Abstract
Purpose
Cardiometabolic disease remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developed nations. Consequently, identifying and understanding factors associated with underlying pathophysiological processes leading to chronic cardio metabolic conditions is critical. Metabolic health, arterial elasticity, and insulin sensitivity (SI) may impact disease risk, and may be determined in part by myofiber type. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that type I myofiber composition would be associated with high SI, greater arterial elasticity, lower blood pressure, and blood lipids; whereas, type IIx myofibers would be associated with lower SI, lower arterial elasticity, higher blood pressure, blood lipids.
Methods
Muscle biopsies were performed on the vastus lateralis in 16 subjects (BMI = 27.62 ± 4.71 kg/m2, age = 32.24 ± 6.37 years, 43% African American). The distribution of type I, IIa, and IIx myofibers was determined via immunohistochemistry performed on frozen cross-sections. Pearson correlation analyses were performed to assess associations between myofiber composition, SI, arterial elasticity, blood pressure, and blood lipid concentrations.
Results
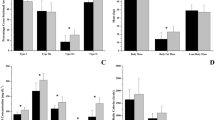
The percentage of type I myofibers positively correlated with SI and negatively correlated with systolic blood pressure SBP, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial pressure (MAP); whereas, the percentage of type IIx myofibers were negatively correlated with SI and large artery elasticity, and positively correlated with LDL cholesterol, SBP, and MAP.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate a potential link between myofiber composition and cardiometabolic health outcomes in a cohort of premenopausal women. Future research is needed to determine the precise mechanisms in which myofiber composition impacts the pathophysiology of impaired glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as vascular dysfunction.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- LAE:
-
Large artery elasticity
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial blood pressure
- SAE:
-
Small artery elasticity
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SI:
-
Insulin sensitivity
- TVI:
-
Total vascular impedance
References
Albers PH, Pedersen AJ, Birk JB, Kristensen DE, Vind BF, Baba O, Nøhr J, Højlund K, Wojtaszewski JF (2015) Human muscle fiber type-specific insulin signaling: impact of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 64(2):485–497. doi:10.2337/db14-0590
Ama PF, Simoneau JA, Boulay MR, Serresse O, Thériault G, Bouchard G (1986) Skeletal muscle characteristics in sedentary black and Caucasian males. J Appl Physiol (1985) 61(5):1758–1761
Bamman MM, Ragan RC, Kim JS, Cross JM, Hill VJ, Tuggle SC, Allman RM (2004) Myogenic protein expression before and after resistance loading in 26- and 64-year-old men and women. J Appl Physiol (1985) 97(4):1329–1337. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01387.2003
Bassett DR (1994) Skeletal muscle characteristics: relationships to cardiovascular risk factors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26(8):957–966
Berliner JA, Heinecke JW (1996) The role of oxidized lipoproteins in atherogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 20(5):707–727
Castro MJ, Apple DF, Staron RS, Campos GE, Dudley GA (1999) Influence of complete spinal cord injury on skeletal muscle within 6 mo of injury. J Appl Physiol (1985) 86(1):350–358
Chang CC, Yang MH, Tung HC, Chang CY, Tsai YL, Huang JP, Yen TH, Hung LM (2014) Resveratrol exhibits differential protective effects on fast- and slow-twitch muscles in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes 6(1):60–67. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12072
Cohn JN, Finkelstein S, McVeigh G, Morgan D, LeMay L, Robinson J, Mock J (1995) Noninvasive pulse wave analysis for the early detection of vascular disease. Hypertension 26(3):503–508
Duey WJ, Bassett DR, Torok DJ, Howley ET, Bond V, Mancuso P, Trudell R (1997) Skeletal muscle fibre type and capillary density in college-aged blacks and whites. Ann Hum Biol 24(4):323–331
Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, Giorico MA, Oleggini M, Graziadei L, Pedrinelli R, Brandi L, Bevilacqua S (1987) Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 317(6):350–357. doi:10.1056/NEJM198708063170605
Frisk-Holmberg M, Essén B, Fredrikson M, Ström G, Wibell L (1983) Muscle fibre composition in relation to blood pressure response to isometric exercise in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Acta Med Scand 213(1):21–26
