Abstract
Purpose
The present report describes the distribution of breast milk and urinary free and total bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations, from 27 postpartum women and their 31 infants, and explores the influence of age, sex, and nutritional source on infant BPA urinary concentration.
Methods
Both free (unconjugated) and total (free plus conjugated) BPA concentrations from women’s breast milk samples and infants’ urine samples were measured by online solid-phase extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography–isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Descriptive statistics and nonparametric tests of group comparisons were conducted.
Results
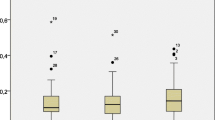
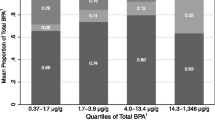
Total BPA was detected in 93 % of urine samples in this healthy infant population aged 3–15 months who were without known environmental exposure to BPA [interquartile range (IQR) = 1.2–4.4 μg/L)]. Similarly, 75 % of the mothers’ breast milk samples had detectable concentrations of total BPA (IQR = 0.4–1.4 μg/L). The magnitude and frequency of detection of free BPA in the children’s urine and the mothers’ breast milk were much lower than the total concentrations.
Conclusions
Total BPA was detected in 93 % of this healthy infant population aged 3–15 months who are without known environmental exposure to BPA. Neither free nor total BPA urinary concentrations differed significantly by infant’s sex or by nutritional source (breast milk and/or formula) while age group was of borderline significance. There were no significant correlations between free or total BPA concentrations in mothers’ breast milk and their infants’ urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPA:
-
Bisphenol A
- CDC:
-
US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- GM:
-
Geometric mean
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- MGH:
-
Massachusetts General Hospital
- HSPH:
-
Harvard School of Public Health
- MS/MS:
-
Tandem mass spectrometry
- NTP:
-
National Toxicology Program
- QC:
-
Quality control
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Becker K, Göen T, Seiwert M, Conrad A, Pick-Fuss H, Müller J, Wittassek M, Schulz C, Kolossa-Gehring M (2009) GerES IV: phthalate metabolites and bisphenol A in urine of German children. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:685–692
Braun JM, Kalkbrenner AE, Calafat AM, Yolton K, Ye X, Dietrich KN, Lanphear BP (2011a) Impact of early-life bisphenol A exposure on behavior and executive function in children. Pediatrics 128(5):873–882
Braun JM, Kalkbrenner AE, Calafat AM, Bernert JT, Ye X, Silva MJ, Barr DB, Sathyanarayana S, Lanphear BP (2011b) Variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 119(1):131–137
Bushnik R, Haines D, Levallois P, Levesque J, Oostdam J, Viau L (2010) Lead and bisphenol A concentrations in the Canadian population. Health Reports, 21(3), Statistics Canada, Catalogue no. 82-003-XPE
Calafat AM, Needham LL (2009) What additional factors beyond state-of-the-art analytical methods are needed for optimal generation and interpretation of biomonitoring data? Environ Health Perspect 117(10):1481–1485
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong LY, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116(1):39–44
Calafat AM, Weuve J, Ye X, Jia LT, Hu H, Ringer S, Huttner K, Hauser R (2009) Exposure to bisphenol A and other phenols in neonatal intensive care unit premature infants. Environ Health Perspect 117(4):639–644
Caudill SP, Schleicher RL, Pirkle JL (2008) Mulit-rule quality control for the age-related eye disease study. Stat Med 27:4094–4106
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2012) Fourth national report on human exposure to environmental chemicals. Updated Tables, Feb 2012. http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/pdf/FourthReport_UpdatedTables_Feb2012.pdf. Accessed 30 Mar 2012
Chevrier C, Petit C, Philippat C, Mortamais M, Slama R, Rouget F, Calafat AM, Ye X, Silva MJ, Charles MA, Cordier S (2012) Maternal urinary phthalates and phenols and male genital anomalies. Epidemiology 23(2):353–356
