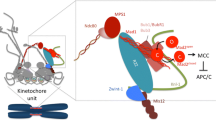
Abstract
The kinetochore, the proteinaceous structure on the mitotic centromere, functions as a mechanical latch that hooks onto microtubules to support directional movement of chromosomes. The structure also brings in a number of signaling molecules, such as kinases and phosphatases, which regulate microtubule dynamics and cell cycle progression. Erroneous microtubule attachment is destabilized by Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation of multiple microtubule-binding protein complexes at the kinetochore, such as the KMN network proteins and the Ska/Dam1 complex, while Plk-dependent phosphorylation of BubR1 stabilizes kinetochore–microtubule attachment by recruiting PP2A-B56. Spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) signaling, which is activated by unattached kinetochores and inhibits the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, depends on kinetochore recruitment of the kinase Bub1 through Mps1-mediated phosphorylation of the kinetochore protein KNL1 (also known as Blinkin in mammals, Spc105 in budding yeast, and Spc7 in fission yeast). Recruitment of protein phosphatase 1 to KNL1 is necessary to silence the SAC upon bioriented microtubule attachment. One of the key unsolved questions in the mitosis field is how a mechanical change at the kinetochore upon microtubule attachment is converted to these and other chemical signals that control microtubule attachment and the SAC. Rapid progress in the field is revealing the existence of an intricate signaling network created right on the kinetochore. Here we review the current understanding of phosphorylation-mediated regulation of kinetochore functions and discuss how this signaling network generates an accurate switch that turns on and off the signaling output in response to kinetochore–microtubule attachment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrieu A, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Kahana JA, Peter M, Castro A, Vigneron S, Lorca T, Cleveland DW, Labbe JC (2001) Mps1 is a kinetochore-associated kinase essential for the vertebrate mitotic checkpoint. Cell 106:83–93
Ahonen LJ, Kallio MJ, Daum JR, Bolton M, Manke IA, Yaffe MB, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2005) Polo-like kinase 1 creates the tension-sensing 3F3/2 phosphoepitope and modulates the association of spindle-checkpoint proteins at kinetochores. Curr Biol 15:1078–1089
Akiyoshi B, Nelson CR, Ranish JA, Biggins S (2009a) Analysis of Ipl1-mediated phosphorylation of the Ndc80 kinetochore protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 183:1591–1595
Akiyoshi B, Nelson CR, Ranish JA, Biggins S (2009b) Quantitative proteomic analysis of purified yeast kinetochores identifies a PP1 regulatory subunit. Genes Dev 23:2887–2899
Akiyoshi B, Sarangapani KK, Powers AF, Nelson CR, Reichow SL, Arellano-Santoyo H, Gonen T, Ranish JA, Asbury CL, Biggins S (2010) Tension directly stabilizes reconstituted kinetochore–microtubule attachments. Nature 468:576–579
Alexander J, Lim D, Joughin BA, Hegemann B, Hutchins JR, Ehrenberger T, Ivins F, Sessa F, Hudecz O, Nigg EA, Fry AM, Musacchio A, Stukenberg PT, Mechtler K, Peters JM, Smerdon SJ, Yaffe MB (2011) Spatial exclusivity combined with positive and negative selection of phosphorylation motifs is the basis for context-dependent mitotic signaling. Sci Signal 4:ra42
Alushin GM, Ramey VH, Pasqualato S, Ball DA, Grigorieff N, Musacchio A, Nogales E (2010) The Ndc80 kinetochore complex forms oligomeric arrays along microtubules. Nature 467:805–810
Andrews PD, Ovechkina Y, Morrice N, Wagenbach M, Duncan K, Wordeman L, Swedlow JR (2004) Aurora B regulates MCAK at the mitotic centromere. Dev Cell 6:253–268
Bentley AM, Normand G, Hoyt J, King RW (2007) Distinct sequence elements of cyclin B1 promote localization to chromatin, centrosomes, and kinetochores during mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 18:4847–4858
