Abstract
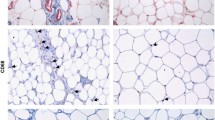
Clinical and experimental evidence suggests that the adipokine leptin may be important for the development of cardiovascular complications associated with obesity, possibly through interaction with its receptor on vascular cells. In the present study, we systematically analysed expression of the leptin receptor in normal and diseased vascular specimens using immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and quantitative real time-PCR. In particular, human atherosclerotic plaques as well as experimental vascular lesions induced in hypercholesterolemic mice and minipigs, respectively, were examined. Our results demonstrate the presence of the leptin receptor in normal vessel wall segments as well as neointimal or atherosclerotic lesions. In the latter, ObR expressing cells were predominantly localised on the luminal border and within the subintima, and coexpression of von Willebrand factor, VEGF receptor-2 or VE cadherin identified them as endothelial cells. Moreover, CD14-positive monocytes/macrophages were strongly positive for the leptin receptor. In contrast, only few ObR-expressing smooth muscle cells could be detected in human atherosclerotic plaques. The findings of the present study thus support a possible action of leptin on the cardiovascular system by demonstrating expression of the leptin receptor in different types of vascular lesions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg AH, Scherer PE (2005) Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 96:939–949
Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Ohman EM, Hirsch AT, Ikeda Y, Mas JL, Goto S, Liau CS, Richard AJ, Rother J, Wilson PW (2006) International prevalence, recognition, and treatment of cardiovascular risk factors in outpatients with atherothrombosis. JAMA 295:180–189
Bodary PF, Westrick RJ, Wickenheiser KJ, Shen YC, Eitzman DT (2002) Effect of leptin on arterial thrombosis following vascular injury in mice. JAMA 287:1706–1709
Bodary PF, Gu S, Shen Y, Hasty AH, Buckler JM, Eitzman DT (2005) Recombinant leptin promotes atherosclerosis and thrombosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:e119–e122
Bodary PF, Shen Y, Ohman M, Bahrou KL, Vargas FB, Cudney SS, Wickenheiser KJ, Myers MG Jr, Eitzman DT (2007) Leptin regulates neointima formation after arterial injury through mechanisms independent of blood pressure and the leptin receptor/STAT3 signaling pathways involved in energy balance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:70–76
Bouloumie A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, Busse R (1998) Leptin, the product of Ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circ Res 83:1059–1066
Buchwald AB, Unterberg C, Nebendahl K, Grone HJ, Wiegand V (1992) Low-molecular-weight heparin reduces neointimal proliferation after coronary stent implantation in hypercholesterolemic minipigs. Circulation 86:531–537
Ciccone M, Vettor R, Pannacciulli N, Minenna A, Bellacicco M, Rizzon P, Giorgino R, De Pergola G (2001) Plasma leptin is independently associated with the intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25:805–810
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL (1996) Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334:292–295
Fei H, Okano HJ, Li C, Lee GH, Zhao C, Darnell R, Friedman JM (1997) Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7001–7005
Gainsford T, Willson TA, Metcalf D, Handman E, McFarlane C, Ng A, Nicola NA, Alexander WS, Hilton DJ (1996) Leptin can induce proliferation, differentiation, and functional activation of hemopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14564–14568
Kang SM, Kwon HM, Hong BK, Kim D, Kim IJ, Choi EY, Jang Y, Kim HS, Kim MS, Kwon HC (2000) Expression of leptin receptor (Ob-R) in human atherosclerotic lesions: potential role in intimal neovascularization. Yonsei Med J 41:68–75
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, Farb A, Guerrero LJ, Hayase M, Kutys R, Narula J, Finn AV, Virmani R (2003) Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med 349:2316–2325
Konstantinides S, Schäfer K, Koschnick S, Loskutoff DJ (2001a) Leptin-dependent platelet aggregation and arterial thrombosis suggests a mechanism for atherothrombotic disease in obesity. J Clin Invest 108:1533–1540
Konstantinides S, Schäfer K, Thinnes T, Loskutoff DJ (2001b) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and its cofactor vitronectin stabilize arterial thrombi after vascular injury in mice. Circulation 103:576–583
Konstantinides S, Schäfer K, Neels JG, Dellas C, Loskutoff DJ (2004) Inhibition of endogenous leptin protects mice from arterial and venous thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:2196–2201
Li L, Mamputu JC, Wiernsperger N, Renier G (2005) Signaling pathways involved in human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression induced by leptin: inhibitory effect of metformin. Diabetes 54:2227–2234
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, Klein AS, Bulkley GB, Bao C, Noble PW, Lane MD, Diehl AM (1998) Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J 12:57–65
