Abstract
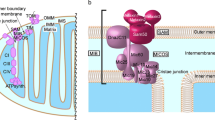
In this study, we carry out a systematic characterisation of the YIPF family of proteins with respect to their subcellular localisation profile, membrane topology and functional effects on the endomembrane system. YIPF proteins primarily localise to the Golgi complex and can be grouped into trans-Golgi-localising YIPFs (YIPF1 and YIPF2) and cis-Golgi-localising YIPFs (YIPF3, YIPF4 and YIPF5), with YIPF6 and YIPF7 showing a broader profile being distributed throughout the Golgi stack. YIPF proteins have a long soluble N-terminal region, which is orientated towards the cytosol, followed by 5 closely stacked transmembrane domains, and a C terminus, orientated towards the lumen of the Golgi. The significance of YIPF proteins for the maintenance of the morphology of the Golgi was tested by RNA interference, revealing a number of specific morphological changes to this organelle on their depletion. We propose a role for this family of proteins in regulating membrane dynamics in the endomembrane system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan BB, Moyer BD, Balch WE (2000) Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289:444–448
Barbero P, Bittova L, Pfeffer SR (2002) Visualization of Rab9-mediated vesicle transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi in living cells. J Cell Biol 156:511–518
Bard F, Casano L, Mallabiabarrena A et al (2006) Functional genomics reveals genes involved in protein secretion and Golgi organization. Nature 439:604–607
Barone V, Mazzoli E, Kunic J et al (2015) Yip1B isoform is localized at ER–Golgi intermediate and cis-Golgi compartments and is not required for maintenance of the Golgi structure in skeletal muscle. Histochem Cell Biol 143:235–243
Barrowman J, Wang W, Zhang Y, Ferro-Novick S (2003) The Yip1p.Yif1p complex is required for the fusion competence of endoplasmic reticulum-derived vesicles. J Biol Chem 278:19878–19884
Behnia R, Munro S (2005) Organelle identity and the signposts for membrane traffic. Nature 438:597–604
Bexiga MG, Simpson JC (2013) Human diseases associated with form and function of the Golgi complex. Int J Mol Sci 14:18670–18681
Bhuin T, Roy JK (2014) Rab proteins: the key regulators of intracellular vesicle transport. Exp Cell Res 328:1–19
Calero M, Winand NJ, Collins RN (2002) Identification of the novel proteins Yip4p and Yip5p as Rab GTPase interacting factors. FEBS Lett 515:89–98
Carpenter AE, Jones TR, Lamprecht MR et al (2006) Cell Profiler: image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol 7:R100
Cox J, Mann M (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26:1367–1372
Cox J, Hein MY, Luber CA et al (2014) Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Mol Cell Proteomics 13:2513–2526
Doms RW, Russ G, Yewdell JW (1989) Brefeldin A redistributes resident and itinerant Golgi proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 109:61–72
Dykstra KM, Pokusa JE, Suhan J, Lee TH (2010) Yip1A structures the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. Mol Biol Cell 21:1556–1568
Füllekrug J, Sönnichsen B, Schäfer U et al (1997) Characterization of brefeldin A induced vesicular structures containing cycling proteins of the intermediate compartment/cis-Golgi network. FEBS Lett 404:75–81
Galea G, Bexiga MG, Panarella A et al (2015) A high-content screening microscopy approach to dissect the role of Rab proteins in Golgi-to-ER retrograde trafficking. J Cell Sci 128:2339–2349
Heidtman M, Chen CZ, Collins RN, Barlowe C (2003) A role for Yip1p in COPII vesicle biogenesis. J Cell Biol 163:57–69
Kano F, Yamauchi S, Yoshida Y et al (2009) Yip1A regulates the COPI-independent retrograde transport from the Golgi complex to the ER. J Cell Sci 122:2218–2227
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yuan LC, Bonifacino JS, Klausner RD (1989) Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell 56:801–813
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Donaldson JG, Schweizer A et al (1990) Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell 60:821–836