Bernard P, Maure JF, Javerzat JP (2001) Fission yeast Bub1 is essential in setting up the meiotic pattern of chromosome segregation. Nat Cell Biol 3:522–526
Biggins S, Murray AW (2001) The budding yeast protein kinase Ipl1/Aurora allows the absence of tension to activate the spindle checkpoint. Genes Dev 15:3118–3129
Booher R, Beach D (1989) Involvement of a type 1 protein phosphatase encoded by bws1 + in fission yeast mitotic control. Cell 57:1009–1016
Boyarchuk Y, Salic A, Dasso M, Arnaoutov A (2007) Bub1 is essential for assembly of the functional inner centromere. J Cell Biol 176:919–928
Burton JL, Solomon MJ (2007) Mad3p, a pseudosubstrate inhibitor of APCCdc20 in the spindle assembly checkpoint. Genes Dev 21:655–667
Buttrick GJ, Lancaster TC, Meadows JC, Millar JB (2012) Plo1 phosphorylates Dam1 to promote chromosome bi-orientation in fission yeast. J Cell Sci 125:1645–1651
Cai S, O'Connell CB, Khodjakov A, Walczak CE (2009) Chromosome congression in the absence of kinetochore fibres. Nat Cell Biol 11:832–838
Carmena M, Pinson X, Platani M, Salloum Z, Xu Z, Clark A, Macisaac F, Ogawa H, Eggert U, Glover DM, Archambault V, Earnshaw WC (2012a) The chromosomal passenger complex activates Polo kinase at centromeres. PLoS Biol 10:e1001250
Carmena M, Wheelock M, Funabiki H, Earnshaw WC (2012b) The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC): from easy rider to the godfather of mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(12):789–803
Ceulemans H, Vulsteke V, De Maeyer M, Tatchell K, Stalmans W, Bollen M (2002) Binding of the concave surface of the Sds22 superhelix to the alpha 4/alpha 5/alpha 6-triangle of protein phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem 277:47331–47337
Chan GK, Schaar BT, Yen TJ (1998) Characterization of the kinetochore binding domain of CENP-E reveals interactions with the kinetochore proteins CENP-F and hBUBR1. J Cell Biol 143:49–63
Chan GK, Jablonski SA, Sudakin V, Hittle JC, Yen TJ (1999) Human BUBR1 is a mitotic checkpoint kinase that monitors CENP-E functions at kinetochores and binds the cyclosome/APC. J Cell Biol 146:941–954
Chan YW, Jeyaprakash AA, Nigg EA, Santamaria A (2012) Aurora B controls kinetochore–microtubule attachments by inhibiting Ska complex–KMN network interaction. J Cell Biol 196:563–571
Chao WC, Kulkarni K, Zhang Z, Kong EH, Barford D (2012) Structure of the mitotic checkpoint complex. Nature 484:208–213
Cheeseman IM, Desai A (2008) Molecular architecture of the kinetochore–microtubule interface. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:33–46
Cheeseman IM, Anderson S, Jwa M, Green EM, Js K, Yates JR, Chan CSM, Drubin DG, Barnes G (2002) Phospho-regulation of kinetochore–microtubule attachments by the Aurora kinase Ipl1p. Cell 111:163–172
Cheeseman IM, Niessen S, Anderson S, Hyndman F, Yates JR 3rd, Oegema K, Desai A (2004) A conserved protein network controls assembly of the outer kinetochore and its ability to sustain tension. Genes Dev 18:2255–2268
Cheeseman IM, Chappie JS, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Desai A (2006) The conserved KMN network constitutes the core microtubule-binding site of the kinetochore. Cell 127:983–997
Chen RH (2002) BubR1 is essential for kinetochore localization of other spindle checkpoint proteins and its phosphorylation requires Mad1. J Cell Biol 158:487–496
Chen RH (2004) Phosphorylation and activation of Bub1 on unattached chromosomes facilitate the spindle checkpoint. EMBO J 23:3113–3121
Chen R-H, Waters JC, Salmon ED, Murray AW (1996) Association of spindle assembly checkpoint component XMAD2 with unattached kinetochores. Science 274:242–246
Chen R-H, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Murray AW (1998) Metaphase arrest induced by an excess of the spindle checkpoint protein Xmad2 is independent of Xmad1. J Cell Biol 143:283–295
