Abstract
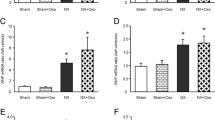
The dinucleotide uridine adenosine tetraphosphate (Up4A), which has both purine and pyrimidine moieties, was reported as a novel endothelium-derived contracting factor. Recently, growing evidence has suggested that Up4A plays an important role in regulation of the cardiovascular function. We previously demonstrated that Up4A-induced vasoconstrictions are altered in arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. We have assessed responses to Up4A shown by renal arteries from type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats (42–46 weeks old) and identified the molecular mechanisms involved. Concentration-dependent contractions to Up4A were greater in renal arterial rings from the GK than age-matched control Wistar group. In both groups, the inhibition of nitric oxide synthase (with N G-nitro-l-arginine) increased the response to Up4A, whereas the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) (with indomethacin) decreased the response. Specific inhibitors of COX-1 (valeroyl salicylate) and COX-2 (NS398), a thromboxane (TX) receptor (TP) antagonist (SQ29548), and P2 receptor antagonist (suramin) also decreased the response to Up4A. Protein expressions of COXs in renal arteries were greater in the GK than Wistar group. The production of TXB2 (a metabolite of TXA2) by Up4A did not differ between these groups. Concentration-dependent contractions to U46619, an agonist of the TP receptor, were greater in renal arteries from the GK than Wistar group. The expression of P2X1 and P2Y2 receptors did not differ between these groups. These results suggest that enhancement of the Up4A-induced contraction in renal arteries from GK rats may be attributable to the increased activation of COXs/TP receptor signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahdadi KJ, Hannan JL, Ergul A, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2011) Internal pudendal artery from type 2 diabetic female rats demonstrate elevated endothelin-1-mediated constriction. J Sex Med 8:2472–2483
Barton M (2010) Obesity and aging: determinants of endothelial cell dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pflugers Arch 460:825–837
Bartoo AC, Nelson MT, Mawe GM (2008) ATP induces guinea pig gallbladder smooth muscle excitability via the P2Y4 receptor and COX-1 activity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G1362–G1368
Burnstock G (2010) Control of vascular tone by purines and pyrimidines. Br J Pharmacol 161:527–529
Carpenter RC, Miao L, Miyagi Y, Bengten E, Zhang JH (2001) Altered expression of P2 receptor mRNAs is the basilar artery in a rat double hemorrhage model. Stroke 32:516–522
Chen D, Balyakina EV, Lawrece M, Christman BW, Meyrick B (2003) Cyclooxygenase is regulating by ET-1 and MAPKs in peripheral lung microvascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284:L614–L621
Delicado EG, Miras-Portugal MT, Carrasquero LM, Leon D, Perez-Sen R, Gualix J (2006) Dinucleotide polyphosphates and their interaction with other nucleotide signaling pathways. Pflugers Arch 452:563–572
Ding H, Triggle CR (2010) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: multiple targets for treatment. Pflugers Arch 459:977–994
Feletou M, Huang Y, Vanhoutte PM (2010) Vasoconstrictor prostanoids. Pflugers Arch 459:941–950
Feletou M, Vanhoutte PM, Verbeuren TJ (2010) The thromboxane/endoperoxide receptor (TP): the common villain. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 55:317–332
Fleming I (2010) Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of eNOS. Pflugers Arch 459:793–806
Flores RV, Hernandez-Perez MG, Aquino E, Garrad RC, Weisman GA, Gonzalez FA (2005) Agonist-induced phosphorylation and desensitization of the P2Y2 nucleotide receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 280:35–45
Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2013) Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev 93:137–188
Goto Y, Kakizaki M, Masaki N (1976) Production of spontaneous diabetic rats by repetition of selective breeding. Tohoku J Exp Med 119:85–90
Gui Y, He G, Walsh MP, Zheng XL (2011) Signaling mechanisms mediating uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 58:654–662
Gui Y, Walsh MP, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Zheng XL (2008) Up4A stimulates endothelium-independent contraction of isolated rat pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L733–L738
Gui Y, Wang Z, Sun X, Walsh MP, Li JJ, Gao J, Zheng XL (2011) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate induces contraction of airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 301:L789–L794
Guo Z, Su W, Allen S, Pang H, Daugherty A, Smart E, Gong MC (2005) COX-2 up-regulation and vascular smooth muscle contractile hyperreactivity in spontaneous diabetic db/db mice. Cardiovasc Res 67:723–735
Hansen PB, Hristovska A, Wolff H, Vanhoutte PM, Jensen BL, Bie P (2010) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate affects contractility of mouse aorta and decreases blood pressure in conscious rats and mice. Acta Physiol 200:171–179
Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Taguchi K, Kamata K, Kobayashi T (2011) Mechanisms underlying altered extracellular nucleotide-induced contractions in mesenteric arteries from rats in later-stage type 2 diabetes: effect of ANG II type 1 receptor antagonism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1850–H1861
Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Taguchi K, Kamata K, Kobayashi T (2012) Protein kinase C delta contributes to increase in EP3 agonist-induced contraction in mesenteric arteries from type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Pflugers Arch 463:593–602
Jankowski V, Meyer AA, Schlattmann P, Gui Y, Zheng XL, Stamcou I, Radtke K, Tran TN, van der Giet M, Tolle M, Zidek W, Jankowski J (2007) Increased uridine adenosine tetraphosphate concentrations in plasma of juvenile hypertensives. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1776–1781
Jankowski V, Schulz A, Kretschmer A, Mischak H, Boehringer F, van der Giet M, Janke D, Schuchardt M, Herwig R, Zidek W, Jankowski J (2013) The enzymatic activity of the VEGF2 receptor for the biosynthesis of dinucleoside polyphosphates. J Mol Med in press
Jankowski V, Tolle M, Vanholder R, Schonfelder G, van der Giet M, Henning L, Schluter H, Paul M, Zidek W, Jankowski J (2005) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate: a novel endothelium-derived vasoconstrictive factor. Nat Med 11:223–227
Kelly-Cobbs A, Elgebaly MM, Li W, Ergul A (2011) Pressure-independent cerebrovascular remodelling and changes in myogenic reactivity in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rat in response to glycaemic control. Acta Physiol 203:245–251
Kim CH, Kim SS, Choi JY, Shin JH, Kim JY, Namkung W, Lee JG, Lee MG, Yoon JH (2004) Membrane-specific expression of functional purinergic receptors in normal human nasal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L835–L842
Kobayashi T, Kaneda A, Kamata K (2003) Possible involvement of IGF-1 receptor and IGF-binding protein in insulin-induced enhancement of noradrenaline response in diabetic rat aorta. Br J Pharmacol 140:285–294
Kobayashi T, Nemoto S, Ishida K, Taguchi K, Matsumoto T, Kamata K (2012) Involvement of CaM kinase II in the impairment of endothelial function and eNOS activity in aortas or type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Sci 123:375–386
Kold-Petersen H, Brondum E, Nilsson H, Flyvbjerg A, Aalkjaer C (2012) Impaired myogenic tone in isolated cerebral and coronary resistance arteries from the Goto-Kakizaki rat model of type 2 diabetes. J Vasc Res 49:267–278
Kon V, Harris RC, Ichikawa I (1990) A regulatory role for large vessels in organ circulation endothelial cells of the main renal artery modulate intrarenal hemodynamics in the rat. J Clin Invest 85:1728–1733
Linder AE, Tumbri M, Linder FF, Webb RC, Leite R (2008) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate induces contraction and relaxation in rat aorta. Vascul Pharmacol 48:202–207
Matsumoto T, Ishida K, Taguchi K, Kobayashi T, Kamata K (2010) Losartan normalizes endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated relaxation by activating Ca2 + −activated K + channels in mesenteric artery from type 2 diabetic GK rat. J Pharmacol Sci 112:299–309
Matsumoto T, Kakami M, Noguchi E, Kobayashi T, Kamata K (2007) Imbalance between endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors in mesenteric arteries from aged OLETF rats, a model of Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1480–H1490
Matsumoto T, Kobayashi T, Ishida K, Taguchi K, Kamata K (2010) Enhancement of mesenteric artery contraction to 5-HT depends on Rho kinase and Src kinase pathways in the ob/ob mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 160:1092–1104
Matsumoto T, Kobayashi T, Wachi H, Seyama Y, Kamata K (2007) Vascular NAD(P)H oxidase mediates endothelial dysfunction in basilar arteries from Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. Atherosclerosis 192:15–24
Matsumoto T, Nakayama N, Ishida K, Kobayashi T, Kamata K (2009) Eicosapentaenoic acid improves imbalance between vasodilator and vasoconstrictor actions of endothelium-derived factors in mesenteric arteries from rats at chronic stage of type 2 diabetes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:324–334
Matsumoto T, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2011) The role of uridine adenosine tetraphosphate in the vascular system. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2011:435132
Matsumoto T, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2011) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H409–H417
Matsumoto T, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2012) Alterations in vasoconstrictor responses to the endothelium-derived contracting factor uridine adenosine tetraphosphate are region specific in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Pharmacol Res 65:81–90
Michel FS, Man GS, Man RY, Vanhoutte PM (2008) Hypertension and the absence of EDHF-mediated responses favour endothelium-dependent contractions in renal arteries of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 155:217–226
Michel FS, Man RY, Vanhoutte PM (2007) Increased spontaneous tone in renal arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1673–H1681
Michel T, Vanhoutte PM (2010) Cellular signaling and NO production. Pflugers Arch 459:807–816
Nemoto S, Kobayashi T, Taguchi K, Matsumoto T, Kamata K (2011) Losartan improves aortic endothelium-dependent relaxation via proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2/Src/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H2383–H2394
