Abstract
Purpose
Decreases in brachial blood pressure (BP) may occur for several hours following a bout of exercise. Although aortic backward waves predict cardiovascular damage independent of brachial BP, whether decreases in aortic backward waves also occur post-exercise in young-to-middle-aged hypertensives, the extent to which these changes exceed brachial BP changes, and the best method of identifying these changes is uncertain.
Methods
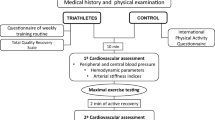
We examined aortic function at baseline and 15-min post-exercise in 20 pre-hypertensive or hypertensive men and women (age 45 ± 7 years). Central aortic pressure, forward (Pf) and backward (Pb) wave pressures, the reflection index (RI) and augmentation pressure (AP) and index (AIx) were determined using applanation tonometry, and SphygmoCor software.
Results
Decreases in central aortic (p < 0.001) but not brachial systolic BP and pulse pressure (PP) occurred post-exercise. In addition, decreases in post-exercise (baseline versus post-exercise) Pb (19 ± 4 vs 13 ± 3 mm Hg p < 0.0001), RI (72.9 ± 22.1 vs 47.6 ± 12.8 %, p < 0.0001), AIx (26.3 ± 10.8 vs 7.8 ± 11.6 %, p < 0.0001) and AP (9.9 ± 3.9 vs 2.8 ± 3.9 mm Hg, p < 0.0001), but not Pf, were noted. However, decreases in AIx were not correlated with decreases in Pb, and whilst decreases in aortic PP correlated with decreases in Pb (p < 0.0001), no correlations were noted with decreases in AP or AIx.
Conclusion
In young-to-middle-aged pre-hypertensive and hypertensive individuals, aortic backward waves decrease post-exercise; this change is not reflected in brachial BP measurements and is poorly indexed by measures of pressure augmentation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Δ:
-
Change in
- AIx:
-
Aortic augmentation index
- AP:
-
Aortic augmentation pressure
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiograph
- Pb:
-
Aortic backward wave pressure
- Pf:
-
Aortic forward wave pressure
- PP:
-
Pulse pressure
- PPc:
-
Central aortic pulse pressure
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- RI:
-
Aortic reflection index
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SBPc:
-
Central aortic systolic blood pressure
- VO2peak :
-
Peak oxygen consumption
References
Aizawa K, Petrella RJ (2008) Acute and chronic impact of dynamic exercise on arterial stiffness in older hypertensives. Open Cardiovasc Med J 2:3–8. doi:10.2174/1874192400802010003
Aizawa K, Mendelsohn ME, Overend TJ, Petrella RJ (2009) Effect of upper body aerobic exercise on arterial stiffness in older adults. J Aging Phys Act 17:468–478
Babcock MC, Lefferts WK, Hughes WE, Fitzgerald KL, Leyer BK, Redmond JG, Heffernan KS (2015) Acute effect of high-intensity cycling exercise on carotid artery hemodynamic pulsatility. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:1037–1045. doi:10.1007/s00421-014-3084-6
Booysen HL, Woodiwiss AJ, Sibiya MJ, Hodson B, Raymond A, Libhaber E, Sareli P, Norton GR (2015) Indexes of aortic pressure augmentation markedly underestimate the contribution of reflected waves toward variations in aortic pressure and left ventricular mass. Hypertension 65:540–546. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04582
Boutcher YN, Hopp JP, Boutcher SH (2011) Acute effect of a single bout of aerobic exercise on vascular and baroreflex function in young males with a family history of hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 25:311–319. doi:10.1038/jhh.2010.62
Cecelja M, Jiang B, McNeill K, Kato B, Ritter J, Spector T, Chowienczyk P (2009) Increased wave reflection rather than central arterial stiffness is the main determinant of raised pulse pressure in women and relates to mismatch in arterial dimensions: a twin study. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:695–703. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.068
Chandrakumar D, Boutcher SH, Boutcher YN (2015) Acute exercise effects on vascular and autonomic function in overweight men. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 55:91–102
Chirinos JA, Zambrano JP, Chakko S, Veerani A, Schob A, Willens HJ, Perez G, Mendez AJ (2005) Aortic pressure augmentation predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with established coronary artery disease. Hypertension 45:980–985. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000165025.16381.44
Chirinos JA, Kips JG, Jacobs DR Jr, Brumback L, Duprez DA, Kronmal R, Bluemke DA, Townsend RR, Vermeersch S, Segers P (2012) Arterial wave reflections and incident cardiovascular events and heart failure: MESA (Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). J Am Coll Cardiol 60:2170–2177. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2012.07.054
Cleroux J, Kouame N, Nadeau ADC, Lacourciere Y (1992) Aftereffects of exercise on regional and systemic hemodynamics in hypertension. Hypertension 19:183–191. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.19.2.183