Cheng L, Zhang J, Ahmad S, Rozier L, Yu H, Deng H, Mao Y (2011) Aurora B regulates formin mDia3 in achieving metaphase chromosome alignment. Dev Cell 20:342–352
Choi E, Choe H, Min J, Choi JY, Kim J, Lee H (2009) BubR1 acetylation at prometaphase is required for modulating APC/C activity and timing of mitosis. EMBO J 28:2077–2089
Chung E, Chen RH (2003) Phosphorylation of Cdc20 is required for its inhibition by the spindle checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 5:748–753
Ciferri C, Pasqualato S, Screpanti E, Varetti G, Santaguida S, Dos Reis G, Maiolica A, Polka J, De Luca JG, De Wulf P, Salek M, Rappsilber J, Moores CA, Salmon ED, Musacchio A (2008) Implications for kinetochore–microtubule attachment from the structure of an engineered Ndc80 complex. Cell 133:427–439
Cimini D, Wan X, Hirel CB, Salmon ED (2006) Aurora kinase promotes turnover of kinetochore microtubules to reduce chromosome segregation errors. Curr Biol 16:1711–1718
Clute P, Pines J (1999) Temporal and spatial control of cyclin B1 destruction in metaphase. Nat Cell Biol 1:82–87
Coffman VC, Wu P, Parthun MR, Wu JQ (2011) CENP-A exceeds microtubule attachment sites in centromere clusters of both budding and fission yeast. J Cell Biol 195:563–572
D'Angiolella V, Mari C, Nocera D, Rametti L, Grieco D (2003) The spindle checkpoint requires cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Genes Dev 17:2520–2525
Dawlaty MM, Malureanu L, Jeganathan KB, Kao E, Sustmann C, Tahk S, Shuai K, Grosschedl R, van Deursen JM (2008) Resolution of sister centromeres requires RanBP2-mediated SUMOylation of topoisomerase IIalpha. Cell 133:103–115
De Antoni A, Maffini S, Knapp S, Musacchio A, Santaguida S (2012) A small-molecule inhibitor of Haspin alters the kinetochore functions of Aurora B. J Cell Biol 199:269–284
De Wulf P, McAinsh AD, Sorger PK (2003) Hierarchical assembly of the budding yeast kinetochore from multiple subcomplexes. Genes Dev 17:2902–2921
DeLuca JG, Howell BJ, Canman JC, Hickey JM, Fang G, Salmon ED (2003) Nuf2 and Hec1 are required for retention of the checkpoint proteins Mad1 and Mad2 to kinetochores. Curr Biol 13:2103–2109
DeLuca JG, Gall WE, Ciferri C, Cimini D, Musacchio A, Salmon ED (2006) Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell 127:969–982
DeLuca KF, Lens SM, DeLuca JG (2011) Temporal changes in Hec1 phosphorylation control kinetochore–microtubule attachment stability during mitosis. J Cell Sci 124:622–634
Ditchfield C, Johnson VL, Tighe A, Ellston R, Haworth C, Johnson T, Mortlock A, Keen N, Taylor SS (2003) Aurora B couples chromosome alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to kinetochores. J Cell Biol 161:267–280
Dohadwala M, Da Cruz e Silva EF, Hall FL, Williams RT, Carbonaro-Hall DA, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Berndt N (1994) Phosphorylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 by cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:6408–6412
Doonan JH, Morris NR (1989) The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phophoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell 57:987–996
Dumont S, Salmon ED, Mitchison TJ (2012) Deformations within moving kinetochores reveal different sites of active and passive force generation. Science 337:355–358
Dunsch AK, Linnane E, Barr FA, Gruneberg U (2011) The astrin–kinastrin/SKAP complex localizes to microtubule plus ends and facilitates chromosome alignment. J Cell Biol 192:959–968
Elia AE, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB (2003) Proteomic screen finds pSer/pThr-binding domain localizing Plk1 to mitotic substrates. Science 299:1228–1231
Elowe S, Hummer S, Uldschmid A, Li X, Nigg EA (2007) Tension-sensitive Plk1 phosphorylation on BubR1 regulates the stability of kinetochore microtubule interactions. Genes Dev 21:2205–2219
Emanuele MJ, Lan W, Jwa M, Miller SA, Chan CSM, Stukenberg PT (2008) Aurora B kinase and protein phosphatase 1 have opposing roles in modulating kinetochore assembly. J Cell Biol 181:241–254
