Abstract
This article reviews the concept of maximal oxygen consumption (\(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\)) from the perspective of multifactorial models of \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) limitation. First, I discuss procedural aspects of \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) measurement: the implications of ramp protocols are analysed within the theoretical work of Morton. Then I analyse the descriptive physiology of \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\), evidencing the path that led to the view of monofactorial cardiovascular or muscular \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) limitation. Multifactorial models, generated by the theoretical work of di Prampero and Wagner around the oxygen conductance equation, represented a radical change of perspective. These models are presented in detail and criticized with respect to the ensuing experimental work. A synthesis between them is proposed, demonstrating how much these models coincide and converge on the same conclusions. Finally, I discuss the cases of hypoxia and bed rest, the former as an example of the pervasive effects of the shape of the oxygen equilibrium curve, the latter as a neat example of adaptive changes concerning the entire respiratory system. The conclusion is that the concept of cardiovascular \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) limitation is reinforced by multifactorial models, since cardiovascular oxygen transport provides most of the \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) limitation, at least in normoxia. However, the same models show that the role of peripheral resistances is significant and cannot be neglected. The role of peripheral factors is greater the smaller is the active muscle mass. In hypoxia, the intervention of lung resistances as limiting factors restricts the role played by cardiovascular and peripheral factors.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Angular coefficient of Whipp’s model of a ramp test
- b :
-
Y-intercept of Whipp’s model of a ramp test
- \({\it{C}}_{\rm a}{\text {O}}_{2}\) :
-
Arterial oxygen concentration
- \(C_{\overline{\text{v}}}{\text{O}}_{2}\) :
-
Mixed venous oxygen concentration
- Dempsey effect:
-
Desaturation of arterial blood at maximal exercise in subjects with high \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\)
- D LO2 :
-
Lung diffusion capacity for oxygen
- D tO2 :
-
Tissue diffusion capacity for oxygen
- F :
-
Fraction
- F IO2 :
-
Inspired oxygen fraction
- F L :
-
Pulmonary fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- F m :
-
Mitochondrial fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- F p :
-
Peripheral fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- F Q :
-
Cardiovascular fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- F t :
-
Tissue fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- F V :
-
Ventilatory fraction of oxygen flow limitation
- G :
-
Conductance
- G L :
-
Pulmonary conductance of oxygen flow
- G m :
-
Mitochondrial conductance of oxygen flow
- G p :
-
Peripheral conductance of oxygen flow
- G Q :
-
Cardiovascular conductance of oxygen flow
- G T :
-
Total conductance of oxygen flow
- G t :
-
Tissue conductance of oxygen flow
- G V :
-
Ventilatory conductance of oxygen flow
- k :
-
Velocity constant
- K p :
-
Dimensionless constant relating \(P_{\overline{\text{v}}}{\text{O}}_{2}\) and \(P_{\overline{\text{c}}} {\text{O}}_{2}\)
- K W :
-
Wagner’s constant (slope of diffusion line)
- P AO2 :
-
Mean alveolar oxygen partial pressure
- P aO2 :
-
Arterial oxygen partial pressure
- P b :
-
Barometric pressure
- \(P_{\overline{\text{c}}}{\text{O}}_{2}\) :
-
Mean capillary oxygen partial pressure
- P IO2 :
-
Inspired oxygen partial pressure
- P mO2 :
-
Mitochondrial oxygen partial pressure
- \({\it{P}}_{\overline{\text{v}}}{\text{O}}_2\) :
-
Mixed venous oxygen partial pressure
- \(\dot{Q}\) :
-
Cardiac output
- \(\dot{Q}_{\text{max} }\) :
-
Maximal cardiac output
- \({\dot{Q}}_{\rm a}{\text {O}}_{2}\) :
-
Oxygen flow in arterial blood (systemic oxygen delivery)
- R :
-
Resistance
- R L :
-
Pulmonary resistance to oxygen flow
- R m :
-
Mitochondrial resistance to oxygen flow
- R p :
-
Peripheral resistance to oxygen flow
- R Q :
-
Cardiovascular resistance to oxygen flow
- R T :
-
Total resistance to oxygen flow
- R t :
-
Tissue resistance to oxygen flow
- R V :
-
Ventilatory resistance to oxygen flow
- S :
-
Ramp slope
- S aO2 :
-
Arterial oxygen saturation
- STPD:
-
Standard temperature and pressure dry
- t :
-
Time
- T :
-
Exhaustion time in a ramp test
- T S :
-
Step duration in a ramp test
- \(\dot{V}\) :
-
Gas flow
- \(\dot{V}_{A}\) :
-
Alveolar ventilation
- \(\dot{V}_{\text{A}} /\dot{Q}\) :
-
Ventilation/perfusion ratio
- V m :
-
Mitochondrial volume
- v :
-
Speed
- \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2}\) :
-
Oxygen uptake
- \(\dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} }\) :
-
Maximal oxygen consumption
- \(\dot{w}\) :
-
Mechanical power
- \(W^{\prime}\) :
-
Work carried out above the critical power in a ramp test
- \(\dot{w}_{\text{cr}}\) :
-
Critical power
- \(\dot{w}_{\text{max} }\) :
-
Maximal mechanical aerobic power
- \(\dot{w}_{\text{peak}}\) :
-
Peak power of a ramp test
- β b :
-
Oxygen transfer coefficient for blood
- β g :
-
Oxygen transfer coefficient for air
- Δ:
-
Before a variable, designates a change in the value of that variable
References
Adami A, Sivieri A, Moia C, Perini R, Ferretti G (2013) Effects of step duration in incremental ramp protocols on peak power and maximal oxygen consumption. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:2647–2653
Aghemo P, Piñera-Limas F, Sassi G (1971) Maximal aerobic power in primitive Indians. Int Z angew Physiol 29:337–342
Amann M, Subudhi A, Foster C (2004) Influence of testing protocol on ventilatory thresholds and cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:613–622
Andersen P, Henriksson J (1977) Capillary supply of the quadriceps skeletal muscle of man: adaptive response to exercise. J Physiol 270:677–690
Andersen P, Saltin B (1985) Maximal perfusion of skeletal muscle in man. J Physiol 366:233–249
Andersen KL, Bolstad A, Loyning A, Irving L (1960) Physical fitness of arctic Indians. J Appl Physiol 15:645–648
Armstrong RB, Delp MD, Goljan MF, Laughlin MH (1987) Distribution of blood flow in muscles of miniature swine during exercise. J Appl Physiol 62:1285–1298
Aspenes ST, Nilsen TI, Skaug EA, Bertheussen GF, Ellingsen Ø, Vatten L, Wisløff U (2011) Peak oxygen uptake and cardiovascular risk factors in 4631 healthy women and men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1465–1473
Astorino TA, Allen RP, Roberson DW, Jurancich M (2012) Effect of high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular function, \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \), and muscular force. J Strength Cond Res 26:398–407
Åstrand PO (1955) New records in human power. Nature 176:922–923
Åstrand PO (1956) Human physical fitness with special reference to sex and age. Physiol Rev 36:307–335
Åstrand I (1960) Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 169:1–92
Åstrand PO, Saltin B (1961) Maximal oxygen uptake and heart rate in various types of muscular activity. J Appl Physiol 16:977–981
Åstrand PO, Rodahl K, Dahl HA, Strømme SB (2003) Textbook of work physiology. Physiological bases of exercise, 4th ed., Human Kinetics, Champaign
Audran M, Gareau R, Matecki S, Durand F, Chenard C, Sicart M, Marion B, Bressolle F (1999) Effects of erythropoietin administration in training athletes and possible indirect detection in doping control. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:639–645
Bailey SJ, Romer LM, Kelly J, Wilkerson DP, DiMenna FJ, Jones AM (2010) Inspiratory muscle training enhances pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics and high-intensity exercise tolerance in humans. J Appl Physiol 109:457–468
Bannister RG, Cunningham DJC (1954) The effects on the respiration and performance during exercise of adding oxygen to the inspired air. J Physiol 125:118–137
Baumgartner WA Jr, Jaryszak EM, Peterson AJ, Presson RG Jr, Wagner WW Jr (2003) Heterogeneous capillary recruitment among adjoining alveoli. J Appl Physiol 95:469–476
Benoit H, Busso T, Castells J, Denis C, Geyssant A (1995) Influence of hypoxic ventilatory response on arterial O2 saturation during maximal exercise in acute hypoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 72:101–105
Berg HE, Dudley GA, Hather B, Tesch PA (1993) Work capacity and metabolic and morphologic characteristics of the human quadriceps muscle in response to unloading. Clin Physiol 13:337–347
