Abstract
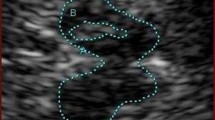
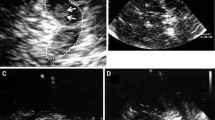
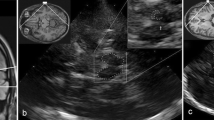
Transcranial sonography (TCS) of the basal ganglia is a non-invasive tool to study movement disorders. Very few studies have addressed the question of whether TCS may detect specific echofeatures in patients with primary dystonia. The basal ganglia including the substantia nigra (SN) and the ventricular system were investigated by TCS in 84 primary dystonia patients and 43 neurologically healthy controls. Any hyperechogenicity of the lenticular nucleus was present in 57.5% of the patients and in 50.0% of the controls (p = 0.453). While marked hyperechogenicity was more frequently present in the patients (17.8 vs. 7.9%), this difference was not significant (p = 0.227). No differences in the occurrence of hyperechogenicity were detectable either in the caudate nucleus (21.6 vs. 39.5%, p = 0.122) or the thalamus (4.1 vs. 0%, p = 0.199). Marked hyperechogenicity of the caudate nucleus was rare in dystonia (4.1%) and absent in controls. There was no relationship between the side of basal ganglia hyperechogenicity and the clinically affected side of cervical dystonia. The area of SN echogenicity was similar in patients and controls (0.19 ± 0.14 vs. 0.20 ± 0.13 cm2), but correlated negatively with increasing disease duration in the dystonia patients (ρ = –0.257, p = 0.028). Width of the third ventricle correlated with increasing age (ρ = 0.511, p = 0.000) and, in patients, with disease duration (ρ = 0.244, p = 0.034) and severity of cervical dystonia (ρ = 0.281, p = 0.038). No characteristic abnormalities were found in the basal ganglia of primary dystonia patients. It remains to be explored whether this is due to a true absence of signal alterations in the basal ganglia of dystonia patients or to limitations of the current technology used.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumgartner RW, Arnold M, Gonner F, Staikow I, Herrmann C, Rivoir A, Muri RM (1997) Contrast-enhanced transcranial color-coded duplex sonography in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 28:2473–2478
Becker G, Naumann M, Scheubeck M, Hofmann E, Deimling M, Lindner A, Gahn G, Reiners C, Toyka KV, Reiners K (1997) Comparison of transcranial sonography, magnetic resonance imaging, and single photon emission computed tomography findings in idiopathic spasmodic torticollis. Mov Disord 12:79–88
Behnke S, Double KL, Duma S, Broe GA, Guenther V, Becker G, Halliday GM (2007) Substantia nigra echomorphology in the healthy very old: correlation with motor slowing. Neuroimage 34:1054–1059
Berg D (2007) Disturbance of iron metabolism as a contributing factor to SN hyperechogenicity in Parkinson’s disease: implications for idiopathic and monogenetic forms. Neurochem Res 32:1646–1654
Berg D, Becker G, Zeiler B, Tucha O, Hofmann E, Preier M, Benz P, Jost W, Reiners K, Lange KW (1999) Vulnerability of the nigrostriatal system as detected by transcranial ultrasound. Neurology 53:1026–1031
Berg D, Roggendorf W, Schroder U, Klein R, Tatschner T, Benz P, Tucha O, Preier M, Lange KW, Reiners K, Gerlach M, Becker G (2002) Echogenicity of the substantia nigra: association with increased iron content and marker for susceptibility to nigrostriatal injury. Arch Neurol 59:999–1005
Berg D, Siefker C, Becker G (2001) Echogenicity of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease and its relation to clinical findings. J Neurol 248:684–689
Breakefield XO, Blood AJ, Li Y, Hallett M, Hanson PI, Standaert DG (2008) The pathophysiological basis of dystonias. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:222–234
Godau J, Wevers AK, Gaenslen A, Di Santo A, Liepelt I, Gasser T, Berg D (2008) Sonographic abnormalities of brainstem structures in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 9:782–789
Hagenah J, Konig IR, Sperner J, Wessel L, Seidel G, Condefer K, Saunders-Pullman R, Klein C, Bruggemann N (2010) Life-long increase of substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in transcranial sonography. Neuroimage 51:28–32
Hagenah JM, Becker B, Bruggemann N, Djarmati A, Lohmann K, Sprenger A, Klein C, Seidel G (2008) Transcranial sonography findings in a large family with homozygous and heterozygous PINK1 mutations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:1071–1074
Hagenah JM, Konig IR, Becker B, Hilker R, Kasten M, Hedrich K, Pramstaller PP, Klein C, Seidel G (2007) Substantia nigra hyperechogenicity correlates with clinical status and number of Parkin mutated alleles. J Neurol 254:1407–1413
Huang YW, Jeng JS, Tsai CF, Chen LL, Wu RM (2007) Transcranial imaging of substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in a Taiwanese cohort of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:550–555
Naumann M, Becker G, Toyka KV, Supprian T, Reiners K (1996) Lenticular nucleus lesion in idiopathic dystonia detected by transcranial sonography. Neurology 47:1284–1290
Schmidauer C, Sojer M, Seppi K, Stockner H, Hogl B, Biedermann B, Brandauer E, Peralta CM, Wenning GK, Poewe W (2005) Transcranial ultrasound shows nigral hypoechogenicity in restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol 58:630–634
Seidel G, Kaps M, Gerriets T (1995) Potential and limitations of transcranial color-coded sonography in stroke patients. Stroke 26:2061–2066
Seidel G, Kaps M, Gerriets T, Hutzelmann A (1995) Evaluation of the ventricular system in adults by transcranial duplex sonography. J Neuroimaging 5:105–108
Walter U, Behnke S, Eyding J, Niehaus L, Postert T, Seidel G, Berg D (2007) Transcranial brain parenchyma sonography in movement disorders: state of the art. Ultrasound Med Biol 33:15–25
Walter U, Krolikowski K, Tarnacka B, Benecke R, Czlonkowska A, Dressler D (2005) Sonographic detection of basal ganglia lesions in asymptomatic and symptomatic Wilson disease. Neurology 64:1726–1732
Walter U, Niehaus L, Probst T, Benecke R, Meyer BU, Dressler D (2003) Brain parenchyma sonography discriminates Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 60:74–77
Walter U, Wagner S, Horowski S, Benecke R, Zettl UK (2009) Transcranial brain sonography findings predict disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 73:1010–1017
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Stefanie Behnke for her help with the data analysis. There was no funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagenah, J., König, I.R., Kötter, C. et al. Basal ganglia hyperechogenicity does not distinguish between patients with primary dystonia and healthy individuals. J Neurol 258, 590–595 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5795-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5795-x