Edginton AN, Ritter L, (2009) Predicting plasma concentrations of bisphenol A in children younger than 2 years of age after typical feeding schedules, using a physiologically based toxicokinetic model. Environ Health Perspect 117(4):645–652 (Epub 2008 Nov 14)
Environment Canada and Health Canada (2008) Screening assessment for the challenge phenol, 4,4′-(1-methylethylidene)bis-(bisphenol A), October 2008. http://www.ec.gc.ca/ese-ees/3C756383-BEB3-45D5-B8D3-E8C800F35243/batch2_80-05-7_en.pdf. Accessed 30 Mar 2012
Ginsberg G, Rice DC (2009) Does rapid metabolism ensure negligible risk from bisphenol A? Environ Health Perspect 117(11):1639–1643
Golub MS, Wu KL, Kaufman FL, Li LH, Moran-Messen F, Zeise L, Alexeeff GV, Donald JM (2010) Bisphenol A: developmental toxicity from early prenatal exposure. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 89(6):441–466
Hornung RW, Reed LD (1990) Estimation of average concentration in the presence of nondetectable values. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 5:46–51
Kasper-Sonnenberg M, Wittsiepe J, Koch HM, Fromme H, Wilhelm M (2012) Determination of bisphenol A in urine from mother–child pairs—results from the Duisburg birth cohort study, Germany. J Toxicol Environ Health A 75:429–437
Kuruto-Niwa R, Tateoka Y, Usuki Y, Nozawa R (2007) Measurement of bisphenol A concentrations in human colostrum. Chemosphere 55:1160–1164
Lakind JS, Levesque J, Dumas P, Bryan S, Clarke J, Naiman DQ (2012) Comparing United States and Canadian population exposures from national biomonitoring surveys: bisphenol A intake as a case study. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. doi:10.1038/jes.2012.1. (Epub ahead of print)
Lee EJ, Arbuckle TE (2009) Urine-sampling methods for environmental chemicals in infants and young children. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 19(7):625–633
Mahalingaiah S, Meeker JD, Pearson KR, Calafat AM, Ye X, Petrozza J, Hauser R (2008) Temporal variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in men and women. Environ Health Perspect 116(2):173–178
Miao M, Yuan W, He Y, Zhou Z, Wang J, Gao E, Li G, Li DK (2011) In utero exposure to bisphenol-A and anogenital distance of male offspring. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 91(10):867–872
Mielke H, Gundert-Remy U (2009) Bisphenol A levels in blood depend on age and exposure. Toxicol Lett 190(1):32–40
Morgan MK, Jones PA, Calafat AM, Ye X, Croghan CW, Chuang JC, Wilson NK, Clifton MS, Figueroa Z, Sheldon LS (2011) Assessing the quantitative relationships between preschool children’s exposures to bisphenol A by route and urinary biomonitoring. Environ Sci Technol 45(12):5309–5316
NTP (2008) NTP Brief on Bisphenol A [CAS NO. 80- 5-07]. http://cerhr.niehs.nih.gov/chemicals/bisphenol/bisphenol.pdf. Accessed 30 Mar 2012
Otaka H, Yasuhara A, Morita M (2003) Determination of bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol in human milk using alkaline digestion and cleanup by solid-phase extraction. Anal Sci 19(12):1663–1666
Padmanabhan V, Siefert K, Ransom S, Johnson T, Pinkerton J, Anderson L, Tao L, Kannan K (2008) Maternal bisphenol-A levels at delivery: a looming problem? J Perinatol 28(4):258–263
Philippat C, Mortamais M, Chevrier C, Petit C, Calafat AM, Ye X, Silva MJ, Brambilla C, Pin I, Charles MA, Cordier S, Slama R (2012) Exposure to phthalates and phenols during pregnancy and offspring size at birth. Environ Health Perspect 120(3):464–470
Rudel RA, Gray JM, Engel CL, Rawsthorne TW, Dodson RE, Ackerman JM, Rizzo J, Nudelman JL, Brody JG (2011) Food packaging and bisphenol A and bis(2-ethyhexyl) phthalate exposure: findings from a dietary intervention. Environ Health Perspect 119(7):914–920
Saarela T, Kokkonen J, Koivisto M (2005) Macronutrient and energy contents of human milk fractions during the first 6 months of lactation. Acta Paediatr 94(9):1176–1181
Sun Y, Irie M, Kishikawa N, Wada M, Kuroda N, Nakashima K (2004) Determination of bisphenol A in human breast milk by HPLC with column-switching and fluorescence detection. Biomed Chromatogr 18(8):501–507
Vandenberg LN, Chahoud I, Heindel JJ, Padmanabhan V, Paumgartten FJ, Schoenfelder G (2010) Urinary, circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread exposure to bisphenol A. Environ Health Perspect 118(8):1055–1070