Bergh U, Ekblom B (1979) Physical performance and peak aerobic power at different body temperatures. J Appl Physiol 46:885–889
Bergh U, Kanstrup IL, Ekblom B (1976) Maximal oxygen uptake during exercise with various combinations of arm and leg work. J Appl Physiol 41:191–196
Berglund B, Ekblom B (1991) Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment on blood pressure and some haematological parameters in healthy men. J Intern Med 229:125–130
Berglund B, Hemmingsson P (1987) Effect of reinfusion of autologous blood in cross-country skiers. Int J Sports Med 8:231–233
Billat V, Lepretre PM, Heugas AM, Laurence MH, Salim D, Koralsztein JP (2003) Training and bioenergetic characteristics in elite male and female Kenyan runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:297–304
Blomqvist CG, Saltin B (1983) Cardiovascular adaptations to physical training. Annu Rev Physiol 45:169–189
Booth FW (1982) Effect of limb immobilization on skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 52:1113–1118
Booth FW, Roberts CK, Laye MJ (2012) Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases. Compr Physiol 2:1143–1211
Bosch AN, Goslin BR, Noakes TD, Dennis SC (1990) Physiological differences between black and white runners during a treadmill marathon. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:68–72
Bouchard C (2012) Genomic predictors of trainability. Exp Physiol 97:347–352
Bouchard C, An P, Rice T, Skinner JS, Wilmore JH, Gagnon J, Pérusse L, Leon AS, Rao DC (1999) Familial aggregation of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) response to exercise training: results from the HERITAGE Family Study. J Appl Physiol 87:1003–1008
Bouchard C, Rankinen T, Timmons JA (2011a) Genomics and genetics in the biology of adaptation to exercise. Compr Physiol 1:1603–1648
Bouchard C, Sarzynski MA, Rice TK, Kraus WE, Church TS, Sung YJ, Rao DC, Rankinen T (2011b) Genomic predictors of the maximal O2 uptake response to standardized exercise training programs. J Appl Physiol 110:1160–1170
Breil FA, Weber SN, Koller S, Hoppeler H, Vogt M (2010) Block training periodization in alpine skiing: effects of 11-day HIT on VO2max and performance. Eur J Appl Physiol 109:1077–1086
Bringard A, Pogliaghi S, Adami A, De Roia G, Lador F, Lucini D, Pizzinelli P, Capelli C, Ferretti G (2010) Cardiovascular determinants of maximal oxygen consumption in upright and supine posture at the end of prolonged bed rest in humans. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 172:53–62
Brink-Elfegoun T, Kaijser L, Gustafsson T, Ekblom B (2007) Maximal oxygen uptake is not limited by a central nervous system governor. J Appl Physiol 102:781–786
Brodal P, Ingjer F, Hermansen L (1977) Capillary supply of skeletal muscle fibers in untrained and endurance-trained men. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 232:H705–H712
Brooks GA (1985) Anaerobic threshold: review of the concept and directions for future research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 17:22–31
Buchfuhrer MJ, Hansen JE, Robinson TE, Sue DY, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ (1983) Optimizing the exercise protocol for cardio-pulmonary assessment. J Appl Physiol 55:1558–1564
Buick FJ, Gledhill N, Froese AB, Spriet LL, Meyers EC (1980) Effect of induced erythrocythemia on aerobic work capacity. J Appl Physiol 48:636–642
Burnley M, Roberts C, Thatcher R, Doust JH (2006) Influence of blood donation on O2 uptake on-kinetics, peak O2 uptake and time to exhaustion during severe-intensity exercise. Exp Physiol 91:499–509
Burtscher M, Nachbauer W, Wilber R (2011) The upper limit of aerobic power in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:2625–2628
Buskirk ER, Hodgson JL (1987) Age and aerobic power: the rate of change in men and women. Fed Proc 46:1824–1829
Calbet JAL, Jensen-Urstad M, Van Hall G, Holmberg HC, Rosdahl H, Saltin B (2004) Maximal muscular vascular conductances during whole body upright exercise in humans. J Physiol 558:319–331
Calbet JA, Gonzalez-Alonso J, Helge JW, Søndergaard H, Munch-Andersen T, Boushel R, Saltin B (2007) Cardiac output and leg and arm blood flow during incremental exercise to exhaustion on the cycle ergometer. J Appl Physiol 103:969–978
Calbet JAL, Rådegran G, Boushel R, Saltin (2009) On the mechanisms that limit oxygen uptake during exercise in acute and chronic hypoxia: role of muscle mass. J Physiol 587:477–490
Camus G, Atchou G, Bruckner JC, Giezendanner D, di Prampero PE (1988) Slow upward drift of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) during constant-load cycling in untrained subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 58:197–202
Capelli C, di Prampero PE (1995) Effects of altitude on top speeds during 1 h unaccompanied cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 71:469–471
Capelli C, Schena F, Zamparo P, Dal Monte A, Faina M, di Prampero PE (1998) Energetics of best performances in track cycling. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:614–624
Capelli C, Antonutto G, Azabji-Kenfack M, Cautero M, Lador F, Moia C, Tam E, Ferretti G (2006) Factors determining the time course of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) decay during bedrest: implications for \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) limitation. Eur J Appl Physiol 98:152–160
Cardus J, Marrades RM, Roca J, Barbera JA, Diaz O, Mascians JR, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Wagner PD (1998) Effect of FIO 2 on leg \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) during cycle ergometry in sedentary subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:697–703
Ceaser TG, Fitzhugh EC, Thompson DL, Bassett DR Jr (2013) Association of physical activity, fitness, and race: NHANES 1999–2004. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:286–293
Celsing F, Svedenhag J, Pihlstedt P, Ekblom B (1987) Effects of anaemia and stepwise-induced polycythaemia on maximal aerobic power in individuals with high and low haemoglobin concentrations. Acta Physiol Scand 129:47–54
Cerretelli P (1976) Limiting factors to oxygen transport on Mount Everest. J Appl Physiol 40:658–667
Cerretelli P (1980) Gas exchange at high altitude. In: West JB (ed) Pulmonary gas exchange, vol II. Academic Press, New York, pp 97–147
Cerretelli P, di Prampero PE (1987) Gas exchange in exercise. In: Farhi LE, Tenney SM (eds) Handbook of physiology. The respiratory system III, vol 4: gas exchange. The American Physiological Society, Bethesda, pp 297–339
Cerretelli P, Hoppeler H (1996) Morphologic and metabolic response to chronic hypoxia. In: Fregly MJ, Blatteis CM (eds) Handbook of physiology. Environmental physiology, sect. 4, vol II. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1155–1181
Cerretelli P, Margaria R (1961) Maximum oxygen consumption at altitude. Int Z Angew Physiol 18:460–464
Cerretelli P, Pendergast DR, Paganelli WC, Rennie DW (1979) Effects of specific muscle training on \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \)-on response and early blood lactate. J Appl Physiol 47:761–769
Chan OL, Duncan MT, Sundsten JW, Thinakaran T, Noh MN, Klissouras V (1976) The maximum aerobic power of the Temiars. Med Sci Sports 8:235–238
Chatterjee S, Saha SK, Saha D, Nag SK (1991) Maximal aerobic capacity of Bengali girl athletes of different sports activities. Jpn J Physiol 41:397–411
Chidnok W, Dimenna FJ, Bailey SJ, Burnley M, Wilkerson DP, Vanhatalo A, Jones AM (2013) \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) is not altered by self-pacing during incremental exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:529–539
Clark AR, Tawhai MH, Hoffman EA, Burrowes KS (2011) The interdependent contributions of gravitational and structural features to perfusion distribution in a multiscale model of the pulmonary circulation. J Appl Physiol 110:943–955
Clausen JP (1977) Effect of physical training on cardiovascular adjustments to exercise in man. Physiol Rev 57:779–815
Clausen JP, Klausen K, Rasmussen B, Trap-Jensen J (1973) Central and peripheral circulation changes after training of arms and legs. Am J Physiol 225:675–682
Convertino VA (1996) Exercise and adaptation to microgravity environments. In: Fregly MJ, Blatteis CM (eds) Handbook of physiology. Environmental physiology, sect. 4, vol I. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 815–843
Convertino VA, Hung J, Goldwater DJ, Debusk RF (1982) Cardiovascular responses to exercise in middle age men after 10 days of bed-rest. Circulation 65:134–140
Convertino VA, Goldwater DJ, Sandler H (1986) Bed rest induced peak \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) reduction associated with age, gender and aerobic capacity. Aviat Space Environ Med 57:17–22