MacDougald OA, Hwang CS, Fan H, Lane MD (1995) Regulated expression of the obese gene product (leptin) in white adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9034–9037
Nakata M, Yada T, Soejima N, Maruyama I (1999) Leptin promotes aggregation of human platelets via the long form of its receptor. Diabetes 48:426–429
Parhami F, Tintut Y, Ballard A, Fogelman AM, Demer LL (2001) Leptin enhances the calcification of vascular cells: artery wall as a target of leptin. Circ Res 88:954–960
Park HY, Kwon HM, Lim HJ, Hong BK, Lee JY, Park BE, Jang Y, Cho SY, Kim HS (2001) Potential role of leptin in angiogenesis: leptin induces endothelial cell proliferation and expression of matrix metalloproteinases in vivo and in vitro. Exp Mol Med 33:95–102
Piatti P, Di Mario C, Monti LD, Fragasso G, Sgura F, Caumo A, Setola E, Lucotti P, Galluccio E, Ronchi C, Origgi A, Zavaroni I, Margonato A, Colombo A (2003) Association of insulin resistance, hyperleptinemia, and impaired nitric oxide release with in-stent restenosis in patients undergoing coronary stenting. Circulation 108:2074–2081
Reilly MP, Iqbal N, Schutta M, Wolfe ML, Scally M, Localio AR, Rader DJ, Kimmel SE (2004) Plasma leptin levels are associated with coronary atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3872–3878
Santos-Alvarez J, Goberna R, Sanchez-Margalet V (1999) Human leptin stimulates proliferation and activation of human circulating monocytes. Cell Immunol 194:6–11
Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM, Ma G, Jaskowiak NT, Rivet DJ III, Flier JS, Lowell BB, Fraker DL, Alexander HR (1997) Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med 185:171–175
Schäfer K, Müller K, Hecke A, Mounier E, Goebel J, Loskutoff DJ, Konstantinides S (2003) Enhanced thrombosis in atherosclerosis-prone mice is associated with increased arterial expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:2097–2103
Schäfer K, Halle M, Goeschen C, Dellas C, Pynn M, Loskutoff DJ, Konstantinides S (2004) Leptin promotes vascular remodeling and neointimal growth in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:112–117
Shamsuzzaman AS, Winnicki M, Wolk R, Svatikova A, Phillips BG, Davison DE, Berger PB, Somers VK (2004) Independent association between plasma leptin and C-reactive protein in healthy humans. Circulation 109:2181–2185
Shin HJ, Oh J, Kang SM, Lee JH, Shin MJ, Hwang KC, Jang Y, Chung JH (2005) Leptin induces hypertrophy via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329:18–24
Sierra-Honigmann MR, Nath AK, Murakami C, Garcia-Cardena G, Papapetropoulos A, Sessa WC, Madge LA, Schechner JS, Schwabb MB, Polverini PJ, Flores-Riveros JR (1998) Biological action of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 281:1683–1686
Soderberg S, Ahren B, Jansson JH, Johnson O, Hallmans G, Asplund K, Olsson T (1999) Leptin is associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction. J Intern Med 246:409–418
Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, Fuster V, Glagov S, Insull W Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW (1995) A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 92:1355–1374
Stephenson K, Tunstead J, Tsai A, Gordon R, Henderson S, Dansky HM (2003) Neointimal formation after endovascular arterial injury is markedly attenuated in db/db mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:2027–2033
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Schwartz SM (2000) Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1262–1275
Wallace AM, McMahon AD, Packard CJ, Kelly A, Shepherd J, Gaw A, Sattar N (2001) Plasma leptin and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS). Circulation 104:3052–3056
Wallerstedt SM, Eriksson AL, Niklason A, Ohlsson C, Hedner T (2004) Serum leptin and myocardial infarction in hypertension. Blood Press 13:243–246
Wolk R, Berger P, Lennon RJ, Brilakis ES, Johnson BD, Somers VK (2004) Plasma leptin and prognosis in patients with established coronary atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:1819–1824
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, Commerford P, Lang CC, Rumboldt Z, Onen CL, Lisheng L, Tanomsup S, Wangai P Jr, Razak F, Sharma AM, Anand SS (2005) Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet 366:1640–1649
Zarkesh-Esfahani H, Pockley G, Metcalfe RA, Bidlingmaier M, Wu Z, Ajami A, Weetman AP, Strasburger CJ, Ross RJ (2001) High-dose leptin activates human leukocytes via receptor expression on monocytes. J Immunol 167:4593–4599
Zarkesh-Esfahani H, Pockley AG, Wu Z, Hellewell PG, Weetman AP, Ross RJ (2004) Leptin indirectly activates human neutrophils via induction of TNF-alpha. J Immunol 172:1809–1814
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Sarah Henkel and Stephanie Minne for expert technical assistance. The present work was supported in part by a grant from the “Novartis Stiftung für therapeutische Forschung” (to K.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeter, M.R., Schneiderman, J., Schumann, B. et al. Expression of the leptin receptor in different types of vascular lesions. Histochem Cell Biol 128, 323–333 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-007-0319-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-007-0319-1