Abstract
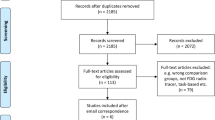
Brain gray matter volume (GMV) reduction has been reported in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI) and in PD patients with dementia (PDD) with cumulative evidence using voxel-based morphometry (VBM). However, the findings of these studies have not been entirely concordant. Whole-brain VBM studies comparing PD-MCI with PD patients without cognitive impairment (PD-NCI) and comparing PDD with PD patients without dementia (PDND) were systematically searched in PubMed and EMBASE databases from January 1995 to December 2015. Coordinates with significant differences were extracted from each cluster. Meta-analysis was performed using AES-SDM to quantitatively evaluate the GMV changes. Five studies comparing 92 PD-MCI with 192 PD-NCI patients were included in the PD-MCI vs. PD-NCI meta-analysis. Ten studies with 168 PDD and 233 PDND patients were included in the PDD vs. PDND meta-analysis. Compared with PD-NCI, GMV reductions were observed in left superior temporal lobe, left insula and left superior frontal lobe in PD-MCI patients. Significant GMV reduction were found in bilateral superior temporal lobe extending to hippocampus, and left superior frontal lobe in PDD patients comparing with PDND. Meta-regression of PDD studies showed that disease duration was negatively correlated with GMV in the left superior frontal lobe. GMV reductions in the frontal-limbic-temporal regions were main features of cognitive decline in PD. Unilateral-to-bilateral development of GMV reduction in the frontal-limbic-temporal regions is a possible indicator for PD-MCI to PDD progression, whereas significant hippocampal GMV reduction may not be a marker for early cognitive decline in PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schapira AH (2015) The measurement and importance of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 22(1):2–3. doi:10.1111/ene.12523
Lee JE, Cho KH, Song SK, Kim HJ, Lee HS, Sohn YH, Lee PH (2014) Exploratory analysis of neuropsychological and neuroanatomical correlates of progressive mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 85 (1):7-16. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2013-305062
Petrou M, Kotagal V, Bohnen NI (2012) An update on brain imaging in parkinsonian dementia. Imaging Med 4(2):201–213. doi:10.2217/iim.12.10
Hu XF, Zhang JQ, Zhang YL, Wu Y, Chen LH, Wang J (2013) Mild cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease: A voxel-based morphometry analysis of gray matter. [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging Technology 29 (1):24-29
Green J, McDonald WM, Vitek JL, Evatt M, Freeman A, Haber M, Bakay RA, Triche S, Sirockman B, DeLong MR (2002) Cognitive impairments in advanced PD without dementia. Neurology 59(9):1320–1324
Aarsland D, Kurz MW (2010) The epidemiology of dementia associated with Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci 289(1–2):18–22. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.034
Hely MA, Morris JG, Reid WG, Trafficante R (2005) Sydney Multicenter Study of Parkinson’s disease: non-l-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov Disord 20(2):190–199. doi:10.1002/mds.20324
Leroi I, McDonald K, Pantula H, Harbishettar V (2012) Cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: impact on quality of life, disability, and caregiver burden. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 25(4):208–214. doi:10.1177/0891988712464823
Pedersen KF, Larsen JP, Tysnes OB, Alves G (2013) Prognosis of mild cognitive impairment in early Parkinson disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. JAMA Neurol 70(5):580–586. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.2110
Carbon M, Marie RM (2003) Functional imaging of cognition in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 16(4):475–480. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000084225.82329.3c
Huang C, Mattis P, Tang C, Perrine K, Carbon M, Eidelberg D (2007) Metabolic brain networks associated with cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 34(2):714–723. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.003
Peraza LR, Colloby SJ, Firbank MJ, Greasy GS, McKeith IG, Kaiser M, O’Brien J, Taylor JP (2015) Resting state in Parkinson’s disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies: commonalities and differences. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 30(11):1135–1146. doi:10.1002/gps.4342
Beyer MK, Janvin CC, Larsen JP, Aarsland D (2007) A magnetic resonance imaging study of patients with Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment and dementia using voxel-based morphometry. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(3):254–259. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.093849
Song SK, Lee JE, Park HJ, Sohn YH, Lee JD, Lee PH (2011) The pattern of cortical atrophy in patients with Parkinson’s disease according to cognitive status. Mov Disord 26(2):289–296. doi:10.1002/mds.23477
Mak E, Zhou J, Tan LC, Au WL, Sitoh YY, Kandiah N (2014) Cognitive deficits in mild Parkinson’s disease are associated with distinct areas of grey matter atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85(5):576–580. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2013-305805
