS2 promotes salt tolerance in part by interacting with the vacuolar H+ -ATPase and upregulating its transport activity. Mol Cell Biol 27:7781–7790
Batistic O, Sorek N, Schueltke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2008) Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:1346–1362
Batistic O, Waadt R, Steinhorst L, Held K, Kudla J (2010) CBL-mediated targeting of CIPKs facilitates the decoding of calcium signals emanating from distinct cellular stores. Plant J 61:211–222
Bechtold N, Pelletier G (1998) In planta Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants by vacuum infiltration. Methods Mol Biol 82:259–266
Berdy SE, Kudla J, Gruissem W, Gillaspy GE (2001) Molecular characterization of At5PTase1, an inositol phosphatase capable of terminating inositol trisphosphate signaling. Plant Physiol 126:801–810
Brandizzi F, Hanton S, DaSilva LL, Boevink P, Evans D, Oparka K, Denecke J, Hawes C (2003) ER quality control can lead to retrograde transport from the ER lumen to the cytosol and the nucleoplasm in plants. Plant J 34:269–281
Catala R, Santos E, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Martinez-Zapater JM, Salinas J (2003) Mutations in the Ca2+/H+ transporter CAX1 increase CBF/DREB1 expression and the cold-acclimation response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:2940–2951
Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Zhu JK, Hirschi KD (2004) The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H(+)/Ca(2+) antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. J Biol Chem 279:2922–2926
Christensen A, Svensson K, Thelin L, Zhang W, Tintor N, Prins D, Funke N, Michalak M, Schulze-Lefert P, Saijo Y, Sommarin M, Widell S, Persson S (2010) Higher plant calreticulins have acquired specialized functions in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 5:1–18
Dodd AN, Kudla J, Sanders D (2010) The language of calcium signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:593–620
Groenendyk J, Lynch J, Michalak M (2004) Calreticulin, Ca2+, and calcineurin—signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cells 17:383–389
Harper JF, Breton G, Harmon A (2004) Decoding Ca2+ signals through plant protein kinases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:263–288
Haseloff J, Siemering KR, Prasher DC, Hodge S (1997) Removal of a cryptic intron and subcellular localization of green fluorescent protein are required to mark transgenic Arabidopsis plants brightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2122–2127
Hawes C, Saint-Jore C, Martin B, Zheng HQ (2001) ER confirmed as the location of mystery organelles in Arabidopsis plants expressing GFP! Trends Plant Sci 6:245–246
Hirschi KD (1999) Expression of Arabidopsis CAX1 in tobacco: altered calcium homeostasis and increased stress sensitivity. Plant Cell 11:2113–2122
Hirschi KD (2004) The calcium conundrum. Both versatile nutrient and specific signal. Plant Physiol 136:2438–2442
Hooker CW, Brindley PJ (1999) Cloning of a cDNA encoding SjIrV1, a Schistosoma japonicum calcium-binding protein similar to calnexin, and expression of the recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1429:331–341
Hruz T, Laule O, Szabo G, Wessendorp F, Bleuler S, Oertle L, Widmayer P, Gruissem W, Zimmermann P (2008) Genevestigator v3: a reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes. Adv Bioinform 2008:420747
Hwang I, Harper JF, Liang F, Sze H (2000) Calmodulin activation of an endoplasmic reticulum-located calcium pump involves an interaction with the N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. Plant Physiol 122:157–168
Iwano M, Entani T, Shiba H, Kakita M, Nagai T, Mizuno H, Miyawaki A, Shoji T, Kubo K, Isogai A, Takayama S (2009) Fine-tuning of the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration is essential for pollen tube growth. Plant Physiol 150:1322–1334
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1997) Calcium signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana responding to drought and salinity. Plant J 12:1067–1078
Lee SC, Lan WZ, Kim BG, Li L, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Lu G, Buchanan BB, Luan S (2007) A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15959–15964
Lemtiri-Chlieh F, MacRobbie EA, Webb AA, Manison NF, Brownlee C, Skepper JN, Chen J, Prestwich GD, Brearley CA (2003) Inositol hexakisphosphate mobilizes an endomembrane store of calcium in guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10091–10095
Li Z, Komatsu S (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of calreticulin, a calcium-binding protein involved in the regeneration of rice cultured suspension cells. Eur J Biochem 267:737–745
Liu J, Zhu JK (1998) A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280:1943–1945
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Liu J, Ishitani M, Halfter U, Kim CS, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana SOS2 gene encodes a protein kinase that is required for salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3730–3734
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Mahajan S, Sopory SK, Tuteja N (2006) Cloning and characterization of CBL-CIPK signalling components from a legume (Pisum sativum). FEBS J 273:907–925
Mery L, Mesaeli N, Michalak M, Opas M, Lew DP, Krause KH (1996) Overexpression of calreticulin increases intracellular Ca2+ storage and decreases store-operated Ca2+ influx. J Biol Chem 271:9332–9339
Michalak M, Groenendyk J, Szabo E, Gold LI, Opas M (2009) Calreticulin, a multi-process calcium-buffering chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J 417:651–666
Moran R (1982) Formulae for determination of chlorophyllous pigments extracted with n, n-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol 69:1376–1381
