Abstract
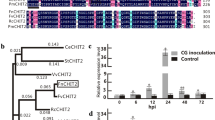
GDSL-type lipase is a hydrolytic enzyme whose amino acid sequence contains a pentapeptide motif (Gly-X-Ser-X-Gly) with active serine (Ser). Pepper GDSL-type lipase (CaGLIP1) gene was isolated and functionally characterized from pepper leaf tissues infected by Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria (Xcv). The CaGLIP1 protein was located in the vascular tissues of Arabidopsis root. The CaGLIP1 gene was preferentially expressed in pepper leaves during the compatible interaction with Xcv. Treatment with salicylic acid, ethylene and methyl jasmonate induced CaGLIP1 gene expression in pepper leaves. Sodium nitroprusside, methyl viologen, high salt, mannitol-mediated dehydration and wounding also induced early and transient CaGLIP1 expression in pepper leaf tissues. Virus-induced gene silencing of CaGLIP1 in pepper conferred enhanced resistance to Xcv, accompanied by the suppressed expression of basic PR1 (CaBPR1) and defensin (CaDEF1) genes. The CaGLIP1 lipase produced in Escherichia coli hydrolyzed the substrates of short and long chain nitrophenyl esters. The CaGLIP1-overexpressing Arabidopsis exhibited enhanced hydrolytic activity toward short and long chain nitrophenyl ester, as well as enhanced susceptibility to the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and the biotrophic oomycete Hyaloperonospora parasitica. SA-induced expression of AtPR1 and AtGST1, also was delayed in CaGLIP1-overexpressing plants by SA application. During seed germination and plant growth, the CaGLIP1 transgenic plants showed drought tolerance and differential expression of drought- and abscisic acid (ABA)-inducible genes AtRD29A, AtADH and AtRab18. ABA treatment differentially regulated seed germination and gene expression in wild-type and CaGLIP1 transgenic Arabidopsis. Overexpression of CaGLIP1 also regulated glucose- and oxidative stress signaling. Together, these results indicate that CaGLIP1 modulates disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- MV:
-
Methyl viologen
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SNP:
-
Sodium nitroprusside
- VIGS:
-
Virus-induced gene silencing
- Xcv :
-
Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Baulcombe DC (1999) Fast forward genetics based on virus-induced gene silencing. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:109–113
Benhamou N, Grenier J, Asselin A, Legrand M (1989) Immunoglod localization of β-1,3-glucanases in two plants infected by vascular wilt fungi. Plant Cell 1:1209–1221
Berto P, Comménil P, Belingheri L, Dehorter B (1999) Occurrence of a lipase in spores of Alternaria brassicicola with a crucial role in the infection of cauliflower leaves. FEMS Microbiol Lett 180:183–189
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brick DJ, Brumlik MJ, Buckley JT, Cao JX, Davies PC, Misra S, Tranbarger TJ, Upton C (1995) A new family of lipolytic enzymes with members in rice, Arabidopsis and maize. FEBS Lett 377:475–480
Camera SL, Geoffroy P, Samaha H, Ndiaye A, Rahim G, Legrand M, Thierry H (2005) A pathogen-inducible patatin-like lipid acyl hydrolase facilitates fungal and bacterial host colonization in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:810–825
Chandra S, Heinstein PF, Low PS (1996) Activation of phospholipase A by plant defense elicitors. Plant Physiol 110:979–986
Cheong YH, Kim KN, Pandy GK, Gupta R, Grant JJ, Luan S (2003) CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1833–1845
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Chung E, Seong E, Kim YC, Chung EJ, Oh SK, Lee S, Park JM, Joung YH, Choi D (2004) A method of high frequency virus-induced gene silencing in chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Bukang). Mol Cell 17:377–380
Chung ES, Oho SK, Park MJ, Choi D (2007) Expression and promoter analyses of pepper CaCDPK4 (Capsicum annuum calcium dependent protein kinase 4) during plant defense response to incompatible pathogen. Plant Pathol J 23: 76–89
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