Costill DL, Daniels J, Evans W, Fink W, Krahenbuhl G, Saltin B (1976) Skeletal muscle enzymes and fiber composition in male and female track athletes. J Appl Physiol 40(149–154):67
Cottin F, Médigue C, Papelier Y (2008) Effect of heavy exercise on spectral baroreflex sensitivity, heart rate, and blood pressure variability in well-trained humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1150–H1155
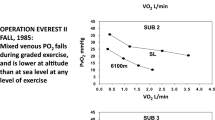
Cymerman A, Reeves JT, Sutton JR, Rock PB, Groves BM, Malconian MK, Young PM, Wagner PD, Houston CM (1989) Operation Everest II: maximal oxygen uptake at extreme altitude. J Appl Physiol 66:2446–2453
Daussin FN, Ponsot E, Dufour SP, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Doutreleau S, Geny B, Piquard F, Richard R (2007) Improvement of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) by cardiac output and oxygen extraction adaptation during intermittent versus continuous endurance training. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:377–383
Davies CTM, Sargeant AJ (1974) Effects of training on the physiological responses of one- and two-leg work. J Appl Physiol 38:377–381
Davies CTM, Barnes C, Fox RH, Osikuto RO, Samueloff AS (1972) Ethnic differences in physical working capacity. J Appl Physiol 33:726–732
Dekerle J, Mucci P, Carter H (2012) Influence of moderate hypoxia on tolerance to high-intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:327–335
Dempsey JA, Wagner PD (1999) Exercise—induced arterial hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 87:1997–2006
Dempsey JA, Hanson PG, Henderson KS (1984) Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in healthy human subjects at sea level. J Physiol 355:161–175
Dempsey JA, McKenzie DC, Haverkamp HC, Eldridge MW (2008) Update in the understanding of respiratory limitations to exercise performance in fit, active adults. Chest 134:613–622
di Prampero PE (1981) Energetics of muscular exercise. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 89:143–222
di Prampero PE (1985) Metabolic and circulatory limitations to \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) at the whole animal level. J Exp Biol 115:319–331
di Prampero PE (1986) The energy cost of human locomotion on land and in water. Int J Sports Med 7:55–72
di Prampero PE (2000) Cycling on Earth, in space, on the Moon. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:345–360
di Prampero PE (2003) Factors limiting maximal performance in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:420–429
di Prampero PE, Cerretelli P (1969) Maximal muscular power (aerobic and anaerobic) in African natives. Ergonomics 12:51–59
di Prampero PE, Ferretti G (1990) Factors limiting maximal oxygen consumption in humans. Respir Physiol 80:113–128
di Prampero PE, Ferretti G (1999) The energetics of anaerobic muscle metabolism: a reappraisal of older and recent concepts. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 118:103–115
di Prampero PE, Piñera-Limas F, Sassi G (1970) Maximal muscular power, aerobic and anaerobic, in 116 athletes performing at the XIXth Olympic Games in Mexico. Ergonomics 13:665–674
di Prampero PE, Cortili G, Mognoni P, Saibene F (1979) Equation of motion of a cyclist. J Appl Physiol 47:201–206
Dill DB, Adams WC (1971) Maximal oxygen uptake at sea level and at 3,090 m altitude in high school champion runners. J Appl Physiol 30(854–859):80
Dill DB, Myhre LG, Phillips EE, Brown DK (1966) Work capacity in acute exposures to altitude. J Appl Physiol 21:1168–1176
Downey AE, Chenoweth LM, Townsend DK, Ranum JD, Ferguson CS, Harms CA (2007) Effects of inspiratory muscle training on exercise responses in normoxia and hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 156:137–146
Duncan MT, Horvath SM (1988) Physiological adaptations to thermal stress in tropical Asians. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:540–544
Duncan GE, Howley ET, Johnson BN (1997) Applicability of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) criteria: discontinuous versus continuous protocols. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:273–278
Duncan GE, Li SM, Zhou XH (2005) Cardiovascular fitness among U.S. adults: NHANES 1999–2000 and 2001–2002. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:1324–1328
Dunham C, Harms CA (2012) Effects of high-intensity interval training on pulmonary function. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:3061–3068
Edwards AM, Cooke CB (2004) Oxygen uptake kinetics and maximal aerobic power are unaffected by inspiratory muscle training in healthy subjects where time to exhaustion is extended. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:139–144
Ekblom B (1969) The effect of physical training on oxygen transport system in man. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 328:1–45
Ekblom B (1986) Factors determining maximal aerobic power. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 556:15–19
Ekblom B, Hermansen L (1968) Cardiac output in athletes. J Appl Physiol 25:619–625
Ekblom B, Huot R (1972) Response to submaximal and maximal exercise at different levels of carboxyhemoglobin. Acta Physiol Scand 86:474–482
Ekblom B, Åstrand PO, Saltin B, Stenberg J, Wallström B (1968) Effect of training on circulatory response to exercise. J Appl Physiol 24:518–528
Ekblom B, Huot R, Stein EM, Thorstensson AT (1975) Effect of changes in arterial oxygen content on circulation and physical performance. J Appl Physiol 39:71–75
Ekblom B, Wilson G, Åstrand PO (1976) Central circulation during exercise after venesection and reinfusion of red blood cells. J Appl Physiol 40:379–383
Eliakim A, Nemet D (2010) Exercise training, physical fitness and the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-1 axis and cytokine balance. Med Sport Sci 55:128–140
Elliott AD, Skowno J, Prabhu M, Noakes TD, Ansley L (2013). Evidence of cardiac functional reserve upon exhaustion during incremental exercise to determine \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). Br J Sports Med. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091752
Ellis CG, Wrigley SM, Groom AC (1994) Heterogeneity of red blood cell perfusion in capillary networks supplied by a single arteriole in resting skeletal muscle. Circ Res 75:357–368
Esposito F, Ferretti G (1997) The effects of breathing He–O2 mixtures on maximal oxygen consumption in normoxic and hypoxic men. J Physiol 503:215–221
Esposito F, Limonta E, Alberti G, Veicsteinas A, Ferretti G (2010) Effect of respiratory muscle training on maximum aerobic power in normoxia and hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 170:268–272
Fagraeus L, Karlsson J, Linnarsson D, Saltin B (1973) Oxygen uptake during maximal work at lowered and raised ambient air pressure. Acta Physiol Scand 87:411–421
Fairshter RD, Walters J, Salness K, Fox M, Minh VD, Wilson AF (1983) A comparison of incremental exercise tests during cycle and treadmill ergometry. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:549–554
Faoro V, Huez S, Vanderpool RR, Groepenhoff H, de Bisschop C, Martinot JB, Lamotte M, Pavelescu A, Guénard H, Naeije R (2014) Pulmonary circulation and gas exchange at exercise in Sherpas at altitude. J Appl Physiol 116:919–926
Favier R, Spielvogel H, Desplanches D, Ferretti G, Kayser B, Grünenfelder A, Leuenberger M, Tüscher L, Caceres E, Hoppeler H (1995) Training in hypoxia vs training in normoxia in high altitude natives. J Appl Physiol 78:2286–2293
Ferretti G (1990) On maximal oxygen consumption in hypoxic humans. Experientia 46:1188–1194
Ferretti G (2003) Limiting factors to oxygen transport on Mount Everest 30 years after: a critique of Paolo Cerretelli’s contribution to the study of altitude physiology. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:344–350
Ferretti G, Capelli C (2009) Maximal O2 consumption: effects of gravity withdrawal and resumption. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 169:S50–S54
Ferretti G, di Prampero PE (1995) Factors limiting maximal O2 consumption: effects of acute changes in ventilation. Respir Physiol 99:259–271
Ferretti G, Atchou G, Grassi B, Marconi C, Cerretelli P (1991) Energetics of locomotion in African pygmies. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:7–10
Ferretti G, Antonutto G, Denis C, Hoppeler H, Minetti AE, Narici MV, Desplanches D (1997a) The interplay of central and peripheral factors in limiting maximal O2 consumption in man after prolonged bed rest. J Physiol 501:677–686
Ferretti G, Moia C, Thomet J, Kayser B (1997b) The decrease of maximal oxygen consumption during hypoxia in man: a mirror image of the oxygen equilibrium curve. J Physiol 498:231–237
