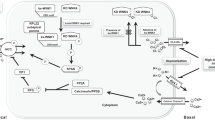
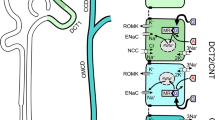
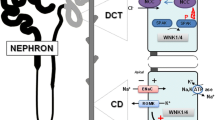
Abstract
Mammalian with-no-lysine [K] (WNK) kinases are a family of four serine-threonine protein kinases, WNK1-4. Mutations of WNK1 and WNK4 in humans cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHA2), an autosomal-dominant disease characterized by hypertension and hyperkalemia. Increased Na+ reabsorption through Na+–Cl− cotransporter (NCC) in the distal convoluted tubule plays an important role in the pathogenesis of hypertension in patients with PHA2. However, how WNK1 and WNK4 regulate NCC and how mutations of WNKs cause activation of NCC have been controversial. Here, we review current state of literature supporting a compelling model that WNK1 and WNK4 both contribute to stimulation of NCC. The precise combined effects of WNK1 and WNK4 on NCC remain unclear but likely are positive rather than antagonistic. The recent discovery that WNK kinases may function as an intracellular chloride sensor adds a new dimension to the physiological role of WNK kinases. Intracellular chloride-dependent regulation of WNK’s may underlie the mechanism of regulation of NCC by extracellular K+. Definite answer yet will require future investigation by tubular perfusion in mice with altered WNK kinase expression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselmo AN, Earnest S, Chen W, Juang YC, Kim SC, Zhao Y, Cobb MH (2006) WNK1 and OSR1 regulate the Na+, K+, 2Cl− cotransporter in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(29):10883–10888
Bazua-Valenti S, Chavez-Canales M, Rojas-Vega L, Gonzalez-Rodriguez X, Vazquez N, Rodriguez-Gama A, Argaiz ER, Melo Z, Plata C, Ellison DH, Garcia-Valdes J, Hadchouel J, and Gamba G (2014) The effect of WNK4 on the Na+–Cl− cotransporter is modulated by intracellular chloride. J Am Soc Nephrol 26
Boyden LM et al (2012) Mutations in kelch-like 3 and cullin 3 cause hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities. Nature 482(7383):98–102
Cai H, Cebotaru V, Wang YH, Zhang XM, Cebotaru L, Guggino SE, Guggino WB (2006) WNK4 kinase regulates surface expression of the human sodium chloride cotransporter in mammalian cells. Kidney Int 69:2162–2170
Castaneda-Bueno M, Cervantes-Perez LG, Vazquez N, Uribe N, Kantesaria S, Morla L, Bobadilla NA, Doucet A, Alessi DR, Gamba G (2012) Activation of the renal Na+:Cl− cotransporter by angiotensin II is a WNK4-dependent process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7929–7934
Chávez-Canales M, Zhang C, Soukaseum C, Moreno E, Pacheco-Alvarez D, Vidal-Petiot E, Castañeda-Bueno M, Vázquez N, Rojas-Vega L, Meermeier NP, Rogers S, Jeunemaitre X, Yang CL, Ellison DH, Gamba G, Hadchouel J et al (2014) WNK-SPAK-NCC cascade revisited: WNK1 stimulates the activity of the Na-Cl cotransporter via SPAK, an effect antagonized by WNK4. Hypertension 64:1047–1053
Cheng CJ, Yoon J, Baum M, Huang CL (2015) STE20/SPS1-related proline/alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) is critical for sodium reabsorption in isolated, perfused thick ascending limb. Am Physiol Renal Physiol 308(5):F437–F443
Chu PY, Cheng CJ, Wu YC, Fang YW, Chau T, Uchida S, Sasaki S, Yang SS, Lin SH (2013) SPAK deficiency corrects pseudohypoaldosteronism II caused by WNK4 mutation. PLoS One 8(9), e72969. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072969
Delaloy C, Lu J, Houot AM, Disse-Nicodeme S, Gasc JM, Corvol P, Jeunemaitre X (2003) Multiple promoters in the WNK1 gene: one controls expression of a kidney-specific kinase-defective isoform. Mol Cell Biol 23:9208–9221
Genschik P, Sumara I, Lechner E (2013) The emerging family of cullin3-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL3s): cellular functions and disease implications. EMBO J 32:2307–2320
Hadchouel J, Delaloy C, Faure S, Achard JM, Jeunemaitre X (2006) Familial hyperkalemic hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:208–217
Hannemann A, Flatman PW (2011) Phosphorylation and transport in the Na-K-2Cl cotransporters, NKCC1 and NKCC2A, compared in HEK-293 cells. PLos One 6:e17992
Ji AX, Prive GG (2013) Crystal structure of KLHL3 in complex with cullin3. PLoS One 8:e60445
Kim GH, Masilamani S, Turner R, Mitchell C, Wade JB, Knepper MA (1998) The thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter is an aldosterone-induced protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:14552–14557
