Abstract
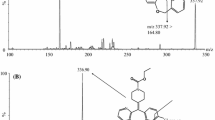
A rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric (LC-MS/MS) method for simultaneous quantification of fentanyl (F), norfentanyl (NF), despropionylfentanyl (DPF), and hydroxynorfentanyl (OHNF) in human plasma and urine specimens has been developed and validated according to international guidelines. Analytes were extracted from 250-μL plasma or urine by liquid–liquid extraction. OHNF in urine affords a second extraction step and analysis with a different column. Calibration curves in plasma were linear from 0.05–10 ng/mL for F, 0.07–0.5 ng/mL for NF, 0.02–1.0 ng/ml for DPF, and 0.67–3.0 ng/mL for OHNF; in urine, from 0.09–10.0, 0.17–50, 0.08–1.0, and 1.0–5.0 ng/mL for F, NF, DPF, and OHNF, respectively. Analytical bias and intra- and inter-assay imprecision were within ±15 % of target, except for OHNF in plasma and DPF in urine at the respective lower quality control level. All analytes were stable in processed samples when stored for 24 h at room temperature. Recoveries and process efficiencies were above 82.9 and 75.1 % for all analytes in plasma and urine. The low level of DPF in plasma indicated with a matrix effect of 71.3 % moderate ion suppression, all other analytes in plasma and urine showed no matrix effects. The lower limit of quantification (LOQ) in plasma was 0.05, 0.07, 0.02 and 0.67 ng/mL for F, NF, DPF, and OHNF, respectively. In urine, the LOQ of F, NF, DPF, and OHNF were 0.09, 0.17, 0.08, and 1.28 ng/mL, respectively. This assay has been applied to human specimens collected during a clinical drug–drug interaction study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jenkins AJ (2007) In: Karch SB, Forrest R (eds) Drug abuse handbook, 2nd edn. Boca Raton, CRC Press
Clotz MA, Nahata MC (1991) Clinical uses of fentanyl, sufentanil, and alfentanil. Clin Pharm 10:581–593
Baselt RC (2011) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man, 9th edn. Biomedical Publications, Foster City
Heishman SJ (2007) In: Karch SB, Forrest R (eds) Drug abuse handbook, 2nd edn. Boca Raton, CRC Press
Marquardt KA, Tharratt RS, Musallam NA (1995) Fentanyl remaining in a transdermal system following three days of continuous use. Ann Pharmacother 29:969–971
Reeves MD, Ginifer CJ (2002) Fatal intravenous misuse of transdermal fentanyl. Med J Aust 177:552–553
Dale E, Ashby F, Seelam K (2009) Report of a patient chewing fentanyl patches who was titrated onto methadone. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2009.1454
Arvanitis ML, Satonik RC (2007) Transdermal fentanyl abuse and misuse. Am J Emerg Med 20:58–59
Hull MJ, Juhascik M, Mazur F, Flomenbaum MA, Behonick GS (2007) Fatalities associated with fentanyl and co-administered cocaine or opiates. J Forensic Sci 52:1383–1388
Labroo RB, Paine MF, Thummel KE, Kharasch ED (1997) Fentanyl metabolism by human hepatic and intestinal cytochrome P450 3A4: implications for interindividual variability in disposition, efficacy, and drug interactions. Drug Metab Dispos 25:1072–1080
Schneider E, Brune K (1986) Opioid activity and distribution of fentanyl metabolites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 334:267–274
Peters FT, Paul LD, Mußhoff F, Aebi B, Auwärter V, Kraemer T, Skopp G (2009) Anhang B. Richtlinie der GTFCh zur Qualitätssicherung bei forensisch-toxikologischen Untersuchungen Anforderungen an die Validierung von Analysenmethoden. Toxichem Krimtech 76:185–208
Ziesenitz VC, König SK, Mahlke N, Jantos R, Skopp G, Weiss J, Haefeli WE, Mikus G (2013) Fentanyl pharmacokinetics is not dependent on hepatic uptake by organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1 in human beings. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 113:43–48
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Food and Drug Administration (2001) Guidance for industry. Bioanalytical method validation. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm. Assessed 17 April 2014
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 75:3019–3030
Day J, Slawson M, Lugo RA, Wilkins D (2003) Analysis of fentanyl and norfentanyl in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using electrospray ionization. J Anal Toxicol 27:513–516
Huynh NH, Tyrefors N, Ekman L, Johansson M (2005) Determination of fentanyl in human plasma and fentanyl and norfentanyl in human urine using LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 37:1095–1100
Cooreman S, Deprez C, Martens F, Van Bocxlaer J, Croes K (2010) A comprehensive LC-MS-based quantitative analysis of fentanyl-like drugs in plasma and urine. J Sep Sci 33:2654–2662
Verplaetse R, Tytgat J (2010) Development and validation of a sensitive ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of fentanyl and its major metabolite norfentanyl in urine and whole blood in forensic context. J Chromatogr B 878:1987–1996
Andresen H, Gullans A, Veselinovic M, Anders S, Schmoldt A, Iwersen-Bergmann S, Mueller A (2012) Fentanyl: toxic or therapeutic? Postmortem and ante mortem blood concentrations after transdermal fentanyl application. J Anal Toxicol 36:182–194
Scarth JP, Spencer HA, Timbers SE, Hudson SC, Hillyer LL (2010) The use of in vitro technologies coupled with high resolution accurate mass LC-MS for studying drug metabolism in equine drug surveillance. Drug Test Anal 2:1–10