Ferretti G, Bringard A, Perini R (2011) An analysis of performance in human locomotion. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:391–401
Fleg JL, Lakatta EG (1989) Role of muscle loss in the age-associated reduction of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). J Appl Physiol 65:1147–1151
Fleg JL, Morrell CH, Bos AG, Brant LJ, Talbot LA, Wright JG, Lakatta EG (2005) Accelerated longitudinal decline of aerobic capacity in healthy older adults. Circulation 112:674–682
Flück M (2010) Myocellular limitations of human performance and their modification through genome-dependent responses at altitude. Exp Physiol 95:451–462
Friman G (1979) Effect of clinical bed rest for seven days on physical performance. Acta Med Scand 205(389–393):103
Fulco CS, Rock PB, Trad L, Forte V, Cymerman A (1988) Maximal cardiorespiratory responses to one- and two-legged cycling during acute and long-term exposure to 4,300 meters altitude. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:761–766
Gaesser GA, Poole DC (1996) The slow component of oxygen uptake kinetics in humans. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 24:35–71
Gaesser GA, Wilson LA (1988) Effects of continuous and interval training on the parameters of the power-endurance time relationship for high-intensity exercise. Int J Sports Med 9:417–421
Gaskill SE, Serfass RC, Bacharach DW, Kelly JM (1999) Responses to training in cross-country skiers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:1211–1217
Gavin TP, Derchak PA, Stager JM (1998) Ventilation’s role in the decline in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and SaO 2 in acute hypoxic exercise. Med Sci Sport Exerc 30:195–199
Gayeski TE, Honig CR (1986) O2 gradients from sarcolemma to cell interior in red muscle at maximal \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \). Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 251:H789–H799
Geiser J, Vogt M, Billeter R, Zuleger C, Belforti F, Hoppeler H (2001) Training high—living low: changes of aerobic performance and muscle structure with training at simulated altitude. Int J Sports Med 22:579–585
Gibala MJ, Little JP, Macdonald MJ, Hawley JA (2012) Physiological adaptations to low-volume, high-intensity interval training in health and disease. J Physiol 590:1077–1084
Giesbrecht GG, Puddy A, Ahmed M, Younes M, Anthonisen NR (1991) Exercise endurance and arterial desaturation in normobaric hypoxia with increased chemosensitivity. J Appl Physiol 70:1770–1774
Gledhill N, Warburton D, Jamnik V (1999) Haemoglobin, blood volume, cardiac function, and aerobic power. Can J Appl Physiol 24:54–65
Glick Z, Schwartz E (1974) Physical working capacity of young men of different ethnic groups in Israel. J Appl Physiol 37:22–26
Gollnick PD, Armstrong RB, Saubert CW IV, Piehl K, Saltin B (1972) Enzyme activity and fiber composition in skeletal muscle of trained and untrained men. J Appl Physiol 33:312–319
Gollnick PD, Armstrong RB, Saltin B, Saubert CW IV, Sembrowich L, Shephard RE (1973) Effect of training on enzyme activity and fiber composition of human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 34:107–111
Gordon D, Mehter M, Gernigon M, Caddy O, Keiller D, Barnes R (2012) The effects of exercise modality on the incidence of plateau at \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 32:394–399
Gordon D, Wood M, Porter A, Vetrivel V, Gernigon M, Caddy O, Merzbach V, Keiller D, Baker J, Barnes R (2014) Influence of blood donation on the incidence of plateau at \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). Eur J Appl Physiol 114:21–27
Gormley SE, Swain DP, High R, Spina RJ, Dowling EA, Kotipalli US, Gandrakota R (2008) Effect of intensity of aerobic training on VO2max. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:1336–1343
Greenleaf JE, Bernauer EM, Ertl AC, Trowbridge TS, Wade CE (1989) Work capacity during 30 days of bed rest with isometric and isotonic exercise. J Appl Physiol 67:1820–1826
Greksa LP, Haas JD, Leatherman TL, Thomas RB, Spielvogel H (1984) Work performance of high-altitude Aymara males. Ann Hum Biol 11:227–233
Grimsmo J, Arnesen H, Maehlum S (2010) Changes in cardiorespiratory function in different groups of former and still active male cross-country skiers: a 28-30-year follow-up study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 20:151–161
Hagberg JM (1987) Effect of training on the decline of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) with aging. Fed Proc 46:1830–1833
Hagberg JM, Coyle EF (1984) Physiological comparison of competitive race walking and running. Int J Sports Med 5:74–77
Hahn AG, Gore CJ, Martin DT, Ashenden MJ, Roberts AD, Logan PA (2001) An evaluation of the concept of living at moderate altitude and training at sea level. Comp Biochem Physiol A 128:777–789
Hawkins SA, Marcell TJ, Victoria Jaque S, Wiswell RA (2001) A longitudinal assessment of change in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and maximal heart rate in master athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1744–1750
Hawkins MN, Raven PB, Snell PG, Stray-Gundersen J, Levine BD (2007) Maximal oxygen uptake as a parametric measure of cardiorespiratory capacity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:103–107
Heath GW, Hagberg JM, Ehsani AA, Holloszy JO (1981) A physiological comparison of young and older endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 51:634–640
Heinonen I, Nesterov SV, Kemppainen J, Nuutila P, Knuuti J, Laitio R, Kjaer M, Boushel R, Kalliokoski KK (2007) Role of adenosine in regulating the heterogeneity of skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 103:2042–2048
Heinonen I, Duncker DJ, Knuuti J, Kalliokoski KK (2012) The effect of acute exercise with increasing workloads on inactive muscle blood flow and its heterogeneity in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:3503–3509
Helgerud J (1994) Maximal oxygen uptake, anaerobic threshold and running economy in women and men with similar performances level in marathons. Eur J Appl Physiol 68:155–161
Helgerud J, Høydal K, Wang E, Karlsen T, Berg P, Bjerkaas M, Simonsen T, Helgesen C, Hjorth N, Bach R, Hoff J (2007) Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) more than moderate training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:665–671
Henriksson J (1977) Training induced adaptation of skeletal muscle and metabolism during submaximal exercise. J Physiol 270:661–675
Henriksson J, Reitmann JS (1977) Time course of changes in human skeletal muscle succinate dehydrogenase and cytochrome oxidase activities and maximal oxygen uptake with physical activity and inactivity. Acta Physiol Scand 99:91–97
Henson LC, Poole DC, Whipp BJ (1989) Fitness as a determinant of oxygen uptake response to constant-load exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 59:21–28
Herbst R (1928) Der Gasstoffwechsel als Mass der körperlichen Leistungsfähigkeit. I. Mitteilung : die Bestimmung des Sauerstoffaufnahmevermögens bein Gesunden. Deut Arch Klin Med 162:33–50
Hermansen L, Saltin B (1969) Oxygen uptake during maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 26:31–37
Hermansen L, Wachtlova M (1971) Capillary density of skeletal muscle in well-trained and untrained men. J Appl Physiol 30:860–863
Heubert R, Bocquet V, Koralsztein JP, Billat VL (2003) Effets de 4 semaines d’entraînement sur le temps limite à \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). Can J Appl Physiol 28:717–736
Heubert RAP, Billat VL, Chasseaing P, Bocquet V, Morton RH, Koralsztein JP, di Prampero PE (2005) Effects of a previous sprint on the parameters of the work-time to exhaustion relationship in high intensity cycling. Int J Sport Med 26:583–592
Hickson RC, Hagberg JM, Ehsani AA, Holloszy JO (1981) Time course of the adaptive responses of aerobic power and heart rate to training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 13:17–20
Hickson RC, Foster C, Pollock ML, Galassi TM, Rich S (1985) Reduced training intensities and loss of aerobic power, endurance, and cardiac growth. J Appl Physiol 58:492–499
Hickson RC, Bomze HA, Holloszy JO (1997) Linear increase in aerobic power induced by a strenuous program of endurance exercise. J Appl Physiol 42:372–376
Hikida RS, Gollnick PD, Dudley GA, Convertino VA, Buchanan P (1989) Structural and metabolic characteristics of human skeletal muscle following 30 days of simulated microgravity. Aviat Space Environ Med 60:664–670
Hildebrandt AL, Pilegaard H, Neufer PD (2003) Differential transcriptional activation of select metabolic genes in response to variations in exercise intensity and duration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E1021–E1027
Hill DW (1993) The critical power concept. Sports Med 16:237–254