Espeut J, Gaussen A, Bieling P, Morin V, Prieto S, Fesquet D, Surrey T, Abrieu A (2008) Phosphorylation relieves autoinhibition of the kinetochore motor Cenp-E. Mol Cell 29:637–643
Espeut J, Cheerambathur DK, Krenning L, Oegema K, Desai A (2012) Microtubule binding by KNL-1 contributes to spindle checkpoint silencing at the kinetochore. J Cell Biol 196:469–482
Fernius J, Hardwick KG (2007) Bub1 kinase targets Sgo1 to ensure efficient chromosome biorientation in budding yeast mitosis. PLoS Genet 3:e213
Firestone AJ, Weinger JS, Maldonado M, Barlan K, Langston LD, O'Donnell M, Gelfand VI, Kapoor TM, Chen JK (2012) Small-molecule inhibitors of the AAA + ATPase motor cytoplasmic dynein. Nature 484:125–129
Fisk HA, Winey M (2001) The mouse Mps1p-like kinase regulates centrosome duplication. Cell 106:95–104
Foley EA, Kapoor TM (2012) Microtubule attachment and spindle assembly checkpoint signalling at the kinetochore. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:25–37
Foley EA, Maldonado M, Kapoor TM (2011) Formation of stable attachments between kinetochores and microtubules depends on the B56-PP2A phosphatase. Nat Cell Biol 13:1265–1271
Foster SA, Morgan DO (2012) The APC/C subunit Mnd2/Apc15 promotes Cdc20 autoubiquitination and spindle assembly checkpoint inactivation. Mol Cell 47:921–932
Francisco L, Wang W, Chan CS (1994) Type 1 protein phosphatase acts in opposition to IpL1 protein kinase in regulating yeast chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol 14:4731–4740
Gascoigne KE, Taylor SS (2008) Cancer cells display profound intra- and interline variation following prolonged exposure to antimitotic drugs. Cancer Cell 14:111–122
Gascoigne KE, Takeuchi K, Suzuki A, Hori T, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM (2011) Induced ectopic kinetochore assembly bypasses the requirement for CENP-A nucleosomes. Cell 145:410–422
Gassmann R, Holland AJ, Varma D, Wan X, Civril F, Cleveland DW, Oegema K, Salmon ED, Desai A (2010) Removal of Spindly from microtubule-attached kinetochores controls spindle checkpoint silencing in human cells. Genes Dev 24:957–971
Gestaut DR, Graczyk B, Cooper J, Widlund PO, Zelter A, Wordeman L, Asbury CL, Davis TN (2008) Phosphoregulation and depolymerization-driven movement of the Dam1 complex do not require ring formation. Nat Cell Biol 10:407–414
Good MC, Zalatan JG, Lim WA (2011) Scaffold proteins: hubs for controlling the flow of cellular information. Science 332:680–686
Gorbsky GJ, Ricketts WA (1993) Differential expression of a phosphoepitope at the kinetochores of moving chromosomes. J Cell Biol 122:1311–1321
Goto H, Kiyono T, Tomono Y, Kawajiri A, Urano T, Furukawa K, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2006) Complex formation of Plk1 and INCENP required for metaphase–anaphase transition. Nat Cell Biol 8:180–187
Guimaraes GJ, Dong Y, McEwen BF, DeLuca JG (2008) Kinetochore–microtubule attachment relies on the disordered N-terminal tail domain of Hec1. Curr Biol 18:1778–1784
Guo Y, Kim C, Ahmad S, Zhang J, Mao Y (2012) CENP-E-dependent BubR1 autophosphorylation enhances chromosome alignment and the mitotic checkpoint. J Cell Biol 198:205–217
Guse A, Carroll CW, Moree B, Fuller CJ, Straight AF (2011) In vitro centromere and kinetochore assembly on defined chromatin templates. Nature 477:354–358
Hached K, Xie SZ, Buffin E, Cladiere D, Rachez C, Sacras M, Sorger PK, Wassmann K (2011) Mps1 at kinetochores is essential for female mouse meiosis I. Development 138:2261–2271
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM (2003) The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore–microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 161:281–294
Hendrickx A, Beullens M, Ceulemans H, Den Abt T, Van Eynde A, Nicolaescu E, Lesage B, Bollen M (2009) Docking motif-guided mapping of the interactome of protein phosphatase-1. Chem Biol 16:365–371