Grimby G, Broberg C, Krotkiewska I, Krotkiewski M (1976) Muscle fiber composition in patients with traumatic cord lesion. Scand J Rehabil Med 8(1):37–42
Groop LC, Saloranta C, Shank M, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E, DeFronzo RA (1991) The role of free fatty acid metabolism in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obesity and noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72(1):96–107
Hales S (1964) Statistical essays. Haemostaticks II. Hafner Publishing, New York
Henriksen EJ, Bourey RE, Rodnick KJ, Koranyi L, Permutt MA, Holloszy JO (1990) Glucose transporter protein content and glucose transport capacity in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol 259(4 Pt 1):E593–E598
James DE, Jenkins AB, Kraegen EW (1985) Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol 248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574
Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Frisk-Holmberg M, Karlsson J, Tesch P (1979) Central and peripheral circulation in relation to muscle-fibre composition in normo- and hyper-tensive man. Clin Sci (Lond) 56(4):335–340
Kim JS, Kosek DJ, Petrella JK, Cross JM, Bamman MM (2005) Resting and load-induced levels of myogenic gene transcripts differ between older adults with demonstrable sarcopenia and young men and women. J Appl Physiol (1985) 99(6):2149–2158. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00513.2005
Kim TN, Park MS, Lim KI, Yang SJ, Yoo HJ, Kang HJ, Song W, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM (2011) Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio is associated with metabolic syndrome and arterial stiffness: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Res Clin Pract 93(2):285–291. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2011.06.013
Laughlin MH, Padilla J, Jenkins NT, Thorne PK, Martin JS, Rector RS, Akter S, Davis JW (2015) Exercise-induced differential changes in gene expression among arterioles of skeletal muscles of obese rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 119(6):583–603. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00316.2015
Lee SW, Youm Y, Kim CO, Lee WJ, Choi W, Chu SH, Park YR, Kim HC (2014) Association between skeletal muscle mass and radial augmentation index in an elderly Korean population. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 59(1):49–55. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2014.01.008
Lillioja S, Young AA, Culter CL, Ivy JL, Abbott WG, Zawadzki JK, Yki-Järvinen H, Christin L, Secomb TW, Bogardus C (1987) Skeletal muscle capillary density and fiber type are possible determinants of in vivo insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest 80(2):415–424. doi:10.1172/JCI113088
Loenneke JP, Fahs CA, Heffernan KS, Rossow LM, Thiebaud RS, Bemben MG (2013) Relationship between thigh muscle mass and augmented pressure from wave reflections in healthy adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 113(2):395–401. doi:10.1007/s00421-012-2449-y
Madamanchi NR, Runge MS (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 100(4):460–473. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000258450.44413.96
Martin MJ, Hulley SB, Browner WS, Kuller LH, Wentworth D (1986) Serum cholesterol, blood pressure, and mortality: implications from a cohort of 361,662 men. Lancet 2(8513):933–936
Martin TP, Stein RB, Hoeppner PH, Reid DC (1992) Influence of electrical stimulation on the morphological and metabolic properties of paralyzed muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 72(4):1401–1406
Nielsen J, Christensen DL (2011) Glucose intolerance in the West African Diaspora: a skeletal muscle fibre type distribution hypothesis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 202(4):605–616. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02272.x
Oberbach A, Bossenz Y, Lehmann S, Niebauer J, Adams V, Paschke R, Schön MR, Blüher M, Punkt K (2006) Altered fiber distribution and fiber-specific glycolytic and oxidative enzyme activity in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29(4):895–900
Ochi M, Kohara K, Tabara Y, Kido T, Uetani E, Ochi N, Igase M, Miki T (2010) Arterial stiffness is associated with low thigh muscle mass in middle-aged to elderly men. Atherosclerosis 212(1):327–332. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.05.026
Olver TD, Ferguson BS, Laughlin MH (2015) Molecular mechanisms for exercise training-induced changes in vascular structure and function: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and the brain. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 135:227–257. doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.07.017
