Abstract
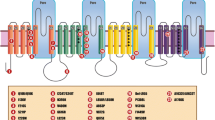
Familial primary erythromelalgia is a rare autosomal dominant disease characterized by redness and painful episodes of the feet and hands, which is often triggered by heat or exercise. In this report, a Taiwanese family with the characteristic features of erythromelalgia is described. Genetic linkage studies established that the disease locus maps to human chromosome 2. Sequence analysis indicated that the disease segregates with a novel mutation in the alpha subunit of the voltage-gated sodium channel (SCN9A or Nav1.7). The change observed is predicted to cause the substitution of a highly conserved isoluecine 136 for a valine within the first segment of the transmembrane domain (D1S1). Using immuno-histochemistry to stain a skin biopsy specimen from the affected region, we demonstrate that there is a significant reduction in the number of small fibers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummins TR, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (2004) Electrophysiological properties of mutant Nav1.7 sodium channels in a painful inherited neuropathy. J Neurosci 24:8232-8236
Davis MD, Sandroni P (2002) Lidocaine patch for pain of erythromelalgia. Arch Dermatol 138:17–19
Davis MD, Sandroni P, Rooke TW, Low PA (2003) Erythromelalgia: vasculopathy, neuropathy, or both? A prospective study of vascular and neurophysiologic studies in erythromelalgia. Arch Dermatol 139:1337–1343
Dib-Hajj SD, Rush AM, Cummins TR, Hisama FM, Novella S, Tyrrell L, Marshall L, Waxman SG (2005) Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain 128:1847–1854
Drenth JP, Finley WH, Breedveld GJ, Testers L, Michiels JJ, Guillet G, Taieb A, Kirby RL, Heutink P (2001) The primary erythermalgia-susceptibility gene is located on chromosome 2q31–32. Am J Hum Genet 68:1277–1282
Drenth JP, te Morsche RH, Guillet G, Taieb A, Kirby RL, Jansen JB (2005) SCN9A mutations define primary erythermalgia as a neuropathic disorder of voltage gated sodium channels. J Invest Dermatol 124:1333–1338
Han C, Rush AM, Dib-Hajj SD, Li S, Xu Z, Wang Y, Tyrrell L, Wang X, Yang Y, Waxman SG (2006) Sporadic onset of erythermalgia: A gain-of-function mutation in Na(v)1.7. Ann Neurol 59:553–558
Kuhnert SM, Phillips WJ, Davis MD (1999) Lidocaine and mexiletine therapy for erythromelalgia. Arch Dermatol 135:1447–1449
Mork C, Kalgaard OM, Kvernebo K (2002) Impaired neurogenic control of skin perfusion in erythromelalgia. J Invest Dermatol 118:699–703
Uno H, Parker F (1983) Autonomic innervation of the skin in primary erythermalgia. Arch Dermatol 119:65–71
Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj SD (2005) Erythromelalgia: A hereditary pain syndrome enters the molecular era. Ann Neurol 57:785–788
Yang Y, Wang Y, Li S, Xu Z, Li H, Ma L, Fan J, Bu D, Liu B, Fan Z, Wu G, Jin J, Ding B, Zhu X, Shen Y (2004) Mutations in SCN9A, encoding a sodium channel alpha subunit, in patients with primary erythermalgia. J Med Genet 41:171–174
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. James Hill for his comments during the preparation of the manuscript. These experiments were supported by a grant (No. NTUH 92A03-5) from the National Taiwan University Hospital. DAS is grateful for finical support of the MRC UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received in revised form: 31 March 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MJ., Yu, HS., Hsieh, ST. et al. Characterization of a familial case with primary erythromelalgia from Taiwan. J Neurol 254, 210–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0328-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0328-3