Völkel W, Colnot T, Csanady GA, Filser JG, Dekant W (2002) Metabolism and kinetics of bisphenol A in humans at low doses following oral administration. Chem Res Toxicol 15(10):1281–1287
Völkel W, Bittner N, Dekant W (2005) Quantitation of bisphenol A and bisphenol A glucuronide in biological samples by high performance liquid chromatography—tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 33(11):1748–1757
Völkel W, Kiranoglu M, Fromme H (2011) Determination of free and total bisphenol A in urine of infants. Environ Res 111:143–148
Welshons WV, Nagel SC, vom Saal FS (2006) Large effects from small exposures. III. Endocrine mechanisms mediating effects of bisphenol A at levels of human exposure. Endocrinology 147(Suppl 6):S56–S69. doi:10.1210/en.2005-1159
WHO (World Health Organization) (2010) Joint FAO/WHO expert meeting to review toxicological and health aspects of bisphenol a: summary report including report of stakeholders meeting on bisphenol A. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/97892141564274_eng.pdf. Accessed 10 Dec 2011
Wolff MS, Engel SM, Berkowitz GS, Ye X, Silva MJ, Zhu C, Wetmur J, Calafat AM (2008) Prenatal phenol and phthalate exposures and birth outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 116(8):1092–1097
Ye X, Kuklenyik Z, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2005) Automated on-line column-switching HPLC-MS/MS method with peak focusing for the determination of nine environmental phenols in urine. Anal Chem 77:5407–5413
Ye X, Kuklenyik Z, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2006) Measuring environmental phenols and chlorinated organic chemicals in breast milk using automated on-line column- switching-high performance liquid chromatography-isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 831(1–2):110–115
Ye X, Bishop AM, Reidy JA, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2007) Temporal stability of the conjugated species of bisphenol A, parabens, and other environmental phenols in human urine. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 17(6):567–572
Ye X, Bishop AM, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2008) Automated on-line column-switching HPLC-MS/MS method with peak focusing for measuring parabens, triclosan, and other environmental phenols in human milk. Anal Chim Acta 622:150–156
Ye X, Zhou X, Bishop AM, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2010) Does the composition of urine change when collected from disposable diapers and other absorbent materials? J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 20(7):644–649
Ye X, Zhou X, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2011) In-vitro oxidation of bisphenol A: is bisphenol A catechol a suitable biomarker for human exposure to bisphenol A? Anal Bioanal Chem 399(3):1071–1079
Yi B, Kim C, Yang M (2010) Biological monitoring of bisphenol A with HLPC/FLD and LC/MS/MS assays. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 878(27):2606–2610
Acknowledgments
Jennifer Ford RN, BSN (Harvard School of Public Health). Dr. Elizabeth Hait, MD (Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA). Xiaoyun Ye, Xiaoliu Zhou, Tao Jia, and Amber Bishop (CDC) for the measurements of BPA. The biospecimen analyses were funded under the Government of Canada’s Chemicals Management Plan. Kaitlin Mendonca was supported by training grant Harvard School of Public Health- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (HSPH-NIEHS) Pilot Grant #P30ES000002.
Conflict of interest
IRB approval was obtained from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Health Canada, and Simmons College. Funding sources had no role in study design, collection, analysis, or interpretation of data or in the decision of whether to publish the results. The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the CDC. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendonca, K., Hauser, R., Calafat, A.M. et al. Bisphenol A concentrations in maternal breast milk and infant urine. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 87, 13–20 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-012-0834-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-012-0834-9