Lu C, Jia JY, Gui YZ, Liu GY, Shi XJ, Li SJ, Yu C (2010) Development of a liquid chromatography-isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for quantification of fentanyl in human plasma. Biomed Chromatogr 24:711–716
Maruyama Y, Hosoya E (1969) Studies on the fate of fentanyl. Keio J Med 18:59–70
Feierman DE, Lasker JM (1996) Metabolism of fentanyl, a synthetic opioid analgesic, by human liver microsomes. Role of CYP3A4. Drug Metab Dispos 24:932–939
Guitton J, Désage M, Alamercery S, Dutruch L, Dautraix S, Perdrix JP, Brazier JL (1997) Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometry and gas chromatographic-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy assay for the simultaneous identification of fentanyl metabolites. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 693:59–70
Tharp AM, Winecker RE, Winston DC (2004) Fatal intravenous fentanyl abuse: four cases involving extraction of fentanyl from transdermal patches. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 25:178–181
Poklis A, Backer R (2004) Urine concentrations of fentanyl and norfentanyl during application of Duragesic transdermal patches. J Anal Toxicol 28:422–425
Teske J, Weller JP, Larsch K, Tröger HD, Karst M (2007) Fatal outcome in a child after ingestion of a transdermal fentanyl patch. Int J Legal Med 121:147–151
Coopman V, Cordonnier J, Pien K, Van Varenbergh D (2007) LC-MS/MS analysis of fentanyl and norfentanyl in a fatality due to application of multiple Durogesic transdermal therapeutic systems. Forensic Sci Int 169:223–227
Musshoff F, Trafkowski J, Kuepper U, Madea B (2006) An automated and fully validated LC-MS/MS procedure for the simultaneous determination of 11 opioids used in palliative care, with 5 of their metabolites. J Mass Spectrom 41:633–640
Marier JF, Lor M, Potvin D, Dimarco M, Morelli G, Saedder EA (2006) Pharmacokinetics, tolerability, and performance of a novel matrix transdermal delivery system of fentanyl relative to the commercially available reservoir formulation in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 46:642–653
Tateishi T, Wood AJ, Guengerich FP, Wood M (1995) Biotransformation of tritiated fentanyl in human liver microsomes. Monitoring metabolism using phenylacetic acid and 2-phenylethanol. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1921–1924
Portier EJ, de Blok K, Butter JJ, van Boxtel CJ (1999) Simultaneous determination of fentanyl and midazolam using high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci App 723:313–318
Silverstein JH, Rieders MF, McMullin M, Schulman S, Zahl K (1993) An analysis of the duration of fentanyl and its metabolites in urine and saliva. Anesth Analg 76:618–621
Koch DE, Isaza R, Carpenter JW, Hunter RP (2004) Simultaneous extraction and quantitation of fentanyl and norfentanyl from primate plasma with LC/MS detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 34:577–584
Peer CJ, Shakleya DM, Younis IR, Kraner JC, Callery PS (2007) Direct-injection mass spectrometric method for the rapid identification of fentanyl and norfentanyl in postmortem urine of six drug-overdose cases. J Anal Toxicol 31:515–521
Pihlainen K, Grigoras K, Franssila S, Ketola R, Kotiaho T, Kostiainen R (2005) Analysis of amphetamines and fentanyls by atmospheric pressure desorption/ionization on silicon mass spectrometry and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and its application to forensic analysis of drug seizures. J Mass Spectrom 40:539–545
Clavijo CF, Thomas JJ, Cromie M, Schniedewind B, Hoffman KL, Christians U, Galinkin JL (2011) A low blood volume LC-MS/MS assay for the quantification of fentanyl and its major metabolites norfentanyl and despropionyl fentanyl in children. J Sep Sci 34:3568–3577
Anderson DT, Muto JJ (2000) Duragesic transdermal patch: postmortem tissue distribution of fentanyl in 25 cases. J Anal Toxicol 24:627–634
Van Rooy HH, Vermeulen MP, Bovill JG (1981) The assay of fentanyl and its metabolites in plasma of patients using gas chromatography with alkali flame ionisation detection and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 223:85–93
Strano-Rossi S, Alvarez I, Tabernero MJ, Cabarcos P, Fernández P, Bermejo AM (2011) Determination of fentanyl, metabolite and analogs in urine by GC/MS. J Appl Toxicol 31:649–654
Bansal R, Aranda JV (1996) High performance liquid chromatography microassay for the simultaneous determination of fentanyl and its major metabolites in biological samples. J Liquid Chromatogr Relat Technol 19:353–364
Goromaru T, Matsuura H, Yoshimura N, Miyawaki T, Sameshima T, Miyao J, Furuta T, Baba S (1984) Identification and quantitative determination of fentanyl metabolites in patients by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anesthesiol 61:73–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahlke, N.S., Ziesenitz, V., Mikus, G. et al. Quantitative low-volume assay for simultaneous determination of fentanyl, norfentanyl, and minor metabolites in human plasma and urine by liquid chromatography—tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Int J Legal Med 128, 771–778 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-014-1040-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-014-1040-y