Abstract
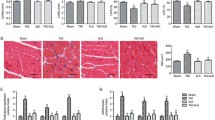
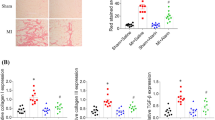
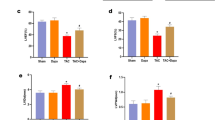
The intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (KCa3.1) channel plays a vital role in myocardial fibrosis induced by angiotensin (Ang) II. However, as the antagonists of Ang II, the effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-angiotensin-(1–7)-Mas axis on KCa3.1 channel during myocardial fibrosis remains unknown. This study was designed to explore the function of KCa3.1 channel in the cardioprotective role of ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas. Wild-type (WT) mice, hACE2 transgenic mice (Tg), and ACE2 deficiency mice (ACE2−/−) were administrated with Ang II by osmotic mini-pumps. As the activator of ACE2, diminazene aceturate (DIZE) inhibited increase of blood pressure, collagen deposition, and KCa3.1 protein expression in myocardium of WT mice induced by Ang II. In Tg and ACE2−/− mice, besides the elevation of blood pressure, Ang II induced transformation of cardiac fibroblast into myofibroblast and resulted in augmentation of hydroxyproline concentration and collagen deposition, as well as KCa3.1 protein expression, but the changes in ACE2−/− mice were more obvious than those in Tg mice. Mas antagonist A779 reduced blood pressure, myocardium fibrosis, and myocardium KCa3.1 protein expression by Ang II in Tg mice, but activation of KCa3.1 with SKA-31 in Tg mice promoted the pro-fibrogenic effects of Ang II. Respectively, in ACE2−/− mice, TRAM-34, the KCa3.1 blocker, and Ang-(1–7) inhibited increase of blood pressure, collagen deposition, and KCa3.1 protein expression by Ang II. Moreover, DIZE and Ang-(1–7) depressed p-ERK1/2/t-ERK increases by Ang II in WT mice, and after blockage of ERK1/2 pathway with PD98059, the KCa3.1 protein expression was reduced in WT mice. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas protects the myocardium from hypertension-induced injury, which is related to its inhibiting effect on KCa3.1 channels through ERK1/2 pathway. Our results reveal that KCa3.1 channel is likely to be a critical target on the ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas axis for its protective role in myocardial fibrosis and changes of KCa3.1 induced by homeostasis of ACE-Ang II-AT1 axis and ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas axis may be a new therapeutic target in myocardial fibrosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alghamri MS, Weir NM, Anstadt MP, Elased KM, Gurley SB, Morris M (2013) Enhanced angiotensin II-induced cardiac and aortic remodeling in ACE2 deficiency mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 18:138–151
Cao X, Yang F, Shi T, Yuan M, Xin Z, Xie R, Li S, Li H, Yang JK (2016) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis activates Akt signaling to ameliorate hepatic steatosis. Sci Rep 6:21592
Chaston DJ, Haddock RE, Howitt L, Morton SK, Brown RD, Matthaei KI, Hill CE (2015) Perturbation of chemical coupling by an endothelial Cx40 mutant attenuates endothelium-dependent vasodilation by KCa channels and elevates blood pressure in mice. Pflugers Arch 467:1997–2009
Fu RG, Zhang T, Wang L, Du Y, Jia LN, Hou JJ, Yao GL, Liu XD, Zhang L, Chen L, Gui BS, Xue RL (2014) Inhibition of the K(+) channel KCa3.1 reduces TGF-β1-induced premature senescence, myofibroblast phenotype transition and proliferation of mesangial cells. PLoS One 9:e87410
Gava E, de Castro CH, Ferreira AJ, Colleta H, Melo MB, Alenina N, Bader M, Oliveira LA, Santos RA, Kitten GT (2012) Angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas is an essential modulator of extracellular matrix protein expression in the heart. Regul Pept 175:30–42
Guimarães GG, Santos SH, Oliveira ML, Pimenta-Velloso EP, Motta DF, Martins AS, Alenina N, Bader M, Santos RA, Campagnole-Santos MJ (2012) Exercise induces renin-angiotensin system unbalance and high collagen expression in the heart of Mas-deficient mice. Peptides 38:54–61
Huang C, Pollock CA, Chen XM (2015) KCa3.1: a new player in progressive kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 24:61–66
Huang C, Shen S, Ma Q, Gill A, Pollock CA, Chen XM (2014) KCa3.1 mediates activation of fibroblasts in diabetic renal interstitial fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:313–324
Huang C, Shen S, Ma Q, Chen J, Gill A, Pollock CA, Chen XM (2013) Blockade of KCa3.1 ameliorates renal fibrosis through the TGF-β1/Smad pathway in diabetic mice. Diabetes 62:2923–2934
Iwanami J, Mogi M, Tsukuda K, Wang XL, Nakaoka H, Ohshima K, Chisaka T, Bai HY, Kanno H, Min LJ, Horiuchi M (2014) Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis in the hypotensive effect of azilsartan. Hypertens Res 37:616–620
Ji Y, Gao F, Sun B, Hao J, Liu Z (2015) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibits apoptosis of pulmonary endothelial cells during acute lung injury through suppressing SMAD2 phosphorylation. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:2203–2212
Ju CH, Wang XP, Gao CY, Zhang SX, Ma XH, Liu C (2015) Blockade of KCa3.1 attenuates left ventricular remodeling after experimental myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1305–1315
Klimas J, Olvedy M, Ochodnicka-Mackovicova K, Kruzliak P, Cacanyiova S, Kristek F, Krenek P, Ochodnicky P (2015) Perinatally administered losartan augments renal ACE2 expression but not cardiac or renal Mas receptor in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cell Mol Med 19:1965–1974
Lu J, Zhang Y, Shi J (2008) Effects of intracerebroventricular infusion of angiotensin-(1-7) on bradykinin formation and the kinin receptor expression after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Res 1219:127–135
McKinney CA, Fattah C, Loughrey CM, Milligan G, Nicklin SA (2014) Angiotensin-(1-7) and angiotensin-(1-9): function in cardiac and vascular remodeling. Clin Sci(Lond) 126:815–827
