Abstract
Purpose
Previous studies have shown vascular dysfunction of main conductance arteries and microvessels after diving. We aim to evaluate the impact of bubble formation on vascular function and haemostasis. To achieve this, we used a vibration preconditioning to influence bubble levels without changing any other parameters linked to the dive.
Methods
Twentty-six divers were randomly assigned to one of three groups: (1) the “vibrations–dive” group (VD; n = 9) was exposed to a whole-body vibration session 30 min prior the dive; (2) the “diving” group (D; n = 9) served as a control for the effect of the diving protocol; (3) The “vibration” protocol (V; n = 8) allowed us to assess the effect of vibrations without diving. Macro- and microvascular function was assessed for each subject before and after the dive, subsequently. Bubble grades were monitored with Doppler according to the Spencer grading system. Blood was taken before and after the protocol to assess any change of platelets or endothelial function.
Results
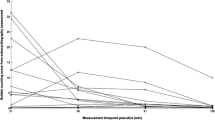
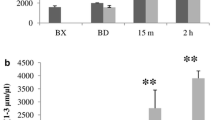
Bubble formation was lower in the VD than the diving group. The other measured parameters remained unchanged after the “vibration” protocol alone. Diving alone induced macrovascular dysfunction, and increased PMP and thrombin generation. Those parameters were no longer changed in the VD group. Conversely, a microvascular dysfunction persists despite a significant decrease of circulating bubbles.
Conclusions
Finally, the results of this study suggest that macro- but not microvascular impairment results at least partly from bubbles, possibly related to platelet activation and generation of pro-coagulant microparticles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baj Z, Olszański R, Majewska E, Konarski M (2000) The effect of air and nitrox divings on platelet activation tested by flow cytometry. Aviat Space Environ Med 71:925–928
Balestra C, Theunissen S, Papadopoulou V et al (2016) Pre-dive whole-body vibration better reduces decompression-induced vascular gas emboli than oxygenation or a combination of both. Front Physiol. doi:10.3389/fphys.2016.00586
Berghoff M, Kathpal M, Kilo S et al (2002) Vascular and neural mechanisms of ACh-mediated vasodilation in the forearm cutaneous microcirculation. J Appl Physiol 92:780–788. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01167.2000
Brubakk AO, Duplancic D, Valic Z et al (2005) A single air dive reduces arterial endothelial function in man: air dive and endothelial function. J Physiol 566:901–906. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089862
Bryckaert M, Rosa J-P, Denis CV, Lenting PJ (2015) Of von Willebrand factor and platelets. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:307–326. doi:10.1007/s00018-014-1743-8
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM et al (1992) Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet Lond Engl 340:1111–1115.
Corretti MC, Anderson TJ, Benjamin EJ et al (2002) Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: a report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:257–265
Dujic Z, Palada I, Valic Z et al (2006) Exogenous nitric oxide and bubble formation in divers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1432–1435. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000228936.78916.23
Ersson A, Walles M, Ohlsson K, Ekholm A (2002) Chronic hyperbaric exposure activates proinflammatory mediators in humans. J Appl Physiol 92:2375–2380. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00705.2001
Fok H, Jiang B, Chowienczyk P, Clapp B (2015) Microbubbles shunting via a patent foramen ovale impair endothelial function. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. doi:10.1177/2048004015601564
Gempp E, Blatteau J-E (2010) Preconditioning methods and mechanisms for preventing the risk of decompression sickness in scuba divers: a review. Res Sports Med 18:205–218. doi:10.1080/15438627.2010.490189
Germonpré P, Balestra C (2017) Preconditioning to reduce decompression stress in Scuba divers. Aerosp Med Hum Perform 88:1–7
Germonpré P, Pontier J-M, Gempp E et al (2009) Pre-dive vibration effect on bubble formation after a 30-m dive requiring a decompression stop. Aviat Space Environ Med 80:1044–1048
Kanaji S, Fahs SA, Shi Q et al (2012) Contribution of platelet vs. endothelial VWF to platelet adhesion and hemostasis: hemostatic effect of platelet VWF in murine VWD. J Thromb Haemost 10:1646–1652. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04797.x
Klinger AL, Pichette B, Sobolewski P, Eckmann DM (2011) Mechanotransductional basis of endothelial cell response to intravascular bubbles. Integr Biol 3:1033. doi:10.1039/c1ib00017a
Lambrechts K, Pontier J-M, Balestra C et al (2013a) Effect of a single, open-sea, air scuba dive on human micro- and macrovascular function. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:2637–2645. doi:10.1007/s00421-013-2676-x
Lambrechts K, Pontier J-M, Balestra C et al (2013b) Effect of a single, open-sea, air scuba dive on human micro-and macrovascular function. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:2637–2645
Lambrechts K, Pontier J-M, Mazur A et al (2013c) Effect of decompression-induced bubble formation on highly trained divers microvascular function. Physiol Rep. doi:10.1002/phy2.142
Lambrechts K, Pontier J-M, Mazur A et al (2015) Mechanism of action of antiplatelet drugs on decompression sickness in rats: a protective effect of anti-GPIIbIIIa therapy. J Appl Physiol 118:1234–1239. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00125.2015
Li Y, Li L, Dong F et al (2015) Plasma von Willebrand factor level is transiently elevated in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2721
Marinovic J, Ljubkovic M, Breskovic T et al (2012) Effects of successive air and nitrox dives on human vascular function. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:2131–2137. doi:10.1007/s00421-011-2187-6
Mazur A, Lambrechts K, Wang Q et al (2016) Influence of decompression sickness on vasocontraction of isolated rat vessels. J Appl Physiol 120:784–791. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00139.2015
Mheid IA, Corrigan F, Shirazi F et al (2014) Circadian variation in vascular function and regenerative capacity in healthy humans. J Am Heart Assoc 3:e000845–e000845. doi:10.1161/JAHA.114.000845