Hill AV, Lupton H (1923) Muscular exercise, lactic acid, and the supply and utilization of oxygen. Q J Med 16:135–171
Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD (1991a) Effect of hemoglobin concentration on maximal O2 uptake in canine gastrocnemius muscle in situ. J Appl Physiol 70:1105–1112
Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD (1991b) Effect of increased Hb-O2 affinity on \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) at constant O2 delivery in dog muscle in situ. J Appl Physiol 70:2656–2662
Holloszy JO, Coyle EF (1984) Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol 56:831–838
Honig CR, Gayeski TE (1993) Resistance to O2 diffusion in anemic red muscle: roles of flux density and cell PO 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 265:H868–H875
Hoppeler H (1986) Exercise-induced ultrastructural changes in skeletal muscle. Int J Sports Med 7:187–204
Hoppeler H (1990) The different relationship of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) to muscle mitochondria in humans and quadrupedal animals. Respir Physiol 80:137–146
Hoppeler H, Flück M (2003) Plasticity of skeletal muscle mitochondria: structure and function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:95–104
Hoppeler H, Weibel ER (2000) Structural and functional limits for oxygen supply to muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 168:445–456
Hoppeler H, Howald H, Conley K, Lindstedt SL, Claassen H, Vock P, Weibel ER (1985) Endurance training in humans: aerobic capacity and structure of skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 59:320–327
Hoppeler H, Kleinert E, Schlegel C, Claassen H, Howald H, Kayar SR, Cerretelli P (1990) Morphological adaptations of human skeletal muscle to chronic hypoxia. Int J Sports Med 11(Suppl 1):S3–S9
Hoppeler H, Klossner S, Vogt M (2008) Training in hypoxia and its effects on skeletal muscle tissue. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18(Suppl 1):38–49
Horvath SM, Bedi JF, Wagner JA, Agnew J (1988) Maximal aerobic capacity at several ambient concentrations of CO at several altitudes. J Appl Physiol 65:2696–2708
Howald H (1982) Training-induced morphological and functional changes in skeletal muscle. Int J Sports Med 3:1–12
Howald H, Hoppeler H, Claassen H, Mathieu O, Straub R (1985) Influences of endurance training on the ultrastructural composition of the different muscle fibre types in humans. Pflügers Arch 403:369–376
Howley ET, Bassett DR Jr, Welch HG (1995) Criteria for maximal oxygen uptake: review and commentary. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:1292–1301
Hunter GR, Weinsier RL, McCarthy JP, Enette Larson-Meyer D, Newcomer BR (2001) Hemoglobin, muscle oxidative capacity, and \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) in African-American and Caucasian women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1739–1743
Ingjer F (1979) Effects of endurance training on muscle fiber ATP-ase activity, capillary supply and mitochondrial content in man. J Physiol 294:419–432
Jenkins DG, Quigley BM (1992) Endurance training enhances critical power. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:1283–1289
Johnson BD, Saupe KW, Dempsey JA (1992) Mechanical constraints on exercise hyperpnea in endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 73:874–886
Jones AM, Vanhatalo A, Burnley M, Morton RH, Poole DC (2010) Critical power: implications for the determination of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and exercise tolerance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1876–1890
Kaijser L (1970) Limiting factors for aerobic muscle performance. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 346:1–96
Kaiser P, Tesch PA, Frisk-Holmberg M, Juhlin-Dannfeldt A, Kaijser L (1986) Effect of beta-1-selective and non-selective beta blockade on work capacity and muscle metabolism. Clin Physiol 6:197–207
Kalliokoski KK, Knuuti J, Nuutila P (2004) Blood transit time heterogeneity is associated to oxygen extraction in exercising human skeletal muscle. Microvasc Res 67:125–132
Kashihara H, Haruna Y, Suzuki Y, Kawakubo K, Takenaka K, Bonde-Petersen F, Gunji A (1994) Effects of mild supine exercise during 20 days bed rest on maximal oxygen uptake rate in young humans. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 616:19–26
Kayser B, Hoppeler H, Claassen H, Cerretelli P (1991) Muscle structure and performance capacity of Himalayan Sherpas. J Appl Physiol 70:1938–1942
Kayser B, Marconi C, Amatya T, Basnyat B, Colombini A, Broers B, Cerretelli P (1994) The metabolic and ventilatory response to exercise in Tibetans born at low altitude. Respir Physiol 98:15–26
Knight DR, Schaffartzik W, Poole DC, Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD (1993) Effects of hyperoxia on maximal leg O2 supply and utilization in humans. J Appl Physiol 75:2586–2594
Koistinen P, Takala T, Martikkala V, Leppaluoto J (1995) Aerobic fitness influences the response of maximal oxygen uptake and lactate threshold in acute hypobaric hypoxia. Int J Sports Med 16:78–81
Krip B, Gledhill N, Jamnik V, Warburton D (1997) Effect of alterations in blood volume on cardiac function during maximal exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:1469–1476
Kruk B, Pekkarinen H, Manninen K, Hänninen O (1991) Comparison in men of physiological responses to exercise of increasing intensity at low and moderate ambient temperatures. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:353–357
Krustrup P, Jones AM, Wilkerson DP, Calbet JA, Bangsbo J (2009) Muscular and pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics during moderate and high-intensity sub-maximal knee-extensor exercise in humans. J Physiol 587:1843–1856
Lawler J, Powers SK, Thompson D (1988) Linear relationship between \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) decrement during exposure to acute hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 64:1486–1992
Lee SM, Schneider SM, Boda WL, Watenpaugh DE, Macias BR, Meyer RS, Hargens AR (2007) Supine LBNP exercise maintains exercise capacity in male twins during 30-d bed rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1315–1326
Lee SM, Schneider SM, Boda WL, Watenpaugh DE, Macias BR, Meyer RS, Hargens AR (2009) LBNP exercise protects aerobic capacity and sprint speed of female twins during 30 days of bed rest. J Appl Physiol 106:919–928
Levine BD (2008) \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \): what do we know, and what do we still need to know? J Physiol 586:25–34
Levine BD, Stray-Gundersen J (1997) ‘Living high-training low’: effect of moderate-altitude acclimatization with low-altitude training on performance. J Appl Physiol 83:102–112
Levine BD, Lane LD, Buckey JC, Friedman DB, Blomqvist CG (1991) Left ventricular pressure–volume and Frank-Starling relations in endurance athletes. Implications for orthostatic tolerance and exercise performance. Circulation 84:1016–1023
Levine BD, Lane LD, Watenpaugh DE, Gaffney FA, Buckey JC, Blomqvist CG (1996) Maximal exercise performance after adaptation to microgravity. J Appl Physiol 81:686–694
Lindstedt SL, Wells DJ, Jones JR, Hoppeler H, Thronson HA (1988) Limitations to aerobic performance in mammals: interaction of structure and demand. Int J Sports Med 9:210–217
Losnegard T, Myklebust H, Spencer M, Hallén J (2013) Seasonal variations in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \), O2-cost, O2-deficit, and performance in elite cross-country skiers. J Strength Cond Res 27:1780–1790
Lucia A, Hoyos J, Chicharro JL (2000) Physiological response to professional road cycling: climbers vs. time trialists. Int J Sports Med 21:505–512
Maksud MG, Coutts KD (1971) Comparison of a continuous and discontinuous graded treadmill test for maximal oxygen uptake. Med Sci Sports 3:63–65
Marconi C, Heisler N, Meyer M, Weitz H, Pendergast DR, Cerretelli P, Piiper J (1988) Blood flow distribution and its temporal variability in stimulated dog gastrocnemius muscle. Respir Physiol 74:1–13
Marconi C, Marzorati M, Grassi B, Basnyat B, Colombini A, Kayser B, Cerretelli P (2004) Second generation Tibetan lowlanders acclimatize to high altitude more quickly than Caucasians. J Physiol 556:661–671
Margaria R, Cerretelli P, Marchi S, Rossi L (1961) Maximum exercise in oxygen. Int Z angew Physiol 18:465–467
Margaria R, Camporesi E, Aghemo P, Sassi G (1972) The effect of O2 breathing on maximal aerobic power. Pflügers Arch 336:225–235
Markov G, Spengler CM, Knopfli-Lenzin C, Stuessi C, Boutellier U (2001) Respiratory muscle training increases cycling endurance without affecting cardiovascular responses to exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:233–239
