Abstract
Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) is enriched in neurons and binds to polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin. It consists of two alternatively spliced isoforms, HAP1A and HAP1B, which differ only in their short C-terminal sequences. Both HAP1A and HAP1B have been also detected in pancreatic β cells, where the loss of HAP1 impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Here, we use time-lapse laser scanning confocal microscopy to provide direct evidence that HAP1A, but not HAP1B, co-localizes and co-migrates with insulin-containing vesicles and actin-based myosin Va motor protein in the INS-1 pancreatic β cell line. Knocking down HAP1 expression using small interfering RNA significantly inhibited actin-based transport of insulin vesicles following glucose stimulation. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated interaction between HAP1A, myosin Va, and phogrin, a transmembrane protein in insulin-containing vesicles. Stimulating INS-1 cells with glucose increased the association of HAP1A with myosin Va, while silencing HAP1 expression reduced the association of myosin Va with phogrin after glucose stimulation, without affecting levels of myosin Va or actin. Our results provide real-time evidence in living cells that HAP1 may help regulate transport of insulin-containing secretory granules along cortical actin filaments. This also raises the possibility that HAP1 may play an important role in actin-based secretory vesicle trafficking in neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asfari M, Janjic D, Meda P, Li G, Halban PA, Wollheim CB (1992) Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology 130(1):167–178
Bjorkqvist M, Fex M, Renstrom E, Wierup N, Petersen A, Gil J, Bacos K, Popovic N, Li JY, Sundler F, Brundin P, Mulder H (2005) The R6/2 transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease develops diabetes due to deficient beta-cell mass and exocytosis. Hum Mol Genet 14(5):565–574. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi053
Canclini L, Wallrabe H, Di Paolo A, Kun A, Calliari A, Sotelo-Silveira JR, Sotelo JR (2014) Association of Myosin Va and Schwann cells-derived RNA in mammal myelinated axons, analyzed by immunocytochemistry and confocal FRET microscopy. Methods 66(2):153–161. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.06.007
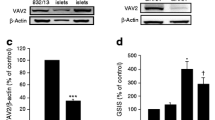
Cape A, Chen X, Wang CE, O’Neill A, Lin YF, He J, Xu XS, Yi H, Li H, Li S, Li XJ (2012) Loss of huntingtin-associated protein 1 impairs insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 69(8):1305–1317. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0692-8
Chan EY, Nasir J, Gutekunst CA, Coleman S, Maclean A, Maas A, Metzler M, Gertsenstein M, Ross CA, Nagy A, Hayden MR (2002) Targeted disruption of huntingtin-associated protein-1 (Hap1) results in postnatal death due to depressed feeding behavior. Hum Mol Genet 11(8):945–959
Dragatsis I, Dietrich P, Zeitlin S (2000) Expression of the huntingtin-associated protein 1 gene in the developing and adult mouse. Neurosci Lett 282(1–2):37–40
Eichler TW, Kogel T, Bukoreshtliev NV, Gerdes HH (2006) The role of myosin Va in secretory granule trafficking and exocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 5):671–674. doi:10.1042/BST0340671
Engelender S, Sharp AH, Colomer V, Tokito MK, Lanahan A, Worley P, Holzbaur EL, Ross CA (1997) huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) interacts with the p150Glued subunit of dynactin. Hum Mol Genet 6(13):2205–2212
Farrer LA (1985) Diabetes mellitus in Huntington disease. Clin Genet 27(1):62–67
Fujinaga R, Yanai A, Nakatsuka H, Yoshida K, Takeshita Y, Uozumi K, Zhao C, Hirata K, Kokubu K, Nagano M, Shinoda K (2007) Anti-human placental antigen complex X-P2 (hPAX-P2) anti-serum recognizes C-terminus of huntingtin-associated protein 1A common to 1B as a determinant marker for the stigmoid body. Histochem Cell Biol 128(4):335–348. doi:10.1007/s00418-007-0315-5