Lalioti MD, Zhang J, Volkman HM, Kahle KT, Hoffmann KE, Toka HR, Nelson-Williams C, Ellison DH, Flavell R, Booth CJ, Lu Y, Geller DS, Lifton RP (2006) Wnk4 controls blood pressure and potassium homeostasis via regulation of mass and activity of the distal convoluted tubule. Nat Genet 38:1124–1132
Louis-Dit-Picard H et al (2012) KLHL3 mutations cause familial hyperkalemic hypertension by impairing ion transport in the distal nephron. Nat Genet 44(4):456–460
Lytle C, Forbush B III (1996) Regulatory phosphorylation of the secretory Na-K-Cl cotransporter: modulation by cytoplasmic Cl. Am J Physiol 270:C437–C448
McCormick JA, Ellison DH (2011) The WNKs: atypical protein kinases with pleiotropic actions. Physiol Rev 91:177–219
McCormick JA, Mutig K, Nelson JH, Saritas T, Hoorn EJ, Yang CL, Rogers S, Curry J, Delpire E, Bachmann S, Ellison DH (2011) A SPAK isoform switch modulates renal salt transport and blood pressure. Cell Metab 14(3):352–364
Moriguchi T, Urushiyama S, Hisamoto N, Iemura S, Uchida S, Natsume T, Matsumoto K, Shibuya H (2005) WNK1 regulates phosphorylation of cation-chloride-coupled cotransporters via the STE20-related kinases, SPAK and OSR1. J Biol Chem 280:42685–42693
Oi K, Sohara E, Rai T, Misawa M, Chiga M, Alessi D, Sasaki S, Uchida S (2012) A minor role of WNK3 in regulating phosphorylation of renal NKCC2 and NCC cotransporters in vivo. Biol Open 1:120–127
O'Reilly M, Marshall E, Speirs HJ, Brown RW (2003) WNK1, a gene within a novel blood pressure control pathway, tissue-specifically generates radically different isoforms with and without a kinase domain. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2447–2456
Piala AT, Moon TM, Akella R, He H, Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ (2014) Chloride sensing by WNK1 involves inhibition of autophosphorylation. Sci Signal 7:ra41
Plata C, Mount DB, Rubio V, Hebert SC, Gamba G (1999) Isoforms of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter in murine TAL II. Functional characterization and activation by cAMP. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F359–F366
Ponce-Coria J, San Cristobal P, Kahle KT, Vazquez N, Pacheco-Alvarez D, De Los HP, Juarez P, Munoz E, Michel G, Bobadilla NA, Gimenez I, Lifton RP, Hebert SC, Gamba G (2008) Regulation of NKCC2 by a chloride-sensing mechanism involving the WNK3 and SPAK kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8458–8463
Rafiqi FH, Zuber AM, Glover M, Richardson C, Fleming S, Jovanović S, Jovanović A, O'Shaughnessy KM, Alessi DR (2010) Role of the WNK-activated SPAK kinase in regulating blood pressure. EMBO Mol Med 2(2):63–75
Richardson C, Rafiqi FH, Karlsson HK, Moleleki N, Vandewalle A, Campbell DG, Morrice NA, Alessi DR (2008) Activation of the thiazide-sensitive Na+–Cl- cotransporter by the WNK-regulated kinases SPAK and OSR1. J Cell Sci 121:675–684
Richardson C, Sakamoto K, de los Heros P, Deak M, Campbell DG, Prescott AR, Alessi DR (2011) Regulation of the NKCC2 ion cotransporter by SPAK-OSR1-dependent and -independent pathways. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 5):789–800
Rinehart J, Kahle KT, De Los Heros P, Vazquez N, Meade P, Wilson FH, Hebert SC, Gimenez I, Gamba G, Lifton RP (2005) WNK3 kinase is a positive regulator of NKCC2 and NCC, renal cation-Cl- cotransporters required for normal blood pressure homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16777–16782
Shibata S, Zhang J, Puthumana J, Stone KL, Lifton RP (2013) Kelch-like 3 and cullin 3 regulate electrolyte homeostasis via ubiquitination and degradation of WNK4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:7838–7843
Sorensen MV, Grossmann S, Roesinger M, Gresko N, Todkar AP, Barmettler G, Ziegler U, Odermatt A, Loffing-Cueni D, Loffing J (2013) Rapid dephosphorylation of the renal sodium chloride cotransporter in response to oral potassium intake in mice. Kidney Int 83:811–824
Susa K, Sohara E, Rai T, Zeniya M, Mori Y, Mori T, Chiga M, Nomura N, Nishida H, Takahashi D, Isobe K, Inoue Y, Takeishi K, Takeda N, Sasaki S, Uchida S (2014) Impaired degradation of WNK1 and WNK4 kinases causes PHAII in mutant KLHL3 knock-in mice. Hum Mol Genet 23(19):5052–5060
Takahashi D, Mori T, Nomura N, Khan MZ, Araki Y, Zeniya M, Sohara E, Rai T, Sasaki S, Uchida S (2014) WNK4 is the major WNK positively regulating NCC in the mouse kidney. Biosci Rep 9:34(3)
