Abstract
Purpose
Salbutamol inhalation is permissible by WADA in athletic competition for asthma management and affects potassium regulation, which is vital for muscle function. Salbutamol effects on arterial potassium concentration ([K+]a) during and after high-intensity continuous exercise (HIcont) and intermittent exercise comprising repeated, brief sprints (HIint), and on performance during HIint are unknown and were investigated.
Methods
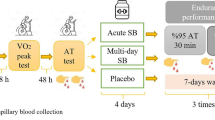
Seven recreationally active men participated in a double-blind, randomised, cross-over design, inhaling 1000 µg salbutamol or placebo. Participants cycled continuously for 5 min at 40 % \( {\dot{\text{V}}} \)O2peak and 60 % \( {\dot{\text{V}}} \)O2peak, then HIcont (90 s at 130 % \( {\dot{\text{V}}} \)O2peak), 20 min recovery, and then HIint (3 sets, 5 × 4 s sprints), with 30 min recovery.
Results
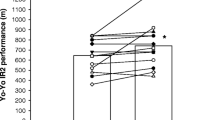
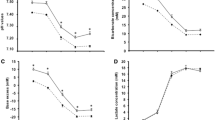
Plasma [K+]a increased throughout exercise and subsequently declined below baseline (P < 0.001). Plasma [K+]a was greater during HIcont than HIint (P < 0.001, HIcont 5.94 ± 0.65 vs HIint set 1, 4.71 ± 0.40 mM); the change in [K+]a from baseline (Δ[K+]a) was 2.6-fold greater during HIcont than HIint (P < 0.001). The Δ[K+] throughout the trial was less with salbutamol than placebo (P < 0.001, treatment main effect, 0.03 ± 0.67 vs 0.22 ± 0.69 mM, respectively); and remained less after correction for fluid shifts (P < 0.001). The Δ[K+] during HIcont was less after salbutamol (P < 0.05), but not during HIint. Blood lactate, plasma pH, and the work output during HIint did not differ between trials.
Conclusions
Inhaled salbutamol modulated the [K+]a rise across the trial, comprising intense continuous and intermittent exercise and recovery, lowering Δ[K+] during HIcont. The limited [K+]a changes during HIint suggest that salbutamol is unlikely to influence systemic [K+] during periods of intense effort in intermittent sports.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HIcont :
-
High-intensity continuous exercise
- HIint :
-
High-intensity intermittent exercise
- VO2peak :
-
Peak oxygen consumption
- [K+]a :
-
Arterial potassium concentration
- Δ[K+]a :
-
Change in [K+]a from baseline
- [K+]v :
-
Venous plasma [K+]
- ΔPVa :
-
Change in arterial plasma volume from rest
- NKA:
-
Na+, K+-ATPase
- WADA:
-
World Anti-Doping Agency
References
Atanasovska T, Petersen AC, Rouffet DM, Billaut F, Ng I, McKenna MJ (2014) Plasma K+ dynamics and implications during and following intense rowing exercise. J Appl Physiol 117(1):60–68. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01027.2013
Bennett JA, Tattersfield AE (1997) Time course and relative dose potency of systemic effects from salmeterol and salbutamol in healthy subjects. Thorax 52(5):458–464
Bishop D, Girard O, Mendez-Villanueva A (2011) Repeated-sprint ability—part II. Sports Med 41(9):741–756
Clark D, Lipworth B (1996) Effect of multiple actuations, delayed inhalation and antistatic treatment on the lung bioavailability of salbutamol via a spacer device. Thorax 51(10):981–984
Clausen T (2003) Na+-K+ pump regulation and skeletal muscle contractility. Physiol Rev 83(4):1269–1324
Clausen T (2013a) Excitation-induced exchange of Na+, K+, and Cl−in rat EDL muscle in vitro and in vivo: physiology and pathophysiology. J Gen Physiol 141(2):179–192
Clausen T (2013b) Quantification of Na+, K+ pumps and their transport rate in skeletal muscle: functional significance. J Gen Physiol 142(4):327–345
Clausen T, Flatman J (1980) β2-Adrenoceptors mediate the stimulating effect of adrenaline on active electrogenic na-k-transport in rat soleus muscle. Br J Pharmacol 68(4):749–755
Collomp K, Candau R, Collomp R, Carra J, Lasne F, Prefaut C, De Ceaurriz J (2000) Effects of acute ingestion of salbutamol during submaximal exercise. Int J Sports Med 21(7):480–484
Collomp K, Le Panse B, Portier H, Lecoq A, Jaffre C, Beaupied H, Richard O, Benhamou L, Courteix D, De Ceaurriz J (2005) Effects of acute salbutamol intake during a Wingate test. Int J Sports Med 26(7):513–517
Duffield R, Marino FE (2007) Effects of pre-cooling procedures on intermittent-sprint exercise performance in warm conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 100(6):727–735
Edner M, Jogestrand T (1990) Oral salbutamol decreases serum digoxin concentration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38(2):195–197