Gauthier LR, Charrin BC, Borrell-Pages M, Dompierre JP, Rangone H, Cordelieres FP, De Mey J, MacDonald ME, Lessmann V, Humbert S, Saudou F (2004) Huntingtin controls neurotrophic support and survival of neurons by enhancing BDNF vesicular transport along microtubules. Cell 118(1):127–138. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.018
Gutekunst CA, Li SH, Yi H, Ferrante RJ, Li XJ, Hersch SM (1998) The cellular and subcellular localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1): comparison with huntingtin in rat and human. J Neurosci 18(19):7674–7686
Han JH, Han JF, Wang GD, Bao W, Fan WY, Li H (2011) Preparation of antibodies against amino terminal and carboxyl terminal poly peptide of huntingtin associated protein 1. J Xinxiang Med Coll 04:401–405
Hu Y, Liang J, Yu S (2014) High prevalence of diabetes mellitus in a five-generation Chinese family with Huntington’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. doi:10.3233/jad-131847
Hurlbert MS, Zhou W, Wasmeier C, Kaddis FG, Hutton JC, Freed CR (1999) Mice transgenic for an expanded CAG repeat in the Huntington’s disease gene develop diabetes. Diabetes 48(3):649–651
Ivarsson R, Jing X, Waselle L, Regazzi R, Renstrom E (2005) Myosin 5a controls insulin granule recruitment during late-phase secretion. Traffic 6(11):1027–1035. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00342.x
Josefsen K, Nielsen MD, Jorgensen KH, Bock T, Norremolle A, Sorensen SA, Naver B, Hasholt L (2008) Impaired glucose tolerance in the R6/1 transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. J Neuroendocrinol 20(2):165–172. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2007.01629.x
Kimura T, Taniguchi S, Toya K, Niki I (2010) Glucose-induced translocation of coronin 3 regulates the retrograde transport of the secretory membrane in the pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395(3):318–323. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.173
Kogel T, Bittins CM, Rudolf R, Gerdes HH (2010) Versatile roles for myosin Va in dense core vesicle biogenesis and function. Biochem Soc Trans 38(Pt 1):199–204. doi:10.1042/BST0380199
Kremer HP, Roos RA, Frolich M, Radder JK, Nieuwenhuijzen Kruseman AC, Van der Velde A, Buruma OJ (1989) Endocrine functions in Huntington’s disease. A two-and-a-half years follow-up study. J Neurol Sci 90(3):335–344
Kuroda TS, Fukuda M (2004) Rab27A-binding protein Slp2-a is required for peripheral melanosome distribution and elongated cell shape in melanocytes. Nat Cell Biol 6(12):1195–1203. doi:10.1038/ncb1197
Lalic NM, Maric J, Svetel M, Jotic A, Stefanova E, Lalic K, Dragasevic N, Milicic T, Lukic L, Kostic VS (2008) Glucose homeostasis in Huntington disease: abnormalities in insulin sensitivity and early-phase insulin secretion. Arch Neurol 65(4):476–480. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.4.476
Li XJ, Li SH (2005) HAP1 and intracellular trafficking. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(1):1–3. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.11.001
Li XJ, Li SH, Sharp AH, Nucifora FC Jr, Schilling G, Lanahan A, Worley P, Snyder SH, Ross CA (1995) A huntingtin-associated protein enriched in brain with implications for pathology. Nature 378(6555):398–402. doi:10.1038/378398a0
Li SH, Gutekunst CA, Hersch SM, Li XJ (1998a) Association of HAP1 isoforms with a unique cytoplasmic structure. J Neurochem 71(5):2178–2185
Li SH, Gutekunst CA, Hersch SM, Li XJ (1998b) Interaction of huntingtin-associated protein with dynactin P150Glued. J Neurosci 18(4):1261–1269
Li SH, Li H, Torre ER, Li XJ (2000) Expression of huntingtin-associated protein-1 in neuronal cells implicates a role in neuritic growth. Mol Cell Neurosci 16(2):168–183. doi:10.1006/mcne.2000.0858
Li H, Wyman T, Yu ZX, Li SH, Li XJ (2003a) Abnormal association of mutant huntingtin with synaptic vesicles inhibits glutamate release. Hum Mol Genet 12(16):2021–2030
Li SH, Yu ZX, Li CL, Nguyen HP, Zhou YX, Deng C, Li XJ (2003b) Lack of huntingtin-associated protein-1 causes neuronal death resembling hypothalamic degeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 23(17):6956–6964
Liao M, Shen J, Zhang Y, Li SH, Li XJ, Li H (2005) Immunohistochemical localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in endocrine system of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 53(12):1517–1524. doi:10.1369/jhc.5A6662.2005