de Torres Zabala M, Fernandez-Delmond I, Niittyla T, Sanchez P, Grant M (2002) Differential expression of genes encoding Arabidopsis phospholipases after challenge with virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas isolates. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 15:808–816
de Torres Zabala M, Truman W, Bennett M, Lafforgue G, Mansfield JW, Egea PR, Bögre L Grant M (2007) Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato hijacks the Arabidopsis abscisic acid signalling pathway to cause disease. EMBO J 26:1434–1443
Dekker BJW, Schuurmans JAMJ, Smeekens SCM (2004) Glucose delays seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 218:579–588
Do HM, Hong JK, Jung HW, Ham JH, Hwang BK (2003) Expression of peroxidase-like genes, H2O2 production and peroxidase activity during the hypersensitive response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria in Capsicum annuum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:196–205
Do HM, Lee SC, Jung HW, Sohn KH, Hwang BK (2004) Differential expression and in situ localization of a pepper defensin (CADEF1) gene in response to pathogen infection, abiotic elicitors and environmental stresses in Capsicum annuum. Plant Sci 166:1297–1305
Faustinella F, Smith LC, Semenkovich CF, Chan L (1991) Structural and functional roles of highly conserved serines in human lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem 266:9481–9485
Feys BJ, Moisan LJ, Newman MA, Parker JE (2001) Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4. EMBO J 20:5400–5411
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14:S15–S45
Fischer U, Men S, Grebe M (2004) Lipid function in plant cell polarity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:670–676
Gazzarrini S, McCourt P (2001) Genetic interactions between ABA, ethylene and sugar signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:387–391
Hong JK, Hwang BK (2002) Induction by pathogen, salt and drought of a basic class II chitinase mRNA and in situ localization in pepper (Capsicum annuum). Physiol Plant 114:549–558
Hong JK, Hwang BK (2005a) Functional characterization of PR-1 protein, β-1,3-glucanase and chitinase genes during defense response to biotic and abiotic stresses in Capsicum annuum. Plant Pathol J 21:195–206
Hong JK, Hwang BK (2005b) Induction of enhanced disease resistance and oxidative stress tolerance by overexpression of pepper basic PR-1 gene in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 124:267–277
Hong JK, Jung HW, Kim YJ, Hwang BK (2000a) Pepper gene encoding a basic class II chitinase is inducible by pathogen and ethephon. Plant Sci 159:39–49
Hong Y, Wang TW, Hudak KA, Schade F, Froese CD, Thompson JE (2000b) An ethylene-induced cDNA encoding a lipase expressed at the onset of senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8717–8722
Hong JK, Jung HW, Lee BK, Lee SC, Lee YK, Hwang BK (2004) An osmotin-like protein gene, CAOSM1, from pepper: differential expression and in situ localization in pepper tissues during pathogen infection and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 64:301–310
Hong JK, Lee SC, Hwang BK (2005) Activation of pepper basic PR-1 gene promoter during defense signaling to pathogen, abiotic and environmental stresses. Gene 356:169–180
Hong JK, Choi HW, Hwang IS, Hwang BK (2007) Role of a novel pathogen-induced pepper C3–H–C4 type RING-finger protein gene, CaRFP1, in disease susceptibility and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 63:571–588
Hu W, Wang Y, Bowers C, Ma H (2003) Isolation, sequence analysis, and expression studies of florally expressed cDNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 53:545–563
Jakab G, Manrique A, Zimmerli L, Métraux JP, Mauchi-Mani B (2003) Molecular characterization of a novel lipase-like pathogen-inducible gene family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132:2230–2239
Jung HW, Hwang BK (2000) Isolation, partial sequencing, and expression of pathogenesis-related cDNA genes from pepper leaves infected by Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:136–142
Katagiri T, Takahashi S, Shinozaki K (2001) Involvement of a novel Arabidopsis phospholipase D, AtPLDδ, in dehydration-inducible accumulation of phosphatidic acid in stress signaling. Plant J 26:595–605
