Abstract
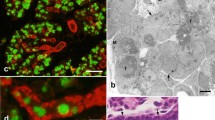
The present immunohistochemical study was attempted to localize in the submandibular glands of mice at various postnatal stages a diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) isoform termed DGKζ which is characterized by a nuclear localization signal and a nuclear export signal. This attempt was based on following facts: the continuous postnatal differentiation of glandular cells in the rodent submandibular gland, the regulatory role of DGK in the activity of protein kinase C (PKC) through attenuation of diacylglycerol (DAG), and the possible involvement of PKC in various cellular activities including the saliva secretion as well as the cell differentiation. As a result, a selective localization of immunoreactivity for DGKζ was detected in terminal tubule (TT) cells which comprise a majority of the newborn acinar structure and differentiate into the intercalated duct cells and/or the acinar cells. The immunoreactivity was deposited in portions of the cytoplasm lateral and basal to the nucleus, but not in the nuclei themselves. Although the immunoreactive TT cells remained until later stages in female specimen than in male, they eventually disappeared in both sexes by young adult stages. The present finding suggests that the regulatory involvement of DGKζ in PKC functions via control of DAG is exerted in the differentiation of the TT cells. In addition, another possible involvement of DGKζ in the regulation of secretion of the TT cells as well as its functional significance of its nuclear localization in the submandibular ganglion cells was also discussed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvares EP, Sesso A (1975) Cell proliferation, differentiation and transformation in the rat submandibular gland during early postnatal growth. A quantitative and morphological study. Arch Histol Jpn 38:177–208
Amano O, Iseki S (1998) Occurrence and nuclear localization of cAMP response element-binding protein in the post-natal development of the rat submandibular gland. Histochem J 30:591–601
Amano O, Tsuji T, Nakamura T, Iseki S (1991) Expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in the submandibular gland of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 39:1707–1711
Ball WD, Nelson NJ (1978) A Stage-Restricted Secretory System in the submandibular gland of the neonatal rat. Differentiation 10:147–158
Ball WD, Hand AR, Moreira JE, Johnson A (1988) A secretory protein restricted to type I cells in neonatal rat submandibular glands. Dev Biol 129:464–475
Barka T (1980) Biologically active polypeptides in submandibular glands. J Histochem Cytochem 28:836–859
Clemens KJ, Trayner I, Menaya J (1992) The role of protein kinase C isoenzymes in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Sci 103:881–887
Culp DJ, Zhang V, Evans RL (2011) Role of calcium and PKC in salivary mucous cell exocrine secretion. J Dent Res 90:1469–1476
Cutler LS, Chaudhry AP (1974) Cytodifferentiation of the acinar cells of the rat submandibular gland. Dev Biol 41:31–41
Denny PC, Chai Y, Pimprapaiporn W, Denny PA (1990) Three-dimensional reconstruction of adult female mouse submandibular gland secretory structures. Anat Rec 226:489–500
Denny PC, Liu P, Denny PA (1999) Evidence of a phonotypically determined ductal cell lineage in mouse salivary glands. Anat Rec 256:84–90
Dvorák M (1969) The secretory cells of the submaxillary gland in the perinatal period of development in the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 99:346–356
Evangelisti C, Astolfi A, Gaboardi GC, Tazzari P, Pession A, Goto K, Martelli AM (2009) TIS21/BTG2/PC3 and cyclin D1 are key determinants of nuclear diacylglycerol kinase-zeta-dependent cell cycle arrest. Cell Signal 21:801–809
Goto K, Kondo H (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of a 90-kDa diacylglycerol kinase that predominantly localizes in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7598–75602
Goto K, Kondo H (1996) A 104-kDa diacylglycerol kinase containing ankyrin-like repeats localizes in the cell nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:11196–11201
Goto K, Funayama M, Kondo H (1994) Cloning and expression of a cytoskeleton-associated diacylglycerol kinase that is dominantly expressed in cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:13042–13046
Goto K, Hozumi Y, Nakano T, Saino-Saito S, Martelli AM (2008) Lipid messenger, diacylglycerol, and its regulator, diacylglycerol kinase, in cells, organs, and animals: history and perspective. Tohoku J Exp Med 214:199–212
Goto K, Tanaka T, Nakano T, Okada M, Hozumi Y, Topham MK, Martelli AM (2013) DGKζ under stress conditions: “To be nuclear or cytoplasmic, that is the question”. Adv Biol Regul 54:242–253
Gresik EW (1975) The postnatal development of the sexually dimorphic duct system and of amylase activity in the submandibular glands of mice. Cell Tissue Res 157:411–422
Gresik EW (1980) Postnatal developmental changes in submandibular glands of rats and mice. J Histochem Cytochem 28:860–870
Hecht R, Connelly M, Marchetti L, Ball W, Hand A (2000) Cell death during development of intercalated ducts in the rat submandibular gland. Anat Rec 258:349–358
Heppner TJ, Fiekers JF (2003) Long-term potentiation of nicotinic synaptic transmission in rat superior cervical ganglia produced by phorbol ester and tetanic stimulation. Auton Neurosci 105:35–44
Hipkaeo W, Wakayama T, Yamamoto M, Iseki S (2004) Expression and localization of the transcription factor JunD in the duct system of mouse submandibular gland. J Histochem Cytochem 52:479–490
Hozumi Y, Ito T, Nakano T, Nakagawa T, Aoyagi M, Kondo H, Goto K (2003) Nuclear localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta in neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:1448–1457
