Abstract
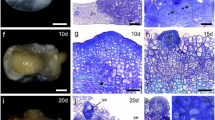
Ribonuclease LE (RNaseLE) from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. Lukullus) belongs to the widespread RNase T2 family of ribonucleases. With the exception of S-RNases of the solanaceous self-incompatibility system the functions of other members of the RNase T2 family are only barely understood. Using a 2.6-kbp putative promoter sequence of RNaseLE in front of the uidA reporter gene, expression of β-glucuronidase in developing phloem tissue and, especially, in the meristematic and elongation zones at root tips was detected. The tissue-specific expression accords with the range of cis-acting elements detected in the RNaseLE promoter. RNaseLE mRNA was localized in developing phloem cells but not in mature phloem tissue, suggesting association of RNaseLE expression with phloem development. Histochemical staining of β-glucuronidase activity as well as detailed inspection of RNaseLE at mRNA, protein and enzyme activity levels revealed that the wound-induced expression of RNaseLE was also restricted to vascular tissue. RNaseLE transcript accumulation detected by in situ hybridization occurred preferentially in phloem and cambial cells of stem sections upon wounding. The data provide evidence for a role of RNaseLE in a tissue-specific wound response and in wound healing of tomato.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase (uidA gene)
- RNaseLE:
-
Tomato ribonuclease LE
- Pi:
-
Inorganic phosphate
References
Abel S, Köck M (2001) Secretory acid ribonucleases from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Methods Enzymol 341:351–368
Abel S, Krauss G-J, Glund K (1989) Ribonuclease in tomato vacuoles: high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of ribonucleolytic activities and base specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta 998:145–150
Bariola PA, Howard CJ, Taylor CB, Verburg MT, Jaglan VD, Green PJ (1994) The Arabidopsis ribonuclease gene RNS1 is tightly controlled in response to phosphate limitation. Plant J 6:673–685
Bevan M, Shufflebottom D, Edwards K, Jefferson R, Schuch W (1989) Tissue- and cell-specific activity of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase promoter in transgenic plants. EMBO J 8:1899–1906
Bosse D, Köck M (1998) Influence of phosphate starvation on phosphohydrolases during development of tomato seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 21:325–332
Dodds PN, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (1996) Molecular characterisation of an S-like RNase of Nicotiana alata that is induced by phosphate starvation. Plant Mol Biol 31:227–238
Eschrich W, Heyser W (1975) Biochemistry of phloem constituents. In: Zimmermann MH, Milburn JA (eds) Transport in plants. I. Phloem transport. Encyclopedia of plant physiology, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–136
Hatton D, Sablowski R, Yung M-H, Smith C, Schuch W, Bevan M (1995) Two classes of cis sequences contribute to tissue-specific expression of a PAL2 promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 7:859–876
Hause B, Hause G, Kutter C, Miersch O, Wasternack C (2003) Enzymes of jasmonate biosynthesis occur in tomato sieve elements. Plant Cell Physiol 44:643–648
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Höfgen R, Willmitzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9877
Ide H, Kimura M, Arai M, Funatsu G (1991) The complete amino acid sequence of ribonuclease from the seeds of bitter gourd (Momordica charantia). FEBS Lett 284:161–164
Irie M (1999) Structure–function relationship of acid ribonucleases: lysosomal, vacuolar, and periplasmic enzymes. Pharmacol Ther 81:77–89
Ito H, Hiraga S, Tsugawa H, Matsui H, Honma M, Otsuki Y, Murakami T, Ohashi Y (2000) Xylem-specific expression of wound-inducible rice peroxidase genes in transgenic plant. Plant Sci 155:85–100
Jacinto T, McGurl B, Francheschi V, Delano-Freier J, Ryan CA (1997) Tomato prosystemin promoter confers wound-inducible, vascular bundle-specific expression of the β-glucuronidase gene in transgenic tomato plants. Planta 203:406–412
Jost W, Bak H, Glund K, Terpstra P, Beintema JJ (1991) Amino acid sequence of an extracellular, phosphate-starvation-induced ribonuclease from cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Eur J Biochem 198:1–6
Kaletta K, Kunze I, Kunze G, Köck M (1998) The peptide HDEF as a new retention signal is necessary and sufficient to direct proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett 434:377–381
Kariu T, Sano K, Shimokawa H, Itoh R, Yamasaki N, Kimura M (1998) Isolation and characterization of a wound-inducible ribonuclease from Nicotiana glutinosa leaves. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1144–1151
Kawata Y, Sakiyama F, Tamaoki H (1988) Amino-acid sequence of ribonuclease T2 from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem 176:683–697
Keller B, Baumgärtner C (1991) Vascular-specific expression of the bean Grp-1.8 gene is negatively regulated. Plant Cell 3:1051–1061
Köck M, Löffler A, Abel S, Glund K (1995) Structural and regulatory properties of a family of starvation induced ribonucleases from tomato. Plant Mol Biol 27:477–485