Goubault C, Perault M, Leleu E, Bouquet S, Legros P, Vandel B, Denjean A (2001) Effects of inhaled salbutamol in exercising non-asthmatic athletes. Thorax 56(9):675–679
Grove A, McFarlane L, Lipworth B (1995) Expression of the beta 2 adrenoceptor partial agonist/antagonist activity of salbutamol in states of low and high adrenergic tone. Thorax 50(2):134–138
Gullestad L, Hallen J, Sejersted O (1995) K+ balance of the quadriceps muscle during dynamic exercise with and without beta-adrenoceptor blockade. J Appl Physiol 78(2):513–523
Hallen J, Saltin B, Sejersted O (1996) K+ balance during exercise and role of beta-adrenergic stimulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 270(6):R1347–R1354
Hopkins SJ (1999) Drugs and pharmacology for nurses. Elsevier Health Sciences, UK
Hostrup M, Kalsen A, Bangsbo J, Hemmersbach P, Karlsson S, Backer V (2014) High-dose inhaled terbutaline increases muscle strength and enhances maximal sprint performance in trained men. Eur J Appl Physiol 114(12):2499–2508
Hostrup M, Kalsen A, Auchenberg M, Bangsbo J, Backer V (2016) Effects of acute and 2-week administration of oral salbutamol on exercise performance and muscle strength in athletes. Scand J Med Sci Sports 26(1):8–16
Juel C, Hellsten Y, Saltin B, Bangsbo J (1999) Potassium fluxes in contracting human skeletal muscle and red blood cells. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 276(1):R184–R188
Kalsen A, Hostrup M, Bangsbo J, Backer V (2014) Combined inhalation of beta2-agonists improves swim ergometer sprint performance but not high-intensity swim performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports 24(5):814–822
Katz A, Sahlin K, Juhlin-Dannfelt A (1985) Effect of beta-adrenoceptor blockade on H+ and K+ flux in exercising humans. J Appl Physiol 59(2):336–341
Kjaer M (1989) Epinephrine and some other hormonal responses to exercise in man: with special reference to physical training. Int J Sports Med 10(1):2–15
Koch S, Ahn JR, Koehle MS (2015) High-dose inhaled salbutamol does not improve 10-km cycling time trial performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47(11):2373–2379
Kowalchuk JM, Heigenhauser G, Lindinger MI, Obminski G, Sutton JR, Jones NL (1988) Role of lungs and inactive muscle in acid-base control after maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 65(5):2090–2096
Krustrup P, Mohr M, Steensberg A, Bencke J, Kjær M, Bangsbo J (2006) Muscle and blood metabolites during a soccer game: implications for sprint performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(6):1165–1174
Larsson K, Gavhed D, Larsson L, Holmér I, Jorfelt L, Ohlsén P (1997) Influence of a beta2-agonist on physical performance at low temperature in elite athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29(12):1631–1636
Le Panse B, Arlettaz A, Portier H, Lecoq AM, De Ceaurriz J, Collomp K (2007) Effects of acute salbutamol intake during supramaximal exercise in women. Br J Sports Med 41(7):430–434
Leitch A, Clancy L, Costello J, Flenley D (1976) Effect of intravenous infusion of salbutamol on ventilatory response to carbon dioxide and hypoxia and on heart rate and plasma potassium in normal men. BMJ 1(6006):365–367
Lindinger MI (1995) Potassium regulation during exercise and recovery in humans: implications for skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27(4):1011–1022
Lindinger MI, McKELVIE RS, Heigenhauser G (1995) K+ and Lac-distribution in humans during and after high-intensity exercise: role in muscle fatigue attenuation? J Appl Physiol 78(3):765–777
Lipworth B, McDevitt D, Struthers A (1989) Systemic beta-adrenoceptor responses to salbutamol given by metered-dose inhaler alone and with pear shaped spacer attachment: comparison of electrocardiographic, hypokalaemic and haemodynamic effects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 27(6):837–842
Mandelberg A, Krupnik Z, Houri S, Smetana S, Gilad E, Matas Z, Priel IE (1999) Salbutamol metered-dose inhaler with spacer for hyperkalemia: how fast? How safe? Chest J 115(3):617–622
McDonough AA, Youn JH (2005) Role of muscle in regulating extracellular [K+]. In: Seminars in nephrology, vol 5. Elsevier, UK, pp 335–342
McKelvie RS, Jones N, Heigenhauser G (1997) Effect of progressive incremental exercise and β-adrenergic blockade on erythrocyte ion concentrations. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 75(1):19–25
McKenna M, Schmidt T, Hargreaves M, Cameron L, Skinner S, Kjeldsen K (1993) Sprint training increases human skeletal muscle Na (+)-K (+)-ATPase concentration and improves K+ regulation. J Appl Physiol 75(1):173–180