Ohnaka K, Numaguchi K, Yamakawa T, Inagami T (2000) Induction of cylooxygenase-2 by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 35:68–75
Pirola L, Balcerczyk A, Okabe J, El-Osta A (2010) Epigenetic phenomena linked to diabetic complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 6:665–675
Potenza MA, Nacci C, Gagliardi S, Montagnani M (2011) Cardiovascular complications in diabetes: lessons from animal models. Curr Med Chem 18:1806–1819
Ramos-Alves FE, de Queiroz DB, Santos-Rocha J, Duarte DP, Xavier FE (2012) Effect of age and COX-2-derived prostanoids on the progression of adult vascular dysfunction in the offspring of diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 166:2198–2208
Ruan YC, Wang Z, Du JY, Zuo WL, Guo JH, Zhang J, Wu ZL, Wong HY, Chung YW, Chan HC, Zhou WL (2008) Regulation of smooth muscle contractility by the epithelium in rat vas deferens: role of ATP-induced release of PGE2. J Physiol 586:4843–4857
Sanchez A, Contreras C, Villalba N, Martinez P, Martinez AC, Briones A, Salaices M, Garcia-Sacristan A, Hernandez M, Prieto D (2010) Altered arachidonic acid metabolism via COX-1 and COX-2 contributes to the endothelial dysfunction of penile arteries from obese Zucker rats. Br J Pharmacol 159:604–616
Schuchardt M, Prufer J, Prufer N, Wiedon A, Huang T, Chebli M, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Schafer-Korting M, Zidek W, van der Giet M, Tolle M (2011) The endothelium-derived contracting factor uridine adenosine tetraphosphate induces P2Y(2)-mediated pro-inflammatory signaling by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 formation. J Mol Med 89:799–810
Schuchardt M, Tolle M, Prufer J, Prufer N, Huang T, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Zidek W, van der Giet M (2012) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate activation of the purinergic receptor P2Y enhances in vitro vascular calcification. Kidney Int 81:256–265
Sena CM, Matafome P, Crisostomo J, Rodrigues L, Fernandes R, Pereira P, Seica RM (2012) Methylglyoxal promotes oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Pharmacol Res 65:497–506
Seye CI, Kong Q, Erb L, Garrad RC, Krugh B, Whang M, Turner JT, Sturek M, Gonzalez FA, Weisman GA (2002) Functional P2Y2 nucleotide receptors mediate uridine 5’-triphosphate-induced intimal hyperplasia in collared rabbit carotid arteries. Circulation 106:2720–2726
Sowers JR (2013) Diabetes mellitus and vascular disease. Hypertension 61:943–947
Taguchi K, Matsumoto T, Kamata K, Kobayashi T (2012) G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2, with β-arrestin 2, impairs insulin-induced Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling in ob/ob mouse aorta. Diabetes 61:1978–1985
Taguchi K, Morishige A, Matsumoto T, Kamata K, Kobayashi T (2012) Enhanced estradiol-induced vasorelaxation in aortas from type 2 diabetic mice may reflect a compensatory role of p38 MAPK-mediated eNOS activation. Pflugers Arch 464:205–215
Tang EH, Vanhoute PM (2010) Endothelial dysfunction: a strategic target in the treatment of hypertension? Pflugers Arch 459:995–1004
Tolle M, Schuchardt M, Wiedon A, Huang T, Klockel L, Jankowski J, Jankowski V, Zidek W, van der Giet M (2010) Differential effects of uridine adenosine tetraphosphate on purinoceptors in the rat isolated perfused kidney. Br J Pharmacol 161:530–540
Wang L, Karlsson L, Moses S, Hultgardh-Nisson A, Andersson M, Boma C, Gudbjartsson T, Jern S, Erlinge D (2002) P2 receptor expression profiles in human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40:841–853
Wiedon A, Tolle M, Bastine J, Schuchardt M, Huang T, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Zidek W, van der Giet M (2012) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate (Up4A) is a strong inductor of smooth muscle cell migration via activation of the P2Y2 receptor and cross-communication to the PDGF receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 417:1035–1040
Woodward DF, Jones RL, Narumiya S (2011) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXIII: classification of prostanoid receptors, updating 15 years of progress. Pharmacol Rev 63:471–538
Yuan W, Wang Z, Li J, Liu D, Bai G, Walsh MP, Gui Y, Zheng XL (2013) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate induces contraction of circular and longitudinal gastric smooth muscle by distinct signaling pathways. IUBMB Life 65:623–632
Zhou Z, Merkus D, Cheng C, Duckers HJ, Jan Danser AH, Duncker DJ (2013) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate is a novel vasodilator in the coronary microcirculation which acts through purinergic P1 but not P2 receptors. Pharmacol Res 67:10–17
Acknowledgments
We thank S. Natori, M. Mori, M. Fujii, Y. Matsuba, C. Kanazu, and M. Toba for technical help. This study was supported in part by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, and by the Science Research Promotion Fund from the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan.
Conflict of interest disclosure
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, T., Watanabe, S., Kawamura, R. et al. Enhanced uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction in renal artery from type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats due to activated cyclooxygenase/thromboxane receptor axis. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 331–342 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1330-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1330-0