Nagano-Saito A, Washimi Y, Arahata Y, Kachi T, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dagher A, Ito K (2005) Cerebral atrophy and its relation to cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 64(2):224–229. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000149510.41793.50
Summerfield C, Junque C, Tolosa E, Salgado-Pineda P, Gomez-Anson B, Marti MJ, Pastor P, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Mercader J (2005) Structural brain changes in Parkinson disease with dementia: a voxel-based morphometry study. Arch Neurol 62(2):281–285. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.2.281
Xia J, Miu J, Ding H, Wang X, Chen H, Wang J, Wu J, Zhao J, Huang H, Tian W (2013) Changes of brain gray matter structure in Parkinson’s disease patients with dementia. Neural Regen Res 8(14):1276–1285. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.14.004
Compta Y, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Pereira JB, Junque C, Bargallo N, Tolosa E, Valldeoriola F, Munoz E, Camara A, Buongiorno M, Marti MJ (2012) Grey matter volume correlates of cerebrospinal markers of Alzheimer-pathology in Parkinson’s disease and related dementia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(8):941–947. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.04.028
Lee SH, Kim SS, Tae WS, Lee SY, Lee KU, Jhoo J (2013) Brain volumetry in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: where are the differences? Acta Radiol 54(5):581–586. doi:10.1177/0284185113476029
Mak E, Su L, Williams GB, O’Brien JT (2015) Neuroimaging correlates of cognitive impairment and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21(8):862–870. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.05.013
Goldman JG, Stebbins GT, Dinh V, Bernard B, Merkitch D, deToledo-Morrell L, Goetz CG (2014) Visuoperceptive region atrophy independent of cognitive status in patients with Parkinson’s disease with hallucinations. Brain 137(Pt 3):849–859. doi:10.1093/brain/awt360
Radua J, Mataix-Cols D, Phillips ML, El-Hage W, Kronhaus DM, Cardoner N, Surguladze S (2012) A new meta-analytic method for neuroimaging studies that combines reported peak coordinates and statistical parametric maps. Eur Psychiatry 27(8):605–611. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.04.001
Radua J, Rubia K, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Pomarol-Clotet E, Fusar-Poli P, Mataix-Cols D (2014) Anisotropic kernels for coordinate-based meta-analyses of neuroimaging studies. Front Psychiatry 5:13. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00013
Sheng L, Ma H, Zhong J, Shang H, Shi H, Pan P (2015) Motor and extra-motor gray matter atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: quantitative meta-analyses of voxel-based morphometry studies. Neurobiol Aging 36(12):3288–3299. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.08.018
Zhong J, Pan P, Dai Z, Shi H (2014) Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in dementia with Lewy bodies. Eur J Radiol 83(10):1870–1874. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.06.014
Pan PL, Shi HC, Zhong JG, Xiao PR, Shen Y, Wu LJ, Song YY, He GX, Li HL (2013) Gray matter atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: evidence from meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Neurol Sci 34(5):613–619. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1250-3
Melzer TR, Watts R, MacAskill MR, Pitcher TL, Livingston L, Keenan RJ, Dalrymple-Alford JC, Anderson TJ (2012) Grey matter atrophy in cognitively impaired Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(2):188–194. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2011-300828
Leff AP, Schofield TM, Crinion JT, Seghier ML, Grogan A, Green DW, Price CJ (2009) The left superior temporal gyrus is a shared substrate for auditory short-term memory and speech comprehension: evidence from 210 patients with stroke. Brain 132(Pt 12):3401–3410. doi:10.1093/brain/awp273
Bigler ED, Mortensen S, Neeley ES, Ozonoff S, Krasny L, Johnson M, Lu J, Provencal SL, McMahon W, Lainhart JE (2007) Superior temporal gyrus, language function, and autism. Dev Neuropsychol 31(2):217–238. doi:10.1080/87565640701190841
Phan KL, Wager T, Taylor SF, Liberzon I (2002) Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: a meta-analysis of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage 16(2):331–348. doi:10.1006/nimg.2002.1087
Dupont S (2002) Investigating temporal pole function by functional imaging. Epileptic Disord Int Epilepsy J Videotape 4(Suppl 1):S17–S22
Henry JD, Crawford JR (2004) Verbal fluency deficits in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Int Neuropsychol Soc JINS 10(4):608–622. doi:10.1017/s1355617704104141
Sanchez-Castaneda C, Rene R, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Campdelacreu J, Gascon J, Falcon C, Calopa M, Jauma S, Juncadella M, Junque C (2009) Correlations between gray matter reductions and cognitive deficits in dementia with Lewy Bodies and Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Mov Disord 24(12):1740–1746. doi:10.1002/mds.22488
Braak H, Braak E (2000) Pathoanatomy of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 247(Suppl 2):ii3–ii10