Hewitt L, Tighe A, Santaguida S, White AM, Jones CD, Musacchio A, Green S, Taylor SS (2010) Sustained Mps1 activity is required in mitosis to recruit O-Mad2 to the Mad1–C-Mad2 core complex. J Cell Biol 190:25–34
Hood EA, Kettenbach AN, Gerber SA, Compton DA (2012) Plk1 regulates the kinesin-13 protein Kif2b to promote faithful chromosome segregation. Mol Biol Cell 23:2264–2274
Hori T, Okada M, Maenaka K, Fukagawa T (2008) CENP-O class proteins form a stable complex and are required for proper kinetochore function. Mol Biol Cell 19:843–854
Howell BJ, McEwen BF, Canman JC, Hoffman DB, Farrar EM, Rieder CL, Salmon ED (2001) Cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin drives kinetochore protein transport to the spindle poles and has a role in mitotic spindle checkpoint inactivation. J Cell Biol 155:1159–1172
Howell BJ, Moree B, Farrar EM, Stewart S, Fang G, Salmon ED (2004) Spindle checkpoint protein dynamics at kinetochores in living cells. Curr Biol 14:953–964
Hsu JY, Sun ZW, Li X, Reuben M, Tatchell K, Bishop DK, Grushcow JM, Brame CJ, Caldwell JA, Hunt DF, Lin R, Smith MM, Allis CD (2000) Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3 is governed by Ipl1/aurora kinase and Glc7/PP1 phosphatase in budding yeast and nematodes. Cell 102:279–291
Hua S, Wang Z, Jiang K, Huang Y, Ward T, Zhao L, Dou Z, Yao X (2011) CENP-U cooperates with Hec1 to orchestrate kinetochore–microtubule attachment. J Biol Chem 286:1627–1638
Huang H, Hittle J, Zappacosta F, Annan RS, Hershko A, Yen TJ (2008) Phosphorylation sites in BubR1 that regulate kinetochore attachment, tension, and mitotic exit. J Cell Biol 183:667–680
Hummer S, Mayer TU (2009) Cdk1 negatively regulates midzone localization of the mitotic kinesin Mklp2 and the chromosomal passenger complex. Curr Biol 19:607–612
Indjeian VB, Murray AW (2007) Budding yeast mitotic chromosomes have an intrinsic bias to biorient on the spindle. Curr Biol 17:1837–1846
Ito D, Saito Y, Matsumoto T (2011) Centromere-tethered Mps1 pombe homolog (Mph1) kinase is a sufficient marker for recruitment of the spindle checkpoint protein Bub1, but not Mad1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:209–214
Jelluma N, Brenkman AB, van den Broek NJ, Cruijsen CW, van Osch MH, Lens SM, Medema RH, Kops GJ (2008) Mps1 phosphorylates Borealin to control Aurora B activity and chromosome alignment. Cell 132:233–246
Jeyaprakash AA, Santamaria A, Jayachandran U, Chan YW, Benda C, Nigg EA, Conti E (2012) Structural and functional organization of the Ska complex, a key component of the kinetochore–microtubule interface. Mol Cell 46:274–286
Jia L, Li B, Warrington RT, Hao X, Wang S, Yu H (2011) Defining pathways of spindle checkpoint silencing: functional redundancy between Cdc20 ubiquitination and p31(comet). Mol Biol Cell 22:4227–4235
Johnson VL, Scott MI, Holt SV, Hussein D, Taylor SS (2004) Bub1 is required for kinetochore localization of BubR1, Cenp-E, Cenp-F and Mad2, and chromosome congression. J Cell Sci 117:1577–1589
Kallio MJ, McCleland ML, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2002) Inhibition of aurora B kinase blocks chromosome segregation, overrides the spindle checkpoint, and perturbs microtubule dynamics in mitosis. Curr Biol 12:900–905
Kang YH, Park JE, Yu LR, Soung NK, Yun SM, Bang JK, Seong YS, Yu H, Garfield S, Veenstra TD, Lee KS (2006) Self-regulated Plk1 recruitment to kinetochores by the Plk1–PBIP1 interaction is critical for proper chromosome segregation. Mol Cell 24:409–422
Kapoor TM, Lampson MA, Hergert P, Cameron L, Cimini D, Salmon ED, McEwen BF, Khodjakov A (2006) Chromosomes can congress to the metaphase plate before biorientation. Science 311:388–391
Kasuboski JM, Bader JR, Vaughan PS, Tauhata SB, Winding M, Morrissey MA, Joyce MV, Boggess W, Vos L, Chan GK, Hinchcliffe EH, Vaughan KT (2011) Zwint-1 is a novel Aurora B substrate required for the assembly of a dynein-binding platform on kinetochores. Mol Biol Cell 22:3318–3330