Navazio L, Mariani P, Sanders D (2001) Mobilization of Ca2+ by cyclic ADP-ribose from the endoplasmic reticulum of cauliflower florets. Plant Physiol 125:2129–2138
Navazio L, Miuzzo M, Royle L, Baldan B, Varotto S, Merry AH, Harvey DJ, Dwek RA, Rudd PM, Mariani P (2002) Monitoring endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi traffic of a plant calreticulin by protein glycosylation analysis. Biochemistry 41:14141–14149
Opas M, Szewczenko-Pawlikowski M, Jass GK, Mesaeli N, Michalak M (1996) Calreticulin modulates cell adhesiveness via regulation of vinculin expression. J Cell Biol 135:1913–1923
Pauly N, Knight MR, Thuleau P, van der Luit AH, Moreau M, Trewavas AJ, Ranjeva R, Mazars C (2000) Control of free calcium in plant cell nuclei. Nature 405:754–755
Persson S, Wyatt SE, Love J, Thompson WF, Robertson D, Boss WF (2001) The Ca2+ status of the endoplasmic reticulum is altered by induction of calreticulin expression in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 126:1092–1104
Persson S, Love J, Tsou PL, Robertson D, Thompson WF, Boss WF (2002) When a day makes a difference. Interpreting data from endoplasmic reticulum-targeted green fluorescent protein fusions in cells grown in suspension culture. Plant Physiol 128:341–344
Qudeimat E, Faltusz AM, Wheeler G, Lang D, Brownlee C, Reski R, Frank W (2008) A PIIB-type Ca2+-ATPase is essential for stress adaptation in Physcomitrella patens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19555–19560
Sanchez DH, Pieckenstain FL, Szymanski J, Erban A, Bromke M, Hannah MA, Kraemer U, Kopka J, Udvardi MK (2011) Comparative functional genomics of salt stress in related model and cultivated plants identifies and overcomes limitations to translational genomics. PLoS One 6:e17094
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S401–S417
Sharma A, Isogai M, Yamamoto T, Sakaguchi K, Hashimoto J, Komatsu S (2004) A novel interaction between calreticulin and ubiquitin-like nuclear protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:684–692
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu J (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:6896–6901
Stockinger EJ, Gilmour SJ, Thomashow MF (1997) Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1035–1040
Sze H, Liang F, Hwang I, Curran AC, Harper JF (2000) Diversity and regulation of plant Ca2+ pumps: insights from expression in yeast. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:433–462
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Trewavas A, Malhó R (1998) Ca2+ signalling in plant cells: the big network! Curr Opin Plant Bio 1:428–433
Tripathi V, Parasuraman B, Laxmi A, Chattopadhyay D (2009) CIPK6, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plants. Plant J 58:778–790
van Engelen FA, Molthoff JW, Conner AJ, Nap JP, Pereira A, Stiekema WJ (1995) pBINPLUS: an improved plant transformation vector based on pBIN19. Transgenic Res 4:288–290
Waadt R, Schmidt LK, Lohse M, Hashimoto K, Bock R, Kudla J (2008) Multicolor bimolecular fluorescence complementation reveals simultaneous formation of alternative CBL/CIPK complexes in planta. Plant J 56:505–516
Wang M, Gu D, Liu T, Wang Z, Guo X, Hou W, Bai Y, Chen X, Wang G (2007) Overexpression of a putative maize calcineurin B-like protein in Arabidopsis confers salt tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 65:733–746
White PJ, Broadley MR (2003) Calcium in plants. Ann Bot 92:487–511
White PJ, Broadley MR (2005) Biofortifying crops with essential mineral elements. Trends Plant Sci 10:586–593
Wu Z, Liang F, Hong B, Young JC, Sussman MR, Harper JF, Sze H (2002) An endoplasmic reticulum-bound Ca2+/Mn2+ pump, ECA1, supports plant growth and confers tolerance to Mn2+ stress. Plant Physiol 130:128–137
Wyatt SE, Tsou PL, Robertson D (2002) Expression of the high capacity calcium-binding domain of calreticulin increases bioavailable calcium stores in plants. Transgenic Res 11:1–10
Xiang Y, Huang Y, Xiong L (2007) Characterization of stress-responsive CIPK genes in rice for stress tolerance improvement. Plant Physiol 144:1416–1428
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell Online 6:251–264
Yang Q, Chen ZZ, Zhou XF, Yin HB, Li X, Xin XF, Hong XH, Zhu JK, Gong Z (2009) Overexpression of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2:22–31
Zeller G, Henz SR, Widmer CK, Sachsenberg T, Ratsch G, Weigel D, Laubinger S (2009) Stress-induced changes in the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome analyzed using whole-genome tiling arrays. Plant J 58:1068–1082
Zhao J, Shigaki T, Mei H, Guo YQ, Cheng NH, Hirschi KD (2009) Interaction between Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ exchangers CAX1 and CAX3. J Biol Chem 284:4605–4615
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Rebecca Boston for the BiP and CRT antibodies, Dr. Wayne Robarge for analytical ICP readings, and Dr. Bill Hoffman for help with measuring stomatal conductance. We also thank Dr. Wendy Boss for her constructive comments and critical reading of the manuscript. GFP fluorescence was imaged in the NCSU Cell and Molecular Imaging Facility, and we thank Shantha Sumanasinghe for help. This research was supported by NASA grant # NAGW-4984, the NC Agricultural Research Service and the supported from the Korean Education Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P.-L. Tsou and S. Y. Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsou, PL., Lee, S.Y., Allen, N.S. et al. An ER-targeted calcium-binding peptide confers salt and drought tolerance mediated by CIPK6 in Arabidopsis . Planta 235, 539–552 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1522-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1522-9