Köck M, Theierl K, Stenzel I, Glund K (1998) Extracellular administration of phosphate sequestering metabolites induces ribonucleases in cultured tomato cells. Planta 204:404–407
LeBrasseur ND, MacIntosh GC, Pérez-Amador MA, Saitoh M, Green PJ (2002) Local and systemic wound-induction of RNase and nuclease activities in Arabidopsis: RNS1 as a marker for a JA-independent systemic signaling pathway. Plant J 29:393–403
Lehmann K, Hause B, Altmann D, Köck M (2001) Tomato ribonuclease LX with the functional ER retention motif HDEF is expressed during physiological cell death processes including xylem differentiation, germination and senescence. Plant Physiol 127:436–449
Lers A, Khalchitski A, Lomaniec E, Burd S, Green PJ (1998) Senescence-induced RNases in tomato. Plant Mol Biol 36:439–449
Leon J, Rojo E, Sánchez-Serrano JJ (2001) Wound signalling in plants. J Exp Bot 52:1-9
Ling H-Q, Krieseleit D, Ganal MW (1998) Effect of ticarcillin/potassium clavulanate on callus growth and shoot regeneration in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Plant Cell Rep 17:843–847
Löffler A, Abel S, Jost W, Beintema JJ, Glund K (1992) Phosphate-regulated induction of intracellular ribonucleases in cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Plant Physiol 98:1472–1478
Löffler A, Glund K, Irie M (1993) Amino acid sequence of an intracellular, phosphate-starvation-induced ribonuclease from cultured tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) cells. Eur J Biochem 214:627–633
Lowry OH, Rosebrough AL, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama F, Clarke AE (1989) Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342:955–957
Nishitani C, Demura T, Fukuda H (2001) Primary phloem-specific expression of a Zinnia elegans homeobox gene. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1210–1218
Nishitani C, Demura T, Fukuda H (2002) Analysis of early processes in wound-induced vascular regeneration using TED3 and ZeHB3 as molecular markers. Plant Cell Physiol 43:79–90
Nürnberger T, Abel S, Jost W, Glund K (1990) Induction of an extracellular ribonuclease in cultured tomato cells upon phosphate starvation. Plant Physiol 92:970–976
Ohgi K, Shiratori Y, Nakajima A, Iwama M, Kobayashi H, Inokuchi N, Koyama T, Köck M, Löffler A, Glund K, Irie M (1997) The base specificities of tomato ribonuclease (RNase LE) and its Asp44 mutant enzyme expressed from yeast cells. Biosci Biotech Biochem 61:432–438
Oparka KJ, Turgeon R (1999) Sieve elements and companion cells—traffic control centers of the phloem. Plant Cell 11:739–750
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T (1995) MatInd and MatInspector—new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4878–4884
Rogers SW, Rogers JC (1999) Cloning and characterization of a gibberellin-induced RNase expressed in barley aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 119:1457–1464
Ryan CA (2000) The systemin signaling pathway: differential activation of plant defensive genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1477:112–121
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sasaki K, Hiraga S, Ito H, Seo S, Matsui H, Ohashi Y (2002) A wound-inducible tobacco peroxidase gene expresses preferentially in the vascular system. Plant Cell Physiol 43:108–117
Schulz A (1990) Wound-sieve elements. In: Behnke H-D, Sjölund RD (eds) Sieve elements. Comparative structure, induction and development. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 199–217
Stenzel I, Hause B, Maucher H, Pitzschke A, Miersch O, Ziegler J, Ryan CA, Wasternack C (2003) Allene oxide cyclase dependence of the wound response and vascular bundle specific generation of jasmonate—amplification in wound-signalling. Plant J 33:577–589
Taylor CB, Bariola PA, DelCardayré SB, Raines RT, Green PJ (1993) RNS2: a senescence-associated RNase of Arabidopsis that diverged from the S-RNases before speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5118–5122
Xu Z-R, Qi W-Q, Ouyang X-Z, Yeung E, Chye M-L (2001) A proteinase inhibitor II of Solanum americanum is expressed in phloem. Plant Mol Biol 47:727–738
Ye Z-H, Droste DL (1996) Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding xylogenesis-associated and wounding-induced ribonucleases in Zinnia elegans. Plant Mol Biol 30:697–709
Yin Y, Chen L, Beachy R (1997) Promoter elements required for phloem-specific gene expression from the RTBV promoter in rice. Plant J 12:1179–1188
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. M. Ganal (IPK Gatersleben) for providing the genomic tomato library and cultivating primary tomato transformants, Dr. S. Hertel and K. Lehmann (Biocenter) for regeneration and selection of PromLE2::uidA tomato lines, K. Eichhorst and K. Klar for technical assistance, and Prof. C. Wasternack (IPB Halle) for critical reading of the manuscript. The support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to M.K. (SFB 363 B9/B16) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köck, M., Groß, N., Stenzel, I. et al. Phloem-specific expression of the wound-inducible ribonuclease LE from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. Lukullus). Planta 219, 233–242 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1227-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1227-4