Kawashima SA, Yamagishi Y, Honda T, Ishiguro K, Watanabe Y (2010) Phosphorylation of H2A by Bub1 prevents chromosomal instability through localizing shugoshin. Science 327:172–177
Kelly AE, Funabiki H (2009) Correcting aberrant kinetochore microtubule attachments: an Aurora B-centric view. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:51–58
Kelly AE, Sampath SC, Maniar TA, Woo EM, Chait BT, Funabiki H (2007) Chromosomal enrichment and activation of the aurora B pathway are coupled to spatially regulate spindle assembly. Dev Cell 12:31–43
Kelly AE, Ghenoiu C, Xue JZ, Zierhut C, Kimura H, Funabiki H (2010) Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 330:235–239
Kemmler S, Stach M, Knapp M, Ortiz J, Pfannstiel J, Ruppert T, Lechner J (2009) Mimicking Ndc80 phosphorylation triggers spindle assembly checkpoint signalling. EMBO J 28:1099–1110
Kim Y, Holland AJ, Lan W, Cleveland DW (2010) Aurora kinases and protein phosphatase 1 mediate chromosome congression through regulation of CENP-E. Cell 142:444–455
King EM, Rachidi N, Morrice N, Hardwick KG, Stark MJ (2007a) Ipl1p-dependent phosphorylation of Mad3p is required for the spindle checkpoint response to lack of tension at kinetochores. Genes Dev 21:1163–1168
King EM, van der Sar SJ, Hardwick KG (2007b) Mad3 KEN boxes mediate both Cdc20 and Mad3 turnover, and are critical for the spindle checkpoint. PLoS One 2:e342
Kitajima TS, Sakuno T, Ishiguro K, Iemura S, Natsume T, Kawashima SA, Watanabe Y (2006) Shugoshin collaborates with protein phosphatase 2A to protect cohesin. Nature 441:46–52
Kitajima TS, Ohsugi M, Ellenberg J (2011) Complete kinetochore tracking reveals error-prone homologous chromosome biorientation in mammalian oocytes. Cell 146:568–581
Kiyomitsu T, Obuse C, Yanagida M (2007) Human Blinkin/AF15q14 is required for chromosome alignment and the mitotic checkpoint through direct interaction with Bub1 and BubR1. Dev Cell 13:663–676
Kiyomitsu T, Murakami H, Yanagida M (2011) Protein interaction domain mapping of human kinetochore protein Blinkin reveals a consensus motif for binding of spindle assembly checkpoint proteins Bub1 and BubR1. Mol Cell Biol 31:998–1011
Klebig C, Korinth D, Meraldi P (2009) Bub1 regulates chromosome segregation in a kinetochore-independent manner. J Cell Biol 185:841–858
Kline SL, Cheeseman IM, Hori T, Fukagawa T, Desai A (2006) The human Mis12 complex is required for kinetochore assembly and proper chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol 173:9–17
Knowlton AL, Lan W, Stukenberg PT (2006) Aurora B is enriched at merotelic attachment sites, where it regulates MCAK. Curr Biol 16:1705–1710
Knowlton AL, Vorozhko VV, Lan W, Gorbsky GJ, Stukenberg PT (2009) ICIS and Aurora B coregulate the microtubule depolymerase Kif2a. Curr Biol 19:758–763
Koivomagi M, Valk E, Venta R, Iofik A, Lepiku M, Balog ER, Rubin SM, Morgan DO, Loog M (2011) Cascades of multisite phosphorylation control Sic1 destruction at the onset of S phase. Nature 480:128–131
Kops GJ, Shah JV (2012) Connecting up and clearing out: how kinetochore attachment silences the spindle assembly checkpoint. Chromosoma 121:509–525
Kulukian A, Han JS, Cleveland DW (2009) Unattached kinetochores catalyze production of an anaphase inhibitor that requires a Mad2 template to prime Cdc20 for BubR1 binding. Dev Cell 16:105–117
Labit H, Fujimitsu K, Bayin NS, Takaki T, Gannon J, Yamano H (2012) Dephosphorylation of Cdc20 is required for its C-box-dependent activation of the APC/C. EMBO J 31:3351–3362
Lampert F, Hornung P, Westermann S (2010) The Dam1 complex confers microtubule plus end-tracking activity to the Ndc80 kinetochore complex. J Cell Biol 189:641–649
Lampson MA, Cheeseman IM (2011) Sensing centromere tension: Aurora B and the regulation of kinetochore function. Trends Cell Biol 21(3):133–140