Ploug T, Galbo H, Vinten J, Jørgensen M, Richter EA (1987) Kinetics of glucose transport in rat muscle: effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol 253(1 Pt 1):E12–E20
Pollare T, Lithell H, Berne C (1990) Insulin resistance is a characteristic feature of primary hypertension independent of obesity. Metabolism 39(2):167–174
Quindry J, Miller L, McGinnis G, Irwin M, Dumke C, Magal M, Triplett NT, McBride J, Urbiztondo Z (2011) Muscle-fiber type and blood oxidative stress after eccentric exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 21(6):462–470
Reaven GM (1988) Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37(12):1595–1607
Ritchie SA, Connell JM (2007) The link between abdominal obesity, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 17(4):319–326. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2006.07.005
Rocchini AP (1991) Insulin resistance and blood pressure regulation in obese and nonobese subjects. Special lecture. Hypertension 17(6 Pt 2):837–842
Rönnback M, Hernelahti M, Hämäläinen E, Groop PH, Tikkanen H (2007) Effect of physical activity and muscle morphology on endothelial function and arterial stiffness. Scand J Med Sci Sports 17(5):573–579. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2006.00603.x
Simoneau JA, Bouchard C (1989) Human variation in skeletal muscle fiber-type proportion and enzyme activities. Am J Physiol 257(4 Pt 1):E567–E572
Stuart CA, McCurry MP, Marino A, South MA, Howell ME, Layne AS, Ramsey MW, Stone MH (2013) Slow-twitch fiber proportion in skeletal muscle correlates with insulin responsiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(5):2027–2036. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-3876
Szlachcic Y, Adkins RH, Govindarajan S, Cao Y, Krause JS (2014) Cardiometabolic changes and disparities among persons with spinal cord injury: a 17-year cohort study. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 20(2):96–104. doi:10.1310/sci2002-96
van Bussel BC, Schouten F, Henry RM, Schalkwijk CG, de Boer MR, Ferreira I, Smulders YM, Twisk JW, Stehouwer CD (2011) Endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation are associated with greater arterial stiffness over a 6-year period. Hypertension 58(4):588–595. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.174557
Yarar-Fisher C, Bickel CS, Windham ST, McLain MM, Bamman AB (2013) Skeletal muscle signaling associated with impaired glucose tolerance in spinal cord-injured men and the effects of contractile activity. J Appl Physiol (1985) 115(5):756–764. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00122.2013
Zierath JR, Hawley JA (2004) Skeletal muscle fiber type: influence on contractile and metabolic properties. PLoS Biol 2(10):e348. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020348
Zierath JR, He L, Gumà A, Odegoard Wahlström E, Klip A, Wallberg-Henriksson H (1996) Insulin action on glucose transport and plasma membrane GLUT4 content in skeletal muscle from patients with NIDDM. Diabetologia 39(10):1180–1189
Acknowledgements
We would like to recognize Brandon Kane for his assistance in coordinating this study. We would also like to thank the UAB Center for Clinical and Translational Science and the Clinical Research Unit for their assistance with the clamp procedure and muscle biopsies. This work was supported by the NIH Grants P30DK56336, P60DK079626, and 2R01DK049779-11A1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GF wrote the manuscript, assisted with data collection, performed data and statistical analysis, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. GH designed the study, assisted with data collection, assisted with data and statistical analysis, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. BG designed the study, assisted with data collection and analysis, and reviewed and edited the manuscript. SW conducted the muscle biopsies and assisted with study design. PG conducted fiber type experiments and assisted with data collection. JW assisted with fiber type experiments and assisted with data collection.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author's declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Carsten Lundby.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisher, G., Windham, S.T., Griffin, P. et al. Associations of human skeletal muscle fiber type and insulin sensitivity, blood lipids, and vascular hemodynamics in a cohort of premenopausal women. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 1413–1422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3634-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3634-9