Kim SH, Hong JK, Lee SC, Sohn KH, Jung HW, Hwang BK (2004) CAZFP1, Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger transcription factor gene functions as a pathogen-induced early-defense gene in Capsicum annuum. Plant Mol Biol 55:883–904
Kim YJ, Hwang BK (2000) Pepper gene encoding a basic pathogenesis-related 1 protein is pathogen and ethylene inducible. Physiol Plant 108:51–60
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of phycocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Kumar D, Klessig DF (2003) High-affinity salicylic acid-binding protein 2 is required for plant innate immunity and has salicylic acid-stimulated lipase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:16101–16106
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee YK, Hippe-Sanwald S, Lee SC, Hohenberg H, Hwang BK (2000) In situ localization of PR-1 mRNA and PR-1 protein in compatible and incompatible interactions of pepper stems with Phytophthora capsici. Protoplasma 211:64–75
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol 148:350–382
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
Lo M, Taylor C, Wang L, Nowack L, Wang TW, Thompson J (2004) Characterization of an ultraviolet B-induced lipase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 135:947–958
Maldonado AM, Doerner P, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Cameron RK (2002) A putative lipid transfer protein involved in systemic resistance signalling in Arabidopsis. Nature 419:399–403
Matsui K, Fukutomi S, Ishii M, Kajiwara T (2004) A tomato lipase homologous to DAD1 (LeLID1) is induced in post-germinative growing stage and encodes a triacylglyceral lipase. FEBS Lett 569:195–200
Melotto M, Underwood W, Koczan J, Nomura K, He SY (2006) Plant stomata function in innate immunity against bacterial invasion. Cell 126:969–980
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Narusaka Y, Narusaka M, Seki M, Fujita M, Ishida J, Nakashima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Kamiya A, Park P, Kobayashi M, Shinozaki K (2003) Expression profiles of Arabidopsis Phospholipase A IIA gene in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 44:1247–1252
Narvaez-Vasquez J, Ryan CA (2004) The cellular localization of prosystemin: a functional role for phloem parenchyma in systemic wound signaling. Planta 218:360–369
Nimchuk Z, Marois E, Kjemtrup S, Leister RT, Katagiri F, Dangle JL (2000) Eukaryotic fatty acylation drives plasma membrane targeting and enhances function of several type III effector proteins from Pseudomonas syringae. Cell 101:353–363
O’Donnell PJ, Calvert C, Atzorn R, Wasternack C, Leyser HMO, Bowles DJ (1996) Ethylene as a signal mediating the wound response of tomato plants. Science 274:1914–1917
Oh BJ, Jeon WB, Kim KS, Lee HS, Cheong SJ, Cho SM, Kim SM, Pyo BS, Kim YS (2004) Differential induction of PepTLP expression via complex regulatory system against fungal infection, wound, and jasmonic acid treatment during pre- and post-ripening of nonclimateric pepper fruit. Plant Pathol J 20:258–263
Oh IS, Park AR, Bae MS, Kwon SJ, Kim SY, Lee JE, Kang NY, Lee S, Cheong H, Park OK (2005) Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Cell 17:2832–2847
Oh SK, Cheong JJ, Hwang I, Choi D (1999) Similarity of tobacco mosaic virus-induced hypersensitive cell death and copper-induced abiotic cell death in tobacco. Plant Pathol J 15:8–13
Ollis DL, Cheah E, Cygler M, Dijkstra B, Frolow F, Franken SM, Harel M, Remington SJ, Silman I, Schrag J (1992) The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng 5:197–211
Pringle D, Dickstein R (2004) Purification of ENOD8 proteins from Medicago sativa root nodules and their characterization as esterases. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:73–79
Reignault P, Frost LN, Richardson H, Daniels MJ, Jones JD, Parker JE (1996) Four Arabidopsis RPP loci controlling resistance to the Noco2 isolate of Peronospora parasitica map to regions known to contain other RPP recognition specificities. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 9:464–473