Masuda K, Okazaki K, Kuno S, Asano K, Shimojo H, Katsuta S (2001) Endurance training under 2500-m hypoxia does not increase myoglobin content in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:486–490
McArdle WD, Katch FI, Pechar GS (1973) Comparison of continuous and discontinuous treadmill and bicycle tests for max \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \). Med Sci Sports 5:156–160
McArdle WD, Magel JR, Lesmes GR, Pechar GS (1976) Metabolic and cardiovascular adjustment to work in air and water at 18, 25 and 33°C. J Appl Physiol 40:85–90
McGuire DK, Levine BD, Williamson JW, Snell PG, Blomqvist CG, Saltin B, Mitchell JH (2001) A 30-year follow-up of the Dallas Bedrest and Training Study: I. Effect of age on the cardiovascular response to exercise. Circulation 104:1350–1357
Mekjavic IB, Golja P, Tipton MJ, Eiken O (2005) Human thermoregulatory function during exercise and immersion after 35 days of horizontal bed-rest and recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol 95:163–171
Mitchell JH, Blomqvist CG (1971) Maximal oxygen uptake. New Engl J Med 284:1018–1022
Miura A, Sato H, Sato H, Whipp BJ, Fukuba Y (2000) The effect of glycogen depletion on the curvature constant parameter of the power-duration curve for cycle ergometry. Ergonomics 43:133–141
Mollard P, Woorons X, Letournel M, Lamberto C, Favret F, Pichon A, Beaudry M, Richalet JP (2007) Determinants of maximal oxygen uptake in moderate acute hypoxia in endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:663–673
Monod H, Scherrer J (1965) The work capacity of a synergic muscular group. Ergonomics 8:329–338
Mooren FC, Viereck J, Krüger K, Thum T (2014) Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers of aerobic exercise capacity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306:H557–H563
Moritani T, Nagata A, deVries HA, Muro M (1981) Critical power as a measure of physical work capacity and anaerobic threshold. Ergonomics 24:339–350
Morton RH (1994) Critical power test for ramp exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 69:435–438
Morton RH (1996) A 3-parameter critical power model. Ergonomics 39:611–619
Morton RH (2011) Why peak power is higher at the end of steeper ramps: an explanation based on the ‘‘critical power’’ concept. J Sport Sci 29:307–309
Morton RH, Billat LV (2004) The critical power model for intermittent exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:303–307
Morton RH, Green S, Bishop D, Jenkins DG (1997) Ramp and constant power trials produce equivalent critical power estimates. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:833–836
Noakes TD (1998) Maximal oxygen uptake: ‘classical’ versus ‘contemporary’ viewpoints: a rebuttal. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:1381–1398
Noakes TD, Peltonen JE, Rusko HK (2001) Evidence that a central governor regulates exercise performance during acute hypoxia and hyperoxia. J Exp Biol 204:3225–3234
Oelz O, Howald H, di Prampero PE, Hoppeler H, Claassen H, Jenni R, Bühlmann A, Ferretti G, Brückner JC, Veicsteinas A, Gussoni M, Cerretelli P (1986) Physiological profile of world class high altitude climbers. J Appl Physiol 60:1734–1742
Ogawa T, Spina RJ, Martin WH 3rd, Kohrt WM, Schechtman KB, Holloszy JO, Ehsani AA (1992) Effects of aging, sex, and physical training on cardiovascular responses to exercise. Circulation 86:494–503
Ogawa T, Hayashi K, Ichinose M, Nishiyasu T (2007) Relationship between rest ventilatory chemosensitivity and maximal oxygen uptake in moderate hypobaric hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 103:1221–1226
Ogawa T, Calbet JAL, Honda Y, Fuji N, Nishiyasu T (2010) The effects of breathing a helium–oxygen gas mixture on maximal pulmonary ventilation and maximal oxygen consumption during exercise in acute moderate hypobaric hypoxia. Eur J Appl Physiol 110:853–861
Ogita F, Hara M, Tabata I (1996) Anaerobic capacity and maximal oxygen uptake during arm stroke, leg kicking and whole body swimming. Acta Physiol Scand 157:435–441
Otis AB (1987) An overview of gas exchange. In: Farhi LE, Tenney SM (eds) Handbook of physiology. The respiratory system, Sect. 3, vol IV. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, pp 1–11
Padilla S, Bourdin M, Barthélémy JC, Lacour JR (1992) Physiological correlates of middle-distance running performance. A comparative study between men and women. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:561–566
Padilla S, Mujika I, Cuesta G, Goiriena JJ (1999) Level ground and uphill cycling ability in professional road cycling. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:878–885
Perini R, Veicsteinas A (2003) Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:317–325
Perry CG, Talanian JL, Heigenhauser GJ, Spriet LL (2007) The effects of training in hyperoxia vs. normoxia on skeletal muscle enzyme activities and exercise performance. J Appl Physiol 102:1022–1027
Perry CGR, Heigenhauser GJF, Bonen A, Spriet LL (2008) High-intensity aerobic interval training increases fat and carbohydrate metabolic capacities in human skeletal muscle. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:1112–1123
Piiper J, Scheid P (1981) Model for capillary-alveolar equilibration with special reference to O2 uptake in hypoxia. Respir Physiol 46:193–208
Piiper J, Dejours P, Haab P, Rahn H (1971) Concepts and basic quantities in gas exchange physiology. Respir Physiol 13:292–304
Piiper J, Meyer M, Scheid P (1984) Dual role of diffusion in tissue gas exchange: blood-tissue equilibration and diffusion shunt. Respir Physiol 56:131–144
Piiper J, Pendergast DR, Marconi C, Meyer M, Heisler N, Cerretelli P (1985) Blood flow distribution in dog gastrocnemius muscle at rest and during stimulation. J Appl Physiol 58:2068–2074
Pirnay F, Dujardin J, Deroanne R, Petit JM (1971) Muscular exercise during intoxication by carbon monoxide. J Appl Physiol 31:573–575
Pirnay F, Deroanne R, Petit JM (1977) Influence of water temperature on thermal, circulatory and respiratory responses to muscular work. Eur J Appl Physiol 37:129–136
Plowman SA, Drinkwater BL, Horvath SM (1979) Age and aerobic power in women: a longitudinal study. J Gerontol 34:512–520
Poole DC, Ward SA, Gardner GW, Whipp BJ (1988) Metabolic and respiratory profile of the upper limit for prolonged exercise in man. Ergonomics 31:1265–1279
Poole DC, Ward SA, Whipp BJ (1990) The effects of training on the metabolic and respiratory profile of high-intensity cycle ergometer exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 59:421–429
Poole DC, Schaffartzik W, Knight DR, Derion T, Kennedy B, Guy HJ, Prediletto R, Wagner PD (1991) Contribution of exercising legs to the slow component of oxygen uptake kinetics in humans. J Appl Physiol 71:1245–1260
Poole DC, Barstow TJ, Gaesser GA, Willis WT, Whipp BJ (1994) \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) slow component: physiological and functional significance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26:1354–1358
Powers SK, Lawler J, Dempsey JA, Dodd S, Landry G (1989) Effects of incomplete pulmonary gas exchange on VO2max. J Appl Physiol 66:2491–2495
Pringle JSM, Jones AM (2002) Maximal lactate steady state, critical power and EMG during cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 88:214–226
Prior SJ, Hagberg JM, Phares DA, Brown MD, Fairfull L, Ferrell RE, Roth SM (2003) Sequence variation in hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF1A): association with maximal oxygen consumption. Physiol Genomics 15:20–26
Prior SJ, Hagberg JM, Paton CM, Douglass LW, Brown MD, McLenithan JC, Roth SM (2006) DNA sequence variation in the promoter region of the VEGF gene impacts VEGF gene expression and maximal oxygen consumption. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H1848–H1855
Proctor DN, Joyner MJ (1997) Skeletal muscle mass and the reduction of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) in trained older subjects. J Appl Physiol 82:1411–1415
Pugh LGCE (1967) Athletes at altitude. J Physiol 192:619–646
Pugh LGCE, Gill MB, Lahiri S, Milledge JS, Ward MP, West JB (1964) Maximal exercise at great altitudes. J Appl Physiol 19:431–440
Rådegran G, Blomstrand E, Saltin B (1999) Peak muscle perfusion and oxygen uptake in humans: importance of precise estimates of muscle mass. J Appl Physiol 87:2375–2380
Rahn H, Fenn WO (1955) A graphical analysis of the respiratory gas exchange. The O2–CO2 diagram. American Physiological Society, Washington
Rice TK, Sarzynski MA, Sung YJ, Argyropoulos G, Stütz AM, Teran-Garcia M, Rao DC, Bouchard C, Rankinen T (2012) Fine mapping of a QTL on chromosome 13 for submaximal exercise capacity training response: the HERITAGE Family Study. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:2969–2978