Lorenz H, Hailey DW, Wunder C, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2006) The fluorescence protease protection (FPP) assay to determine protein localization and membrane topology. Nat Protoc 1:276–279
Maxfield FR (2014) Role of endosomes and lysosomes in human disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6:a016931
Misumi Y, Misumi Y, Miki K et al (1986) Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 261:11398–11403
Otsu N (1979) A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9:62–66
Poser I, Sarov M, Hutchins JRA et al (2008) BAC TransgeneOmics: a high-throughput method for exploration of protein function in mammals. Nat Methods 5:409–415
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Roussel BD, Kruppa AJ, Miranda E et al (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in neurological disease. Lancet Neurol 12:105–118
Saraste J, Lahtinen U, Goud B (1995) Localization of the small GTP-binding protein rab1p to early compartments of the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 4):1541–1552
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Schröder K, Martoglio B, Hofmann M et al (1999) Control of glycosylation of MHC class II-associated invariant chain by translocon-associated RAMP4. EMBO J 18:4804–4815
Shakoori A, Fujii G, Yoshimura S-I et al (2003) Identification of a five-pass transmembrane protein family localizing in the Golgi apparatus and the ER. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:850–857
Simpson JC (2009) Screening the secretion machinery: high throughput imaging approaches to elucidate the secretory pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:903–909
Simpson JC, Joggerst B, Laketa V et al (2012) Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies human proteins with a regulatory function in the early secretory pathway. Nat Cell Biol 14:764–774
Singan VR, Jones TR, Curran KM, Simpson JC (2011) Dual channel rank-based intensity weighting for quantitative co-localization of microscopy images. BMC Bioinform 12:407
Tang BL, Ong YS, Huang B et al (2001) A membrane protein enriched in endoplasmic reticulum exit sites interacts with COPII. J Biol Chem 276:40008–40017
Tanimoto K, Suzuki K, Jokitalo E et al (2011) Characterization of YIPF3 and YIPF4, cis-Golgi Localizing Yip domain family proteins. Cell Struct Funct 36:171–185
Thyberg J, Moskalewski S (1985) Microtubules and the organization of the Golgi complex. Exp Cell Res 159:1–16
Tisdale EJ, Bourne JR, Khosravi-Far R et al (1992) GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol 119:749–761
Wendler F, Gillingham AK, Sinka R et al (2010) A genome-wide RNA interference screen identifies two novel components of the metazoan secretory pathway. EMBO J 29:304–314
Yang X, Matern HT, Gallwitz D (1998) Specific binding to a novel and essential Golgi membrane protein (Yip1p) functionally links the transport GTPases Ypt1p and Ypt31p. EMBO J 17:4954–4963
Yoshida Y, Suzuki K, Yamamoto A et al (2008) YIPF5 and YIF1A recycle between the ER and the Golgi apparatus and are involved in the maintenance of the Golgi structure. Exp Cell Res 314:3427–3443
Yoshimura S-I, Gerondopoulos A, Linford A et al (2010) Family-wide characterization of the DENN domain Rab GDP-GTP exchange factors. J Cell Biol 191:367–381
Zahraoui A, Touchot N, Chardin P, Tavitian A (1989) The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem 264:12394–12401
Acknowledgements
This work was partly funded by The Irish Research Council (IRC), the UCD Bioinformatics and Systems Biology PhD programme, and a Principal Investigator (PI) Grant (09/IN.1/B2604) from Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) to JCS. This work was carried out in the UCD Cell Screening Laboratory, supported by a grant from the UCD College of Science. The authors thank Maeve Long, George Galea and Mariana G. Bexiga for valuable feedback and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kranjc, T., Dempsey, E., Cagney, G. et al. Functional characterisation of the YIPF protein family in mammalian cells. Histochem Cell Biol 147, 439–451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1527-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1527-3