Reumann S, Ma C, Lemke S, Babujee L (2004) AraPerox. A database of putative Arabidopsis proteins from plant peroxisomes. Plant Physiol 136:2587–2608
Ruiz C, Falcocchio S, Xoxi E, Pastor FIJ, Diaz P, Saso L (2004) Activation and inhibition of Candida rugosa and Bacillus-related lipases by saturated fatty acids, evaluated by a new colorimetric microassay. Biochim Biophys Acta 1672:184–191
Rustérucci C, Aviv DH, Holt III BF, Dangle JL, Parker JE (2001) The disease resistance signaling components EDS1 and PAD4 are essential regulators of the cell death pathway controlled by LSD1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2211–2224
Sang Y, Cui D, Wang D (2001) Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid-mediated generation of superoxide in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:1449–1458
Schilmiller AL, Howe GA (2005) Systemic signaling in the wound response. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:369–377
Tameling WIL, Elzinga SDJ, Darmin PS, Vossen JH, Takken FLW, Haring MA, Cornelissen BJC (2002) The tomato R gene products I-2 and Mi-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 14:2929–2939
Titarenko E, Rojo E, León J, Sánchez-Serrano JJ (1997) Jasmonic acid-dependent and -independent signaling pathways control wound-induced gene activation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 115:817–826
To JPC, Reiterm WD, Gibson SI (2002) Mobilization of seed storage lipid by Arabidopsis seedlings is retarded in the presence of exogenous sugars. BMC Plant Biol 2:4
Tsuchiya T, Ohta H, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Shimada H, Masuda T, Takamiya K (1999) Cloning of chlorophyllase, the key enzyme in chlorophyll degradation: Finding of a lipase motif and the induction by methyl jasmonate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 26:15362–15367
Upton C, Buckley JT (1995) A new family of lipolytic enzymes? Trends Biochem Sci 20:178–179
Voigt CA, Schäfer W, Salomon S (2005) A secreted lipase from Fusarium graminearum is a virulence factor required for infection of cereals. Plant J 42:364–375
Wang C, Zien CA, Afitlhile M, Welti R, Hildebrand DF, Wang X (2000) Involvement of phospholipase D in wounded-induced accumulation of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:2237–2246
Wang X (2002) Phospholipase D in hormonal and stress signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:408–414
Welti R, Li W, Li M, Sang Y, Biesiada H, Zhou HE, Rajashekar CB, Williams TD, Wang X (2002) Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses. J Biol Chem 277:31994–32002
Yaeno T, Matsuda O, Iba K (2004) Role of chloroplast trienoic fatty acids in plants disease defense responses. Plant J 40:931–941
Young SA, Guo A, Guikema JA, White FF, Leach JE (1995) Rice cationic peroxidase accumulates in xylem vessels during incompatible interactions with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Physiol 107:1333–1341
Zhao J, Wang X (2004) Arabidopsis phospholipase Dα1 interacts with the heterotrimeric G-protein α-subunit through a motif analogous to the DRY motif in G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 279:1794–1800
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant (CG1133) from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the twenty-first Century, the Frontier Research Program funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Republic of Korea, a grant from the Center for Plant Molecular Genetics and Breeding Research, Seoul National University, Korea and a grant (20070401034028) from the BioGreen 21 Program, Rural Development Administration, Korea. We thank Dr. S. P. Dinesh-Kumar for the pTRV1 and pTRV2 vectors, and Dr. Kay Gillian for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported here has been deposited in the GenBank database under the accession number AY775336.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J.K., Choi, H.W., Hwang, I.S. et al. Function of a novel GDSL-type pepper lipase gene, CaGLIP1, in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 227, 539–558 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0637-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0637-5