Richardson RS, Kennedy B, Knight DR, Wagner PD (1995a) High muscle blood flows are not attenuated by recruitment of additional muscle mass. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 269:H1545–H1552
Richardson RS, Knight DR, Poole DC, Kurdak SS, Hogan MC, Grassi B, Wagner PD (1995b) Determinants of maximal exercise \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) during single leg knee-extensor exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 268:H1453–H1461
Richardson RS, Noyszewski EA, Kendrick KF, Leigh JS, Wagner PD (1995c) Myoglobin O2 desaturation during exercise. Evidence of limited O2 transport. J Clin Invest 96:1916–1926
Richardson RS, Grassi B, Gavin TP, Haseler LJ, Tagore K, Roca J, Wagner PD (1999) Evidence of O2 supply-dependent \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) in the exercise-trained human quadriceps. J Appl Physiol 86:1048–1053
Richardson RS, Newcomer SC, Noyszewski EA (2001) Skeletal muscle intracellular PO 2 assessed by myoglobin desaturation: response to graded exercise. J Appl Physiol 91:2679–2685
Roach RC, Koskolou MD, Calbet JA, Saltin B (1999) Arterial O2 content and tension in regulation of cardiac output and leg blood flow during exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 276:H438–H445
Robertson EY, Saunders PU, Pyne DB, Gore CJ, Anson JM (2010) Effectiveness of intermittent training in hypoxia combined with live high/train low. Eur J Appl Physiol 110:379–387
Robinson S (1938) Experimental studies of physical fitness in relation to age. Arbeitphysiol 10:251–323
Robinson S, Edwards HT, Dill DB (1937) New records in human power. Science 85:409–410
Robinson S, Dill DB, Tzankoff SP, Wagner JA, Robinson RD (1975) Longitudinal studies of aging in 37 men. J Appl Physiol 38:263–267
Robinson S, Dill DB, Robinson RD, Tzankoff SP, Wagner JA (1976) Physiological aging of champion runners. J Appl Physiol 41:46–51
Roca J, Hogan MC, Story D, Bebout DE, Haab P, Gonzalez R, Ueno O, Wagner PD (1989) Evidence for tissue diffusion limitation of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) in normal humans. J Appl Physiol 67:291–299
Roca J, Agusti AG, Alonso A, Poole DC, Viegas C, Barbera JA, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Ferrer A, Wagner PD (1992) Effects of training on muscle O2 transport at \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). J Appl Physiol 73:1067–1076
Rode A, Shephard RJ (1971) Cardio-respiratory fitness of an artic community. J Appl Physiol 31:519–526
Rode A, Shephard RJ (1984) Ten years of “civilization” fitness of Canadian Inuit. J Appl Physiol 56:1472–1477
Rodríguez FA, Truijens MJ, Townsend NE, Stray-Gundersen J, Gore CJ, Levine BD (2007) Performance of runners and swimmers after four weeks of intermittent hypobaric hypoxic exposure plus sea level training. J Appl Physiol 103:1523–1535
Roels B, Bentley DJ, Coste O, Mercier J, Millet GP (2007) Effects of intermittent hypoxic training on cycling performance in well-trained athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:359–368
Rogers MA, Hagberg JM, Martin WH 3rd, Ehsani AA, Holloszy JO (1990) Decline in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) with aging in master athletes and sedentary men. J Appl Physiol 68:2195–2199
Roi GS, Giacometti M, von Duvillard SP (1999) Marathons in altitude. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:723–728
Rossiter HB, Ward SA, Kowalchuk JM, Howe FA, Griffiths JR, Whipp BJ (2001) Effects of prior exercise on oxygen uptake and phosphocreatine kinetics during high-intensity knee-extension exercise in humans. J Physiol 537:291–303
Rowell LB (1974) Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol Rev 54:75–159
Rowell LB, Saltin B, Kiens B, Christensen NJ (1986) Is peak quadriceps blood flow in humans even higher during exercise with hypoxemia? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 251:H1038–H1044
Rusko HK (1992) Development of aerobic power in relation to age and training in cross-country skiers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:1040–1047
Russell G, Gore CJ, Ashenden MJ, Parisotto R, Hahn AG (2002) Effects of prolonged low doses of recombinant human erythropoietin during submaximal and maximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:442–449
Saltin B (1977) The interplay between peripheral and central factors in the adaptive response to exercise and training. Ann N Y Acad Sci 301:224–231
Saltin B, Åstrand PO (1967) Maximal oxygen uptake in athletes. J Appl Physiol 23:353–358
Saltin B, Rowell LB (1980) Functional adaptations to physical activity and inactivity. Fed Proc 39:1506–1513
Saltin B, Strange S (1992) Maximal oxygen uptake: “old” and “new” arguments for a cardiovascular limitation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:30–37
Saltin B, Blomqvist CG, Mitchell RC, Johnson RL, Wildenthal K, Chapman CB (1968) Response to exercise after bed rest and after training. Circulation 38(Suppl 7):1–78
Saltin B, Nazar K, Costill DL, Stein E, Jansson E, Essén B, Gollnick PD (1976) The nature of the training response: peripheral and central adaptations to one-legged exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 96:289–305
Saltin B, Larsen H, Terrados N, Bangsbo J, Bak T, Kim CK, Svedenhag J, Rolf CJ (1995) Aerobic exercise capacity at sea level and at altitude in Kenyan boys, junior and senior runners compared with Scandinavian runners. Scand J Med Sci Sports 5:209–221
Sanada K, Kuchiki T, Miyachi M, McGrath K, Higuchi M, Ebashi H (2007) Effects of age on ventilatory threshold and peak oxygen uptake normalised for regional skeletal muscle mass in Japanese men and women aged 20–80 years. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:475–483
Sawka MN, Young AJ, Muza SR, Gonzalet RR, Pandolf KB (1987) Erythrocyte reinfusion and maximal aerobic power. J Am Med Ass 257:1496–1499
Schaffartzik W, Barton ED, Poole DC, Tsukimoto K, Hogan MC, Bebout DE, Wagner PD (1993) Effect of reduced hemoglobin concentration on leg oxygen uptake during maximal exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 75:491–498
Scheuer J, Tipton CM (1977) Cardiovascular adaptations to physical training. Annu Rev Physiol 39:221–251
Secher N, Ruberg-Larsen H, Binkhorst RA, Bonde-Petersen F (1974) Maximal oxygen uptake during arm cranking and combined arm plus leg exercise. J Appl Physiol 36:515–518
Seene T, Kaasik P, Alev K (2011) Muscle protein turnover in endurance training: a review. Int J Sports Med 32:905–911
Shephard RJ (1969) A non-linear solution of the oxygen conductance equation: applications to performance at sea level and at an altitude of 7,350 ft. Int Z Angew Physiol 27:212–225
Sloth M, Sloth D, Overgaard K, Dalgas U (2013) Effects of sprint interval training on \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and aerobic exercise performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports 23:341–352
Smorawinski J, Nazar K, Kaciuba-Uscilko H, Kaminska E, Cybulski G, Kodrzycka A, Bicz B, Greenleaf JE (2001) Effects of 3-day bed rest on physiological responses to graded exercise in athletes and sedentary men. J Appl Physiol 91:249–257
Sonetti DA, Wetter TJ, Pegelow DF, Dempsey JA (2001) Effects of respiratory muscle training versus placebo on endurance exercise performance. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 127:185–199
Spaak J, Montmerle S, Sundblad P, Linnarsson D (2005) Long-term bed rest-induced reductions in stroke volume during rest and exercise: cardiac dysfunction vs. volume depletion. J Appl Physiol 98:648–654
Spriet LL, Gledhill N, Froese AB, Wilkes DL (1986) Effect of graded erythrocythemia on cardiovascular and metabolic responses to exercise. J Appl Physiol 61:1942–1948
Steinacker JM, Liu Y, Böning D, Halder A, Maassen N, Thomas A, Stauch M (1996) Lung diffusion capacity, oxygen uptake, cardiac output and oxygen transport during exercise before and after an Himalayan expedition. Eur J Appl Physiol 74:187–193
Stray-Gundersen J, Levine BD (2008) Live high, train low at natural altitude. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18(Suppl 1):21–28
Stray-Gundersen J, Chapman RF, Levine BD (2001) “Living high-training low” altitude training improves sea level performance in male and female elite runners. J Appl Physiol 91:1113–1120
Stremel RW, Convertino VA, Bernauer EM, Greenleaf JE (1976) Cardiorespiratory deconditioning with static and dynamic leg exercise during bed rest. J Appl Physiol 41:905–909
Strømme FB, Ingjer F, Meen HD (1977) Assessment of maximal aerobic power in specifically trained athletes. J Appl Physiol 42:833–837