Lampson MA, Renduchitala K, Khodjakov A, Kapoor TM (2004) Correcting improper chromosome-spindle attachments during cell division. Nat Cell Biol 6:232–237
Lan W, Zhang X, Kline-Smith SL, Rosasco SE, Barrett-Wilt GA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Walczak CE, Stukenberg PT (2004) Aurora B phosphorylates centromeric MCAK and regulates its localization and microtubule depolymerization activity. Curr Biol 14:273–286
Lara-Gonzalez P, Scott MI, Diez M, Sen O, Taylor SS (2011) BubR1 blocks substrate recruitment to the APC/C in a KEN-box-dependent manner. J Cell Sci 124:4332–4345
Lawrimore J, Bloom KS, Salmon ED (2011) Point centromeres contain more than a single centromere-specific Cse4 (CENP-A) nucleosome. J Cell Biol 195:573–582
Lee S, Thebault P, Freschi L, Beaufils S, Blundell TL, Landry CR, Bolanos-Garcia VM, Elowe S (2012) Characterization of spindle checkpoint kinase Mps1 reveals domain with functional and structural similarities to tetratricopeptide repeat motifs of Bub1 and BubR1 checkpoint kinases. J Biol Chem 287:5988–6001
Lenart P, Petronczki M, Steegmaier M, Di Fiore B, Lipp JJ, Hoffmann M, Rettig WJ, Kraut N, Peters JM (2007) The small-molecule inhibitor BI 2536 reveals novel insights into mitotic roles of polo-like kinase 1. Curr Biol 17:304–315
Lens SM, Rodriguez JA, Vader G, Span SW, Giaccone G, Medema RH (2006) Uncoupling the central spindle-associated function of the chromosomal passenger complex from its role at centromeres. Mol Biol Cell 17:1897–1909
Li Y, Benezra R (1996) Identification of a human mitotic checkpoint gene: hsMAD2. Science 274:246–248
Li H, Liu XS, Yang X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Turner JR, Liu X (2010) Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Plk1 and CK2 promotes timely formation of kinetochore–microtubule attachments. EMBO J 29:2953–2965
Lin YT, Chen Y, Wu G, Lee WH (2006) Hec1 sequentially recruits Zwint-1 and ZW10 to kinetochores for faithful chromosome segregation and spindle checkpoint control. Oncogene 25:6901–6914
Liu ST, Chan GK, Hittle JC, Fujii G, Lees E, Yen TJ (2003) Human MPS1 kinase is required for mitotic arrest induced by the loss of CENP-E from kinetochores. Mol Biol Cell 14:1638–1651
Liu D, Vader G, Vromans MJM, Lampson MA, Lens SMA (2009) Sensing chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of aurora B kinase from kinetochore substrates. Science 323:1350–1353
Liu D, Vleugel M, Backer CB, Hori T, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM, Lampson MA (2010) Regulated targeting of protein phosphatase 1 to the outer kinetochore by KNL1 opposes Aurora B kinase. J Cell Biol 188:809–820
Liu D, Davydenko O, Lampson MA (2012) Polo-like kinase-1 regulates kinetochore–microtubule dynamics and spindle checkpoint silencing. J Cell Biol 198:491–499
Logarinho E, Resende T, Torres C, Bousbaa H (2008) The human spindle assembly checkpoint protein bub3 is required for the establishment of efficient kinetochore–microtubule attachments. Mol Biol Cell 19:1798–1813
London N, Ceto S, Ranish JA, Biggins S (2012) Phosphoregulation of Spc105 by Mps1 and PP1 regulates Bub1 localization to kinetochores. Curr Biol 22:900–906
Luo X, Yu H (2008) Protein metamorphosis: the two-state behavior of Mad2. Structure 16:1616–1625
Maciejowski J, George KA, Terret ME, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Jallepalli PV (2010) Mps1 directs the assembly of Cdc20 inhibitory complexes during interphase and mitosis to control M phase timing and spindle checkpoint signaling. J Cell Biol 190:89–100
Magidson V, O'Connell CB, Loncarek J, Paul R, Mogilner A, Khodjakov A (2011) The spatial arrangement of chromosomes during prometaphase facilitates spindle assembly. Cell 146:555–567
Maldonado M, Kapoor TM (2011) Constitutive Mad1 targeting to kinetochores uncouples checkpoint signalling from chromosome biorientation. Nat Cell Biol 13:475–482