Terker AS, Zhang C, McCormick JA, Lazelle RA, Zhang C, Meermeier NP, Siler DA, Park HJ, Fu Y, Cohen DM, Weinstein AM, Wang WH, Yang CL, Ellison DH (2015) Potassium modulates electrolyte balance and blood pressure through effects on distal cell voltage and chloride. Cell Metab 21:39–50
Thastrup JO, Rafiqi FH, Vitari AC, Pozo-Guisado E, Deak M, Mehellou Y, Alessi DR (2012) SPAK/OSR1 regulate NKCC1 and WNK activity: analysis of WNK isoform interactions and activation by T-loop trans-autophosphorylation. Biochem J 441:325–337
Unwin R, Capasso G, Giebisch G (1994) Potassium and sodium transport along the loop of Henle: effects of altered dietary potassium intake. Kidney Int 46:1092–1099
Vallon V, Schroth J, Lang F, Kuhl D, Uchida S (2009) Expression and phosphorylation of the Na+–Cl cotransporter NCC in vivo is regulated by dietary salt, potassium, and SGK1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F704–F712
Verissimo F, Jordan P (2001) WNK kinases, a novel protein kinase subfamily in multicellular organisms. Oncogene 20:5562–5569
Vidal-Petiot E, Cheval L, Faugeroux J, Malard T, Doucet A, Jeunemaitre X, Hadchouel J (2012) A new methodology for quantification of alternatively spliced exons reveals a highly tissue-specific expression pattern of WNK1 isoforms. PLoS One 7:e37751
Vidal-Petiot E, Elvira-Matelot E, Mutig K, Soukaseum C, Baudrie V, Wu S, Cheval L, Huc E, Cambillau M, Bachmann S, Doucet A, Jeunemaitre X, Hadchouel J (2013) WNK1-related familial hyperkalemic hypertension results from an increased expression of L-WNK1 specifically in the distal nephron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(35):14366–14371
Vitari AC, Deak M, Morrice NA, Alessi DR (2005) The WNK1 and WNK4 protein kinases that are mutated in Gordon’s hypertension syndrome phosphorylate and activate SPAK and OSR1 protein kinases. Biochem J 391:17–24
Vitari AC, Thastrup J, Rafiqi FH, Deak M, Morrice NA, Karlsson HK, Alessi DR (2006) Functional interactions of the SPAK/OSR1 kinases with their upstream activator WNK1 and downstream substrate NKCC1. Biochem J 397:223–231
Wakabayashi M, Mori T, Isobe K, Sohara E, Susa K, Araki Y, Chiga M, Kikuchi E, Nomura N, Mori Y, Matsuo H, Murata T, Nomura S, Asano T, Kawaguchi H, Nonoyama S, Rai T, Sasaki S, Uchida S (2013) Impaired KLHL3-mediated ubiquitination of WNK4 causes human hypertension. Cell Rep 3:858–868
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM et al (2001) Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 293:1107–1112
Wilson FH, Kahle KT, Sabath E, Lalioti MD, Rapson AK, Hoover RS, Hebert SC, Gamba G, Lifton RP (2003) Molecular pathogenesis of inherited hypertension with hyperkalemia: the Na-Cl cotransporter is inhibited by wild-type but not mutant WNK4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:680–684
Xu B, English JM, Wilsbacher JL, Stippec S, Goldsmith EJ, Cobb MH (2000) WNK1, a novel mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase lacking the catalytic lysine in subdomain II. J Biol Chem 275:16795–16801
Yang CL, Angell J, Mitchell R, Ellison DH (2003) WNK kinases regulate thiazide sensitive Na-Cl cotransport. J Clin Invest 111:1039–1045
Yang CL, Zhu X, Wang Z, Subramanya AR, Ellison DH (2005) Mechanisms of WNK1 and WNK4 interaction in the regulation of thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransport. J Clin Invest 115:1379–1387
Yang SS, Lo YF, Wu CC, Lin SW, Yeh CJ, Chu P, Sytwu HK, Uchida S, Sasaki S, Lin SH (2010) SPAK-knockout mice manifest Gitelman syndrome and impaired vasoconstriction. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(11):1868–1877
Yang SS, Morimoto T, Rai T, Chiga M, Sohara E, Ohno M, Uchida K, Lin SH, Moriguchi T, Shibuya H, Kondo Y, Sasaki S, Uchida S (2007) Molecular pathogenesis of pseudohypoaldosteronism type II: generation and analysis of a Wnk4(D561A/+) knockin mouse model. Cell Metab 5(5):331–344
Acknowledgments
Work in authors’ lab is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health of USA (DK59530 to CLH) and from National Science Council of Taiwan (MOST 103-2628-B-016-001-MY3 to CJC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CL., Cheng, CJ. A unifying mechanism for WNK kinase regulation of sodium-chloride cotransporter. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 467, 2235–2241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1708-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1708-2