Talbot LA, Metter EJ, Fleg JL (2000) Leisure-time physical activities and their relationship to cardiorespiratory fitness in healthy men and women 18–95 years old. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:417–425
Tam E, Rossi H, Moia C, Berardelli C, Rosa G, Capelli C, Ferretti G (2012) Energetics of running in top-level marathon runners from Kenya. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:3797–3806
Tanabe N, Todoran TM, Zenk GM, Bunton BR, Wagner WW Jr, Presson RG Jr (1998) Perfusion heterogeneity in the pulmonary acinus. J Appl Physiol 84:933–938
Taunton JE, Banister EW, Patrick TR, Ofordsag P, Duncan WR (1970) Physical work capacity in hyperbaric environments and conditions of hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol 28:421–427
Taylor CR (1987) Structural and functional limits to oxidative metabolism: insights from scaling. Annu Rev Physiol 49:135–146
Taylor CR, Weibel ER (1981) Design of the mammalian respiratory system. I. Problem and strategy. Respir Physiol 44:1–10
Taylor HL, Buskirk E, Henschel A (1955) Maximal oxygen uptake as an objective measure of cardiorespiratory performance. J Appl Physiol 8:73–80
Tesch PA, Karlsson J (1985) Muscle fiber types and size in trained and untrained muscles of elite athletes. J Appl Physiol 59:1716–1720
Thomsen JJ, Rentsch RL, Robach P, Calbet JAL, Boushel R, Rasmussen P, Juel C, Lundby C (2007) Prolonged administration of recombinant human erythropoietin increases submaximal performance more than maximal aerobic power. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:481–486
Thomson JM, Stone JA, Ginsburg AD, Hamilton P (1982) Oxygen transport during exercise following blood reinfusion. J Appl Physiol 53:1213–1219
Trappe T, Trappe S, Lee G, Widrick J, Fitts R, Costill D (2006) Cardiorespiratory responses to physical work during and following 17 days of bed rest and spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 100:951–957
Turner DL, Hoppeler H, Noti C, Gurtner HP, Gerber H, Schena F, Kayser B, Ferretti G (1993) Limitations to VO2max in humans after blood retransfusion. Respir Physiol 92:329–341
Valli G, Cogo A, Passino C, Bonardi D, Morici G, Fasano V, Agnesi M, Bernardi L, Ferrazza AM, Ward SA, Palange P (2011) Exercise intolerance at high altitude (5050 m): critical power and W’. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 177:333–341
Vanderburgh PM, Katch FI (1996) Ratio scaling of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) penalizes women with larger percent body fat, not lean body mass. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:1204–1208
Vanhatalo A, Jones AM (2009) Influence of prior sprint exercise on the parameters of the all-out critical power test in men. Exp Physiol 94:255–263
Veicsteinas A, Samaja M, Gussoni M, Cerretelli P (1984) Blood O2 affinity and maximal O2 consumption in elite bicycle racers. J Appl Physiol 57:52–58
Ventura N, Hoppeler H, Seiler R, Binggeli A, Mullis P, Vogt M (2003) The response of trained athletes to six weeks of endurance training in hypoxia or normoxia. Int J Sports Med 24:166–172
Vogel JA, Gleser MA (1972) Effect of carbon monoxide on oxygen transport during exercise. J Appl Physiol 32(234–239):287
Vogel JA, Hansen JE, Harris CW (1967) Cardiovascular responses in man during exhaustive work at sea level and high altitude. J Appl Physiol 23:531–539
Vogiatzis I, Zakynthinos S, Boushel R, Athanasopoulos D, Guenette JA, Wagner H, Roussos C, Wagner PD (2008) The contribution of intrapulmonary shunts to the alveolar-to-arterial oxygen difference during exercise is very small. J Physiol 586:2381–2391
Wagner PD (1992) Gas exchange and peripheral diffusion limitation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:54–58
Wagner PD (1993) Algebraic analysis of the determinants of \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \). Respir Physiol 93:221–237
Wagner PD (1995) Muscle O2 transport and O2 dependent control of metabolism. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:47–53
Wagner PD (1996a) Determinants of maximal oxygen transport and utilization. Annu Rev Physiol 58:21–50
Wagner PD (1996b) A theoretical analysis of factors determining \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) at sea level and altitude. Respir Physiol 106:329–343
Wagner PD (2010) The physiological basis of reduced \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) in operation everest II. High Alt Med Biol 11:209–215
Wagner PD (2012) Muscle intracellular oxygenation during exercise: optimization for oxygen transport, metabolism, and adaptive change. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:1–8
Wagner PD, Gillespie JR, Landgren GL, Fedde MR, Jones BW, DeBowes RM, Pieschl RL, Erickson HH (1989) Mechanism of exercise-induced hypoxemia in horses. J Appl Physiol 66:1227–1233
Wagner PD, Erickson BK, Seaman J, Kubo K, Hiraga A, Kai M, Yamaya Y (1996) Effects of altered FIO 2 on maximum \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2} \) in the horse. Respir Physiol 105:123–134
Wehrlin JP, Hallén J (2006) Linear decrease in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) and performance with increasing altitude in endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 96:404–412
Weibel E (1984) The pathway for oxygen. Harvard University Press, Boston
Weibel ER (1987) Scaling of structural and functional variables in the respiratory system. Annu Rev Physiol 49:147–159
Welch HG, Pedersen PK (1981) Measurement of metabolic rate in hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol 51:725–731
West JB (1983) Climbing Mt. Everest without oxygen: an analysis of maximal exercise during extreme hypoxia. Respir Physiol 52:265–279
West JB, Boyer SJ, Graber DJ, Hackett PH, Maret KH, Milledge JS, Peters RM, Pizzo CJ, Samaja M, Sarnquist FH, Schoene RB, Winslow RM (1983) Maximal exercise at extreme altitude on Mount Everest. J Appl Physiol 55:688–698
Weston AR, Mbambo Z, Myburgh KH (2000) Running economy of African and Caucasians distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1130–1134
Whipp BJ (1994) The bioenergetic and gas exchange basis of exercise testing. Clin Chest Med 15:173–192
Wilhite DP, Mickleborough TD, Laymon AS, Chapman RF (2013) Increases in \( \dot{V}\hbox{O}_{2\text{max} } \) with “live high-train low” altitude training: role of ventilatory acclimatization. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:419–426
Wilmore JH, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rice T, Mandel S, Leon AS, Rao DC, Skinner JS, Bouchard C (2001) Cardiac output and stroke volume changes with endurance training: the HERITAGE Family Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:99–106
Woodson RD, Wills RE, Lenfant C (1978) Effect of acute and established anemia on O2 transport at rest, submaximal and maximal work. J Appl Physiol 44:36–43
Woorons X, Mollard P, Lamberto C, Letournel M, Richalet JP (2005) Effect of acute hypoxia on maximal exercise in trained and sedentary women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:147–154
Wyndham CH, Strydom NB, Morrison JF, Peter J, Williams CG, Bredell GAG, Joffe A (1963) Differences between ethnic groups in physical working capacity. J Appl Physiol 18:361–366
Zhang YY, Johnson MC 2nd, Chow N, Wasserman K (1991) Effect of exercise testing protocol on parameters of aerobic function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:625–630
Zoladz JA, Rademaker ACHJ, Sargeant AJ (1995) Non-linear relationship between O2 uptake and power output at high intensities of exercise in humans. J Physiol 488:211–217
Zumstein A, Mathieu O, Howald H, Hoppeler H (1983) Morphometric analysis of the capillary supply in skeletal muscles of trained and untrained subjects. Its limitations in muscle biopsies. Pflügers Arch 397:277–283
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Swiss National Science Foundation Grant 32003B_143427, Switzerland, and by the Health&Wealth@Unibs strategic plan, University of Brescia, Italy. I thank all the friends and colleagues with whom I had joyful and enriching discussions on the matters treated in this review, all the collaborators from Brescia and Geneva who had been involved in the 20-year-long experimental work supporting this paper. My admiration goes to Pietro Enrico di Prampero and Peter Wagner, who demonstrated so vividly that research consists mainly of innovative thinking, and who traced the way along which I have been walking.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Nigel A.S. Taylor.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferretti, G. Maximal oxygen consumption in healthy humans: theories and facts. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 2007–2036 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2911-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2911-0