Nossum V, Hjelde A, Brubakk AO (2002) Small amounts of venous gas embolism cause delayed impairment of endothelial function and increase polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:209–214
Obad A, Palada I, Valic Z et al (2007a) The effects of acute oral antioxidants on diving-induced alterations in human cardiovascular function: antioxidants and endothelium-dependent dilatation after field diving. J Physiol 578:859–870. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.122218
Obad A, Valic Z, Palada I et al (2007b) Antioxidant pretreatment and reduced arterial endothelial dysfunction after diving. Aviat Space Environ Med 78:1114–1120
Obad A, Marinovic J, Ljubkovic M et al (2010) Successive deep dives impair endothelial function and enhance oxidative stress in man: deep trimix dives impair endothelial function. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 30:432–438. doi:10.1111/j.1475-097X.2010.00962.x
Papadopoulou V, Tang M-X, Balestra C et al (2014) Circulatory bubble dynamics: from physical to biological aspects. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 206:239–249. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2014.01.017
Pontier J-M, Blatteau J-E, Vallée N (2008a) Blood platelet count and severity of decompression sickness in rats after a provocative dive. Aviat Space Environ Med 79:761–764
Pontier J-M, Jimenez C, Blatteau J-E (2008b) Blood platelet count and bubble formation after a dive to 30 msw for 30 min. Aviat Space Environ Med 79:1096–1099
Pontier J-M, Vallee N, Bourdon L (2009) Bubble-induced platelet aggregation in a rat model of decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol 107:1825–1829. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.91644.2008
Pontier J-M, Gempp E, Ignatescu M (2012) Blood platelet-derived microparticles release and bubble formation after an open-sea air dive. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37:888–892. doi:10.1139/h2012-067
Pyke KE, Tschakovsky ME (2005) The relationship between shear stress and flow-mediated dilatation: implications for the assessment of endothelial function: The shear stress stimulus-flow-mediated dilatation relationship. J Physiol 568:357–369. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089755
Roustit M, Cracowski J-L (2012) Non-invasive assessment of skin microvascular function in humans: an insight into methods: methods to assess skin microvascular function. Microcirculation 19:47–64. doi:10.1111/j.1549-8719.2011.00129.x
Sobolewski P, Kandel J, Klinger AL, Eckmann DM (2011) Air bubble contact with endothelial cells in vitro induces calcium influx and IP3-dependent release of calcium stores. AJP Cell Physiol 301:C679–C686. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00046.2011
Theunissen S, Guerrero F, Sponsiello N et al (2013a) Nitric oxide-related endothelial changes in breath-hold and scuba divers. Undersea Hyperb Med J Undersea Hyperb Med Soc Inc 40:135–144
Theunissen S, Schumacker J, Guerrero F et al (2013b) Dark chocolate reduces endothelial dysfunction after successive breath-hold dives in cool water. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:2967–2975. doi:10.1007/s00421-013-2732-6
Theunissen S, Sponsiello N, Rozloznik M et al (2013c) Oxidative stress in breath-hold divers after repetitive dives. Diving Hyperb Med 43:63–66
Theunissen S, Balestra C, Boutros A et al (2015) The effect of pre-dive ingestion of dark chocolate on endothelial function after a scuba dive. Diving Hyperb Med 45:4–9
Thom SR, Yang M, Bhopale VM et al (2011) Microparticles initiate decompression-induced neutrophil activation and subsequent vascular injuries. J Appl Physiol 110:340–351. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00811.2010
Thom SR, Yang M, Bhopale VM et al (2013) Intramicroparticle nitrogen dioxide is a bubble nucleation site leading to decompression-induced neutrophil activation and vascular injury. J Appl Physiol 114:550–558. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01386.2012
Thom SR, Bennett M, Banham ND et al (2015) Association of microparticles and neutrophil activation with decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol 119:427–434. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00380.2015
Turner J, Belch JJF, Khan F (2008) Current concepts in assessment of microvascular endothelial function using laser doppler imaging and iontophoresis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 18:109–116. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2008.02.001
van Hinsbergh VWM (2012) Endothelium—role in regulation of coagulation and inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 34:93–106. doi:10.1007/s00281-011-0285-5
Wang Q, Belhomme M, Guerrero F et al (2013) Diving under a microscope—a new simple and versatile in vitro diving device for fluorescence and confocal microscopy allowing the controls of hydrostatic pressure, gas pressures, and kinetics of gas saturation. Microsc Microanal 19:608–616. doi:10.1017/S1431927613000378
Wang Q, Guerrero F, Mazur A et al (2015) Reactive oxygen species, mitochondria, and endothelial cell death during in vitro simulated dives. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47:1362–1371. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000000563
Yang M, Barak OF, Dujic Z et al (2015a) Ascorbic acid supplementation diminishes microparticle elevations and neutrophil activation following SCUBA diving. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 309:R338–R344. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00155.2015
Yang M, Bhopale VM, Thom SR (2015b) Separating the roles of nitrogen and oxygen in high pressure-induced blood-borne microparticle elevations, neutrophil activation, and vascular injury in mice. J Appl Physiol 119:219–222. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00384.2015
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the PHYPODE European network. This study was supported by the European Commission under the FP7-PEOPLE-2010-ITN program (Grant Agreement No. 264816).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Guido Ferretti.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambrechts, K., Balestra, C., Theron, M. et al. Venous gas emboli are involved in post-dive macro, but not microvascular dysfunction. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 335–344 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3537-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3537-9