McKenna MJ, Heigenhauser GJ, McKelvie RS, MacDougall JD, Jones NL (1997) Sprint training enhances ionic regulation during intense exercise in men. J Physiol 501(3):687–702
McKenna MJ, Gissel H, Clausen T (2003) Effects of electrical stimulation and insulin on Na+–K+-ATPase ([3H] ouabain binding) in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 547(2):567–580
McKenna MJ, Bangsbo J, Renaud JM (2008) Muscle K+, Na+, and Cl− disturbances and Na+-K+ pump inactivation: implications for fatigue. J Appl Physiol 104(1):288–295
Medbø J, Sejersted O (1990) Plasma potassium changes with high intensity exercise. J Physiol 421(1):105–122
Mohr M, Rasmussen P, Drust B, Nielsen B, Nybo L (2006) Environmental heat stress, hyperammonemia and nucleotide metabolism during intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 97(1):89–95
Mohr M, Krustrup P, Nielsen JJ, Nybo L, Rasmussen MK, Juel C, Bangsbo J (2007) Effect of two different intense training regimens on skeletal muscle ion transport proteins and fatigue development. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292(4):R1594–R1602
Mohr M, Nielsen JJ, Bangsbo J (2011) Caffeine intake improves intense intermittent exercise performance and reduces muscle interstitial potassium accumulation. J Appl Physiol 111(5):1372–1379
Newnham D, Wheeldon N, Lipworth B, McDevitt D (1993) Single dosing comparison of the relative cardiac beta 1/beta 2 activity of inhaled fenoterol and salbutamol in normal subjects. Thorax 48(6):656–658
Pluim BM, de Hon O, Staal JB, Limpens J, Kuipers H, Overbeek SE, Zwinderman AH, Scholten RJ (2011) β2-agonists and physical performance. Sports Med 41(1):39–57
Rolett E, Strange S, Sjogaard G, Kiens B, Saltin B (1990) Beta 2-adrenergic stimulation does not prevent potassium loss from exercising quadriceps muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 258(5):R1192–R1200
Sejersted OM, Sjøgaard G (2000) Dynamics and consequences of potassium shifts in skeletal muscle and heart during exercise. Physiol Rev 80(4):1411–1481
Signorile JF, Kaplan TA, Applegate B, Perry AC (1992) Effects of acute inhalation of the bronchodilator, albuterol, on power output. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24(6):638–642
Sostaric SM, Skinner SL, Brown MJ, Sangkabutra T, Medved I, Medley T, Selig SE, Fairweather I, Rutar D, McKenna MJ (2006) Alkalosis increases muscle K+ release, but lowers plasma [K+] and delays fatigue during dynamic forearm exercise. J Physiol 570(1):185–205
Struthers A, Quigley C, Brown M (1988) Rapid changes in plasma potassium during a game of squash. Clin Sci 74:397–401
Tobin AE, Pellizzer AM, Santamaria JD (2006) Mechanisms by which systemic salbutamol increases ventilation. Respirology 11(2):182–187
Van Baak M, Mayer L, Kempinski R, Hartgens F (2000) Effect of salbutamol on muscle strength and endurance performance in nonasthmatic men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(7):1300–1306
WADA (2016) 2016 List of prohibited substances and methods. http://list.wada-ama.org/list/s3-beta-2-agonists/#salbutamol. Accessed 17 June 2016
Whyte K, Addis G, Whitesmith R, Reid J (1987) The mechanism of salbutamol-induced hypokalaemia. Br J Clin Pharmacol 23(1):65–71
Wylie LJ, Mohr M, Krustrup P, Jackman SR, Ermιdis G, Kelly J, Black MI, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Jones AM (2013) Dietary nitrate supplementation improves team sport-specific intense intermittent exercise performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 113(7):1673–1684
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants for their contributions and Dr Tania Atanasovska, Mr Trevor Farr, Mr Bradley Gatt and Ms Jessica Meilak, who assisted in some trials. We acknowledge assistance by Ms Maria Loder from St Vincent’s Hospital, Melbourne, in the use of salbutamol and sourcing the placebo propellant. Dr Aaron Petersen was part-funded through the Australian Government Collaborative Research Network Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Michael Lindinger.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altarawneh, M.M., Petersen, A., Smith, R. et al. Salbutamol effects on systemic potassium dynamics during and following intense continuous and intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 116, 2389–2399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3481-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3481-0