Liao M, Chen X, Han J, Yang S, Peng T, Li H (2010) Selective expression of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in b-cells of the rat pancreatic islets. J Histochem Cytochem 58(3):255–263. doi:10.1369/jhc.2009.954479
Lin YF, Xu X, Cape A, Li S, Li XJ (2010) Huntingtin-associated protein-1 deficiency in orexin-producing neurons impairs neuronal process extension and leads to abnormal behavior in mice. J Biol Chem 285(21):15941–15949. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.107318
Luesse HG, Schiefer J, Spruenken A, Puls C, Block F, Kosinski CM (2001) Evaluation of R6/2 HD transgenic mice for therapeutic studies in Huntington’s disease: behavioral testing and impact of diabetes mellitus. Behav Brain Res 126(1–2):185–195
Mackenzie KD, Duffield MD, Peiris H, Phillips L, Zanin MP, Teo EH, Zhou XF, Keating DJ (2014) Huntingtin-associated protein 1 regulates exocytosis, vesicle docking, readily releasable pool size and fusion pore stability in mouse chromaffin cells. J Physiol 592(7):1505–1518. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2013.268342
McCaffrey MW, Lindsay AJ (2012) Roles for myosin Va in RNA transport and turnover. Biochem Soc Trans 40(6):1416–1420. doi:10.1042/bst20120172
McGuire JR, Rong J, Li SH, Li XJ (2006) Interaction of huntingtin-associated protein-1 with kinesin light chain: implications in intracellular trafficking in neurons. J Biol Chem 281(6):3552–3559. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509806200
Podolsky S, Leopold NA (1977) Abnormal glucose tolerance and arginine tolerance tests in Huntington’s disease. Gerontology 23(1):55–63
Podolsky S, Leopold NA, Sax DS (1972) Increased frequency of diabetes mellitus in patients with Huntington’s chorea. Lancet 1(7765):1356–1358
Pouli AE, Emmanouilidou E, Zhao C, Wasmeier C, Hutton JC, Rutter GA (1998) Secretory-granule dynamics visualized in vivo with a phogrin-green fluorescent protein chimaera. Biochem J 333(1):193–199
Rong J, McGuire JR, Fang ZH, Sheng G, Shin JY, Li SH, Li XJ (2006) Regulation of intracellular trafficking of huntingtin-associated protein-1 is critical for TrkA protein levels and neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 26(22):6019–6030. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.1251-06.2006
Rong J, Li S, Sheng G, Wu M, Coblitz B, Li M, Fu H, Li XJ (2007a) 14-3-3 protein interacts with huntingtin-associated protein 1 and regulates its trafficking. J Biol Chem 282(7):4748–4756. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609057200
Rong J, Li SH, Li XJ (2007b) Regulation of intracellular HAP1 trafficking. J Neurosci Res 85(14):3025–3029. doi:10.1002/jnr.21326
Rorsman P, Renstrom E (2003) Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 46(8):1029–1045. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1153-1
Rutter GA, Hill EV (2006) Insulin vesicle release: walk, kiss, pause… then run. Physiology 21:189–196. doi:10.1152/physiol.00002.2006
Schubotz R, Hausmann L, Kaffarnik H, Zehner J, Oepen H (1976) Fatty acid patterns and glucose tolerance in Huntington’s chorea (author’s transl). Res Exp Med 167(3):203–215
Sheng G, Chang GQ, Lin JY, Yu ZX, Fang ZH, Rong J, Lipton SA, Li SH, Tong G, Leibowitz SF, Li XJ (2006) Hypothalamic huntingtin-associated protein 1 as a mediator of feeding behavior. Nat Med 12(5):526–533. doi:10.1038/nm1382
Smith R, Bacos K, Fedele V, Soulet D, Walz HA, Obermuller S, Lindqvist A, Bjorkqvist M, Klein P, Onnerfjord P, Brundin P, Mulder H, Li JY (2009) Mutant huntingtin interacts with β-tubulin and disrupts vesicular transport and insulin secretion. Hum Mol Genet 18(20):3942–3954. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp336
Somers G, Blondel B, Orci L, Malaisse WJ (1979) Motile events in pancreatic endocrine cells. Endocrinology 104(1):255–264
Tang TS, Tu H, Orban PC, Chan EY, Hayden MR, Bezprozvanny I (2004) HAP1 facilitates effects of mutant huntingtin on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca release in primary culture of striatal medium spiny neurons. Eur J Neurosci 20(7):1779–1787. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03633.x