Collier SR, Diggle MD, Heffernan KS, Kelly EE, Tobin MM, Fernhall B (2010) Changes in arterial distensibility and flow-mediated dilation after acute resistance vs. aerobic exercise. J Strength Cond Res 24:2846–2852. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181e840e0
Doonan RJ, Scheffler P, Yu A, Egiziano G, Mutter A, Bacon S, Carli F, Daskalopoulos ME, Daskalopoulou SS (2011) Altered arterial stiffness and subendocardial viability ratio in young healthy light smokers after acute exercise. PLoS One 6:e26151. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026151
Fok H, Guilcher A, Li Y, Brett S, Shah A, Clapp B, Chowienczyk P (2014) Augmentation pressure is influenced by ventricular contractility/relaxation dynamics: novel mechanism of reduction of pulse pressure by nitrates. Hypertension 63:1050–1055. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02955
Forjaz CL, Matsudaira Y, Rodrigues FB, Nunes N, Negrão CE (1998) Post-exercise changes in blood pressure, heart rate and rate pressure product at different exercise intensities in normotensive humans. Braz J Med Biol Res 31:1247–1255. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X1998001000003
Gkaliagkous E, Gavriilaki E, Nikolaidou B, Triantafyllou G, Douma S (2014) Exercise-induced pulse wave velocity changes in untreated patients with essential hypertension: the effect of an angiotensin receptor antagonist. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 16:482–487. doi:10.1111/jch.12340
Guidry MA, Blanchard BE, Thompson PD, Maresh CM, Seip RL, Taylor AL, Pescatello LS (2006) The influence of short and long duration on the blood pressure response to an acute bout of dynamic exercise. Am Heart J 151:1322. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2006.03.010 e5–12
Hanssen H, Nussbaumer M, Moor C, Cordes M, Schindler C, Schmidt-Trucksass A (2015) Acute effects of interval versus continuous endurance training on pulse wave reflection in young men. Atherosclerosis 238:399–406. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.038
Heffernan KS, Collier SR, Kelly EE, Jae SY, Fernhall B (2007) Arterial stiffness and baroreflex sensitivity following bouts of aerobic and resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med 28:197–203. doi:10.1055/s-2006-924290
Hughes AD, Park C, Davies J, Francis D, McG Thom SA, Mayet J, Parker KH (2013) Limitations of augmentation index in the assessment of wave reflection in normotensive healthy individuals. PLoS One 8:e59371. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059371
Kenney MJ, Seals DR (1993) Postexercise hypotension key features, mechanisms, and clinical significance. Hypertension 22:653–664. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.22.5.653
Kips JG, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, Westerhof BE, Gillebert TC, Van Bortel LM, Segers P (2009) Evaluation of noninvasive methods to assess wave reflection and pulse transit time from the pressure waveform alone. Hypertension 53:142–149. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.123109
Lefferts WK, Augistine JA, Heffernan KS (2014) Effect of acute resistance exercise on carotid artery stiffness and cerebral blood flow pulsatility. Front Physiol 5:101. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00101
London GM, Blacher J, Pannier B, Guérin AP, Marchais SJ, Safar ME (2001) Arterial wave reflections and survival in end-stage renal failure. Hypertension 38:434–438. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.38.3.434
MacDonald JR, Rosenfeld JM, Tarnopolsky MA, Hogben CD, Ballantyne CS, MacDougall JD (2002) Post exercise hypotension is not mediated by the serotonergic system in borderline hypertensive individuals. J Hum Hypertens 6:33–39. doi:10.1038/sj/jhh/1001290
Müller J, Wilms M, Oberhoffer R (2015) Acute effects of submaximal endurance training on arterial stiffness in healthy middle- and long-distance runners. J Clin Hypertens 17:371–374. doi:10.1111/jch.12530
Munir S, Jiang B, Guilcher A, Brett S, Redwood S, Marber M, Chowienczyk P (2008) Exercise reduces arterial pressure augmentation through vasodilation of muscular arteries in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H1645–H1650. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01171.2007
Norton GR, Majane OHI, Maseko MJ, Libhaber C, Redelinghuys M, Kruger D, Veller M, Sareli P, Woodiwiss AJ (2012) Brachial blood pressure-independent relations between radial late systolic shoulder-derived aortic pressures and target organ changes. Hypertension 59:885–892. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.187062
Pescatello LS, Kulikowich JM (2001) The aftereffects of dynamic exercise on ambulatory blood pressure. Med Sci Sports Exercise 33:1855–1861. doi:10.1097/00005768-200111000-00009
Pescatello LS, Franklin BA, Fagard R, Farquhar WB, Kelley GA, Chester A, Ray CA (2004) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and hypertension. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:533–553. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000115224.88514.3A
Qasem A, Avolio A (2008) Determination of aortic pulse wave velocity from waveform decomposition of the central aortic pressure pulse. Hypertension 51:188–195. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.092676