Hozumi Y, Watanabe M, Goto K (2010) Signaling cascade of diacylglycerol kinase β in the pituitary intermediate lobe: dopamine D2 receptor/phospholipase Cb4/diacylglycerol kinase β/protein kinase Cα. J Histochem Cytochem 58:119–129
Hozumi Y, Matsui H, Sakane F, Watanabe M, Goto K (2013) Distinct expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase isozymes in rat retina. J Histochem Cytochem 61:462–476
Kamaishi H, Endoh T, Suzuki T (2004) Multiple signal pathways coupling VIP and PACAP receptors to calcium channels in hamster submandibular ganglion neurons. Auton Neurosci 111:15–26
Kanoh H, Yamada K, Sakane F (1990) Diacylglycerol kinase: a key modulator of signal transduction? Trends Biochem Sci 15:47–50
Kanoh H, Yamada K, Sakane F (2002) Diacylglycerol kinases: emerging downstream regulators in cell signaling systems. J Biochem 131:629–633
Kim H, Han SH, Quan HY, Jung YJ, An J, Kang P, Park JB, Yoon BJ, Seol GH, Min SS (2012) Bryostatin-1 promotes long-term potentiation via activation of PKCα and PKCε in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 226:348–355
Lee SY, Choi HK, Kim ST, Chung S, Park MK, Cho JH, Ho WK, Cho H (2010) Cholesterol inhibits M-type K+ channels via protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation in sympathetic neurons. J Biol Chem 285:10939–10950
Leeson CR, Jacoby F (1959) An electron microscopic study of the rat submaxillary gland during its post-natal development and in the adult. J Anat 93:287–295
Los AP, Vinke FP, de Widt J, Topham MK, van Blitterswijk WJ, Divecha N (2006) The retinoblastoma family proteins bind to and activate diacylglycerol kinase zeta. J Biol Chem 281:858–866
Melvin JE, Yule D, Shuttleworth T, Begenisich T (2005) Regulation of fluid and electrolyte secretion in salivary gland acinar cells. Annu Rev Physiol 67:445–469
Moreira JE, Ball WD, Mirels L, Hand AR (1991) Accumulation and localization of two adult acinar cell secretory proteins during development of the rat submandibular gland. Am J Anat 191:167–184
Nauntofte B, Poulsen JH (1986) Effects of Ca2+ and furosemide on Cl− transport and O2 uptake in rat parotid acini. Am J Physiol 251:C175–C185
Nishizuka Y (1984) The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature 308:693–698
Okada M, Hozumi Y, Ichimura T, Tanaka T, Hasegawa H, Yamamoto M, Takahashi N, Iseki K, Yagisawa H, Shinkawa T, Isobe T, Goto K (2011) Interaction of nucleosome assembly proteins abolishes nuclear localization of DGKζ by attenuating its association with importins. Exp Cell Res 317:2853–2863
Putney JW Jr, McKinney JS, Aub DL, Leslie BA (1983) Phorbol ester-induced protein secretion in rat parotid gland. Relationship to the role of inositol lipid breakdown and protein kinase C activation in stimulus-secretion coupling. Mol Pharmacol 26:261–266
Rasmussen H (1986) The calcium messenger system (1) (2). N Engl J Med 314:1094/1164–1101/1170
Sasaki H, Hozumi Y, Hasegawa H, Ito T, Takagi M, Ogino T, Watanabe M, Goto K (2006) Gene expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase isozymes in the rat spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Cell Tissue Res 326:35–42
Soltoff SP, Toker A (1995) Carbachol, substance P, and phorbol ester promote the tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase C delta in salivary gland epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 270:13490–13495
Srivastava HC (1977) Development of acinar cells in the rat submandibular gland. J Anat 123:459–465
Sumner AD, Margiotta JF (2008) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) alters parasympathetic neuron gene expression in a time-dependent fashion. J Mol Neurosci 36:141–156
Takuma T, Ichida T (1986) Phorbol ester stimulates amylase secretion from rat parotid cells. FEBS Lett 199:53–56
Tanaka T, Okada M, Hozumi Y, Tachibana K, Kitanaka C, Hamamoto Y, Martelli AM, Topham MK, Iino M, Goto K (2013) Cytoplasmic localization of DGKζ exerts a protective effect against p53-mediated cytotoxicity. J Cell Sci 126:2785–2797
Tojyo Y, Tanimura A, Matsui S, Matsumoto Y (1993) Carbachol-induced potassium release in rat parotid acini: comparison of the roles of cytosolic Ca2+ and protein kinase C. Jpn J Pharmacol 63:439–446
Turner RJ, Sugiya H (2002) Understanding salivary fluid and protein secretion. Oral Dis 8:3–11
Yamada E, Endoh T, Suzuki T (2002) Angiotensin II-induced inhibition of calcium currents via G(q/11)-protein involving protein kinase C in hamster submandibular ganglion neurons. Neurosci Res 43:179–189
Yamashina S, Barka T (1972) Localization of peroxidase activity in the developing submandibular gland of normal and isoproterenol-treated rats. J Histochem Cytochem 20:855–872
Yoshimura K, Fujita-Yoshigaki J, Murakami M, Segawa A (2002) Cyclic AMP has distinct effects from Ca(2+) in evoking priming and fusion/exocytosis in parotid amylase secretion. Pflugers Arch 444:586–596
Zajicek G, Yagil C, Michaeli Y (1985) The streaming submandibular gland. Anat Rec 213:150–158
Zinzen KM, Hand AR, Yankova M, Ball WD, Mirels L (2004) Molecular cloning and characterization of the neonatal rat and mouse submandibular gland protein SMGC. Int J Genes Genomes 334:23–33
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the research grants from Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University (Nos. I57326 and RG57301).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hipkaeo, W., Chomphoo, S., Pakkarato, S. et al. Selective localization of diacylglycerol kinase (DGK)ζ in the terminal tubule cells in the submandibular glands of early postnatal mice. Histochem Cell Biol 144, 185–193 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1328-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1328-0