Tsuboi T, da Silva Xavier G, Leclerc I, Rutter GA (2003) 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase controls insulin-containing secretory vesicle dynamics. J Biol Chem 278(52):52042–52051. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307800200
Tsuboi T, Ravier MA, Parton LE, Rutter GA (2006) Sustained exposure to high glucose concentrations modifies glucose signaling and the mechanics of secretory vesicle fusion in primary rat pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 55(4):1057–1065
Varadi A, Tsuboi T, Rutter GA (2005) Myosin Va transports dense core secretory vesicles in pancreatic MIN6 beta-cells. Mol Biol Cell 16(6):2670–2680. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-11-1001
Wagner W, Brenowitz SD, Hammer JA 3rd (2011) Myosin-Va transports the endoplasmic reticulum into the dendritic spines of Purkinje neurons. Nat Cell Biol 13(1):40–48. doi:10.1038/ncb2132
Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2006) Hap1 and GABA: thinking about food intake. Cell Metab 3(6):388–390. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.007
Wu LL, Zhou XF (2009) Huntingtin associated protein 1 and its functions. Cell Adhes Migr 3(1):71–76
Wu LL, Fan Y, Li S, Li XJ, Zhou XF (2010) Huntingtin-associated protein-1 interacts with pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mediates its transport and release. J Biol Chem 285(8):5614–5623. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.073197
Yang M, Lim Y, Li X, Zhong JH, Zhou XF (2011) Precursor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF) forms a complex with huntingtin-associated protein-1 (HAP1) and sortilin that modulates proBDNF trafficking, degradation, and processing. J Biol Chem 286(18):16272–16284. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.195347
Ye CF, Li H (2009) HSP40 ameliorates impairment of insulin secretion by inhibiting huntingtin aggregation in a HD pancreatic beta cell model. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73(8):1787–1792
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171155) to HL. We are grateful to Professor Guy Rutter of Imperial College London for the kind gift of phogrin-EGFP plasmid.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 2034 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MPG 3850 kb)
418_2015_1311_MOESM3_ESM.tif
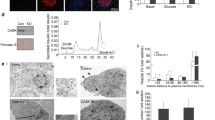
Fig. S1 Partial co-localization of myosin Va/actin and HAP1/actin. Immunofluorescence double labeling with antibodies against myosin Va (red) or HAP1(both HAP1A and HAP1B) (red) and actin (green) in INS-1 cells. Confocal microscopy was used to capture serial sections at 1-μm intervals of (A) myosin Va/actin and (B) HAP1/actin. Myosin Va and HAP1 partially co-localized with actin (arrows). (TIFF 985 kb)
418_2015_1311_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Fig. S2. Diffuse localization of HAP1B in the cytoplasm. INS-1 cultured in 6-well plates were transfected with 0.5, 1.0 or 2.0 μg per well of plasmid encoding EGFP-HAP1B (green) or pJred-HAP1B (red). Confocal microscopy showed a homogeneous cytoplasmic distribution of HAP1B. (TIFF 848 kb)
418_2015_1311_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Fig. S3 Dephosphorylated HAP1A binds more myosin Va than wild-type HAP1A. (A) INS-1 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing EGFP fusions of wild-type HAP1A (EGFP-HAP1A) or HAP1A(T598A) mutant (EGFP-T598A), and the ability of these fusion proteins to co-precipitate endogenous myosin Va was investigated. Immunoprecipitates were probed by Western blotting using a rabbit anti-GFP antibody. EGFP-T598A bound more myosin Va than wild-type HAP1A. (B) Densitometric analysis of the ratio of endogenous myosin Va to EGFP-HAP1A or EGFP-T598A from 3 experiments. (TIFF 304 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Peng, T., Wu, H. et al. HAP1 helps to regulate actin-based transport of insulin-containing granules in pancreatic β cells. Histochem Cell Biol 144, 39–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1311-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1311-9