Mendoza-Torres E, Oyarzún A, Mondaca-Ruff D, Azocar A, Castro PF, Jalil JE, Chiong M, Lavandero S, Ocaranza MP (2015) ACE2 and vasoactive peptides: novel players in cardiovascular/renal remodeling and hypertension. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 9:217–237
Mishra RC, Belke D, Wulff H, Braun AP (2013) SKA-31, a novel activator of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels, increases coronary flow in male and female rat hearts. Cardiovasc Res 97:339–348
Mishra RC, Mitchell JR, Gibbons-Kroeker C, Wulff H, Belenkie I, Tyberg JV, Braun AP (2016) A pharmacologic activator of endothelial KCa channels increases systemic conductance and reduces arterial pressure in an anesthetized pig model. Vasc Pharmacol 79:24–31
Mishra RC, Wulff H, Hill MA, Braun AP (2015) Inhibition of myogenic tone in rat cremaster and cerebral arteries by SKA-31, an activator of endothelial KCa2.3 and KCa3.1 channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 66:118–127
Mishra RC, Wulff H, Cole WC, Braun AP (2014) A pharmacologic activator of endothelial KCa channels enhances coronary flow in the hearts of type 2 diabetic rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 72:364–373
Moon JY (2013) Recent update of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Electrolyte Blood Press 11:41–45
Radtke J, Schmidt K, Wulff H, Köhler R, de Wit C (2013) Activation of KCa3.1 by SKA-31 induces arteriolar dilatation and lowers blood pressure in normo- and hypertensive connexin40-deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol 170:293–303
Su XL, Wang Y, Zhang W, Li GR, Deng XL (2011) Insulin-mediated upregulation of KCa3.1 channels promotes cell migration and proliferation in rat vascular smooth muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 51:51–57
Tikellis C, Bernardi S, Burns WC (2011) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a key modulator of the renin-angiotensin system in cardiovascular and renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20:62–68
Uekawa K, Hasegawa Y, Senju S, Nakagata N, Ma M, Nakagawa T, Koibuchi N, Kim-Mitsuyama S (2016) Intracerebroventricular infusion of angiotensin-(1–7) ameliorates cognitive impairment and memory dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis
Wang LP, Wang Y, Zhao LM, Li GR, Deng XL (2013) Angiotensin II upregulates KCa3.1 channels and stimulates cell proliferation in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol 85:1486–1494
Xu P, Sriramula S, Lazartigues E (2011) ACE2/ANG-(1–7)/Mas pathway in the brain: the axis of good. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R804–R817
Yamaleyeva LM, Pulgar VM, Lindsey SH, Yamane L, Varagic J, McGee C, daSilva M, Lopes Bonfa P, Gurley SB, Brosnihan KB (2015) Uterine artery dysfunction in pregnant ACE2 deficiency mice is associated with placental hypoxia and reduced umbilical blood flow velocity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 309:E84–E94
Yang XH, Deng W, Tong Z, Liu YX, Zhang LF, Zhu H, Gao H, Huang L, Liu YL, Ma CM, Xu YF, Ding MX, Deng HK, Qin C (2007) Mice transgenic for human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 provide an animal model for SARS coronavirus. Comp Med 57(5):450–459
Yu ZH, Xu JR, Wang YX, Xu GN, Xu ZP, Yang K, Wu DZ, Cui YY, Chen HZ (2013) Targeted inhibition of KCa3.1 channel attenuates airway inflammation and remodeling in allergic asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 48:685–693
Zhang Y, Liu J, Luo JY, Tian XY, Cheang WS, Xu J, Lau CW, Wang L, Wong WT, Wong CM, Lan HY, Yao X, Raizada MK, Huang Y (2015) Upregulation of angiotensin (1-7)-mediated signaling preserves endothelial function through reducing oxidative stress in diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:880–892
Zhang Y, Lu J, Shi J, Lin X, Dong J, Zhang S, Liu Y, Tong Q (2008) Central administration of angiotensin-(1-7) stimulates nitric oxide release and upregulates the endothelial nitricoxide synthase expression following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neuropeptides 42:593–600
Zhang Y, Wang SJ, Han ZH, Li YQ, Xue JH, Gao DF, Wu XS, Wang CX (2014) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a role in enhancement of eNOS activity by recombinant human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:8112–8117
Zhao LM, Su XL, Wang Y, Li GR, Deng XL (2013) KCa3.1 channels mediate the increase of cell migration and proliferation by advanced glycation endproducts in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Lab Investig 93:159–167
Zhao LM, Zhang W, Wang LP, Li GR, Deng XL (2014) Advanced glycation end products promote proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts by upregulation of KCa3.1 channels. Pflugers Arch 464:613–621
Zhao LM, Wang LP, Wang HF, Ma XZ, Zhou DX, Deng XL (2015) The role of KCa3.1 channels in cardiac fibrosis induced by pressure overload in rats. Pfluger Arch 467:2275–2285
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (grant no. H2015209153) and Colleges and Universities Science and Technology Research Project of Hebei Province (grant no. QN2016003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
Experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of North China University of Science and Technology and conformed to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health, USA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LP., Fan, SJ., Li, SM. et al. Protective role of ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas in myocardial fibrosis by downregulating KCa3.1 channel via ERK1/2 pathway. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 468, 2041–2051 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1875-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1875-9