Segers P, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, De Bacquer D, Van Bortel LM, De Backer G, Gillebert TC, Verdonck PR (2007) Assessment of pressure wave reflection: getting the timing right! Physiol Meas 28:1045–1056. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/28/9/006
Sharman JE, McEniery CM, Dhakam ZR, Coombes JS, Wilkinson IB, Cockcroft JR (2007) Pulse pressure amplification during exercise is significantly reduced with age and hypercholesterolemia. J Hypertens 25:1249–1254. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3280be5911
Shiburi CP, Staessen JA, Maseko M, Wojciechowska W, Thijs L, Van Bortel LM, Woodiwiss AJ, Norton GR (2006) Reference values for SphygmoCor measurements in South Africans of African ancestry. Am J Hypertens 19:40–46. doi:10.1016/amjhyper.2005.06.018
Sibiya MJ, Woodiwiss AJ, Booysen HL, Raymond A, Millen AM, Maseko MJ, Majane OH, Sareli P, Libhaber E, Norton GR (2015) Reflected rather than forward wave pressures account for brachial pressure-independent relations between aortic pressure and end-organ changes in an African community. J Hypertens 33:2083–2090. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000000682
Tabara Y, Yuasa T, Oshiumi A, Kobayashi T, Miyawaki Y, Miki T, Kohara K (2007) Effects of acute and long-term aerobic exercise on arterial stiffness in the elderly. Hypertens Res 30:895–902. doi:10.1291/hypres.30.895
Teixeira L, Ritti-Dias RM, Tinucci T Mion JD, Forjaz CL (2011) Post-concurrent exercise hemodynamics and cardiac autonomic modulation. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:2069–2078. doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1811-1
Thompson PD, Crouse SF, Goodpaster B, Kelley D, Moyna N, Pescatello L (2001) The acute versus the chronic response to exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:S438–S445. doi:10.1097/00005768-200106001-00012
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, O’Rourke MF, Safar ME, Baou K, Stefanadis C (2010a) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with central haemodynamics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 31:1865–1871. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq024
Vlachopoulos C, Kardara D, Anastasakis A, Baou K, Terentes-Printzios D, Tousoulis D, Stefanadis C (2010b) Arterial stiffness and wave reflections in marathon runners. Am J Hypertens 23:974–979. doi:10.1038/ajh.2010.99
Wang KL, Cheng HM, Sung SH, Chuang SY, Li CH, Spurgeon HA, Ting CT, Najjar SS, Lakatta EG, Yin FC, Chou P, Chen CH (2010) Wave reflection and arterial stiffness in the prediction of 15-year all-cause and cardiovascular mortalities: a community-based study. Hypertension 55:799–805. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.139964
Weber T, Auer J, O’Rourke MF, Kvas E, Lassnig E, Lamm G, Stark N, Rammer M, Eber B (2005) Increased arterial wave reflections predict severe cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Eur Heart J 26:2657–2663. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi504
Weber T, Wassertheurer S, Rammer M, Haiden A, Hametner B, Eber B (2012) Wave reflections, assessed with a novel method for pulse wave separation, are associated with end-organ damage and clinical outcomes. Hypertension 60:534–541. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.194571
Westerhof BE, Guelen I, Westerhof N, Karemaker JM, Avolio A (2006) Quantification of wave reflection in the human aorta from pressure alone: a proof of principle. Hypertension 48:595–601. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000238330.08894.17
Yan H, Ranadive SM, Heffernan KS, Lane AD, Kappus RM, Cook MD, Wu PT, Sun P, Harvey IS, Woods JA, Wilund KR, Fernhall B (2014) Hemodynamic and arterial stiffness differences between African-Americans and Caucasians after maximal exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306:H60–H68. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00710.2013
Yoon ES, Jung SJ, Cheun SK, Oh YS, Kim SH, Jae SY (2010) Effects of acute resistance exercise on arterial stiffness in young men. Korean Circ J 40:16–22. doi:10.4070/kcj.2010.40.1.16
Acknowledgments
This study would not have been possible without the voluntary collaboration of the participants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Sources of funding
This study was supported by the University Research Council of the University of the Witwatersrand, the South African National Research Foundation, the Carnegie Corporation and the Ernst and Ethel Eriksen Trust.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Pagani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millen, A.M.E., Woodiwiss, A.J. & Norton, G.R. Post-exercise effects on aortic wave reflection derived from wave separation analysis in young- to middle-aged pre-hypertensives and hypertensives. Eur J Appl Physiol 116, 1321–1329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3391-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3391-1