Mattila PM, Rinne JO, Helenius H, Dickson DW, Roytta M (2000) Alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive cortical Lewy bodies are associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 100(3):285–290
Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junque C, Segura B, Baggio HC, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Bargallo N, Tolosa E (2012) Progression of cortical thinning in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(14):1746–1753. doi:10.1002/mds.25240
Compta Y, Pereira JB, Rios J, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Junque C, Bargallo N, Camara A, Buongiorno M, Fernandez M, Pont-Sunyer C, Marti MJ (2013) Combined dementia-risk biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease: a prospective longitudinal study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19(8):717–724. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.03.009
Greene SJ, Killiany RJ (2010) Subregions of the inferior parietal lobule are affected in the progression to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 31(8):1304–1311. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.026
Pennanen C, Testa C, Laakso MP, Hallikainen M, Helkala EL, Hanninen T, Kivipelto M, Kononen M, Nissinen A, Tervo S, Vanhanen M, Vanninen R, Frisoni GB, Soininen H (2005) A voxel based morphometry study on mild cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(1):11–14. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.035600
Apostolova LG, Morra JH, Green AE, Hwang KS, Avedissian C, Woo E, Cummings JL, Toga AW, Jack CR Jr, Weiner MW, Thompson PM (2010) Automated 3D mapping of baseline and 12-month associations between three verbal memory measures and hippocampal atrophy in 490 ADNI subjects. Neuroimage 51(1):488–499. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.125
Rousseaux MW, Marcogliese PC, Qu D, Hewitt SJ, Seang S, Kim RH, Slack RS, Schlossmacher MG, Lagace DC, Mak TW, Park DS (2012) Progressive dopaminergic cell loss with unilateral-to-bilateral progression in a genetic model of Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(39):15918–15923. doi:10.1073/pnas.1205102109
Junque C, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Tolosa E, Summerfield C, Marti MJ, Pastor P, Gomez-Anson B, Mercader JM (2005) Amygdalar and hippocampal MRI volumetric reductions in Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Mov Disord 20(5):540–544. doi:10.1002/mds.20371
Apostolova LG, Beyer M, Green AE, Hwang KS, Morra JH, Chou YY, Avedissian C, Aarsland D, Janvin CC, Larsen JP, Cummings JL, Thompson PM (2010) Hippocampal, caudate, and ventricular changes in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Mov Disord 25(6):687–695. doi:10.1002/mds.22799
Zarei M, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Compta Y, Hough M, Junque C, Bargallo N, Tolosa E, Marti MJ (2013) Cortical thinning is associated with disease stages and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(8):875–881. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-304126
Wang WY, Yu JT, Liu Y, Yin RH, Wang HF, Wang J, Tan L, Radua J, Tan L (2015) Voxel-based meta-analysis of grey matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 4:6. doi:10.1186/s40035-015-0027-z
Jellinger KA (2005) Alpha-synuclein lesions in normal aging, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease: evidence from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(6):554
Du AT, Schuff N, Amend D, Laakso MP, Hsu YY, Jagust WJ, Yaffe K, Kramer JH, Reed B, Norman D, Chui HC, Weiner MW (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging of the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71(4):441–447
Ramirez-Ruiz B, Marti MJ, Tolosa E, Bartres-Faz D, Summerfield C, Salgado-Pineda P, Gomez-Anson B, Junque C (2005) Longitudinal evaluation of cerebral morphological changes in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. J Neurol 252(11):1345–1352. doi:10.1007/s00415-005-0864-2
Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Tolosa E, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Bargallo N, Junque C (2008) Hippocampal head atrophy predominance in Parkinson’s disease with hallucinations and with dementia. J Neurol 255(9):1324–1331. doi:10.1007/s00415-008-0885-8
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127(Pt 4):791–800. doi:10.1093/brain/awh088
Ramirez-Ruiz B, Marti MJ, Tolosa E, Gimenez M, Bargallo N, Valldeoriola F, Junque C (2007) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease patients with visual hallucinations. Eur J Neurol 14(7):750–756. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01768.x
Acknowledgments
We thank all the authors of the included studies. We especially thank Dr. Tracy Melzer for his kind help and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest concerning this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Yang, J., Hu, X. et al. Voxel-based meta-analysis of gray matter volume reductions associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 263, 1178–1187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8122-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8122-3