Malureanu LA, Jeganathan KB, Hamada M, Wasilewski L, Davenport J, van Deursen JM (2009) BubR1 N terminus acts as a soluble inhibitor of cyclin B degradation by APC/C(Cdc20) in interphase. Dev Cell 16:118–131
Manning AL, Bakhoum SF, Maffini S, Correia-Melo C, Maiato H, Compton DA (2010) CLASP1, astrin and Kif2b form a molecular switch that regulates kinetochore–microtubule dynamics to promote mitotic progression and fidelity. EMBO J 29:3531–3543
Mansfeld J, Collin P, Collins MO, Choudhary JS, Pines J (2011) APC15 drives the turnover of MCC-CDC20 to make the spindle assembly checkpoint responsive to kinetochore attachment. Nat Cell Biol 13:1234–1243
Mao Y, Abrieu A, Cleveland DW (2003) Activating and silencing the mitotic checkpoint through CENP-E-dependent activation/inactivation of BubR1. Cell 114:87–98
Mao Y, Desai A, Cleveland DW (2005) Microtubule capture by CENP-E silences BubR1-dependent mitotic checkpoint signaling. J Cell Biol 170:873–880
Maresca TJ, Salmon ED (2009) Intrakinetochore stretch is associated with changes in kinetochore phosphorylation and spindle assembly checkpoint activity. J Cell Biol 184:373–381
Maresca TJ, Salmon ED (2010) Welcome to a new kind of tension: translating kinetochore mechanics into a wait-anaphase signal. J Cell Sci 123:825–835
Martinez-Exposito MJ, Kaplan KB, Copeland J, Sorger PK (1999) Retention of the BUB3 checkpoint protein on lagging chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:8493–8498
Martin-Lluesma S, Stucke VM, Nigg EA (2002) Role of Hec1 in spindle checkpoint signaling and kinetochore recruitment of Mad1/Mad2. Science 297:2267–2270
Matson DR, Demirel PB, Stukenberg PT, Burke DJ (2012) A conserved role for COMA/CENP-H/I/N kinetochore proteins in the spindle checkpoint. Genes Dev 26:542–547
Matsumura S, Toyoshima F, Nishida E (2007) Polo-like kinase 1 facilitates chromosome alignment during prometaphase through BubR1. J Biol Chem 282:15217–15227
Maure JF, Kitamura E, Tanaka TU (2007) Mps1 kinase promotes sister-kinetochore bi-orientation by a tension-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol 17:2175–2182
Mayer C, Filopei J, Batac J, Alford L, Paluh JL (2006) An extended anaphase signaling pathway for Mad2p includes microtubule organizing center proteins and multiple motor-dependent transitions. Cell Cycle 5:1456–1463
Meadows JC, Shepperd LA, Vanoosthuyse V, Lancaster TC, Sochaj AM, Buttrick GJ, Hardwick KG, Millar JB (2011) Spindle checkpoint silencing requires association of PP1 to both Spc7 and kinesin-8 motors. Dev Cell 20:739–750
Meraldi P, Sorger PK (2005) A dual role for Bub1 in the spindle checkpoint and chromosome congression. EMBO J 24:1621–1633
Meraldi P, Draviam VM, Sorger PK (2004) Timing and checkpoints in the regulation of mitotic progression. Dev Cell 7:45–60
Miller SA, Johnson ML, Stukenberg PT (2008) Kinetochore attachments require an interaction between unstructured tails on microtubules and Ndc80(Hec1). Curr Biol 18:1785–1791
Minoshima Y, Hori T, Okada M, Kimura H, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Bao YC, Kawashima T, Kitamura T, Fukagawa T (2005) The constitutive centromere component CENP-50 is required for recovery from spindle damage. Mol Cell Biol 25:10315–10328
Minshull J, Sun H, Tonks NK, Murray AW (1994) MAP-kinase dependent mitotic feedback arrest in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell 79:475–486
Morrow CJ, Tighe A, Johnson VL, Scott MI, Ditchfield C, Taylor SS (2005) Bub1 and aurora B cooperate to maintain BubR1-mediated inhibition of APC/CCdc20. J Cell Sci 118:3639–3652
Musacchio A, Salmon ED (2007) The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:379–393
Nagaoka SI, Hassold TJ, Hunt PA (2012) Human aneuploidy: mechanisms and new insights into an age-old problem. Nat Rev Genet 13:493–504
Nicklas RB, Ward SC, Gorbsky GJ (1995) Kinetochore chemistry is sensitive to tension and may link mitotic forces to a cell cycle checkpoint. J Cell Biol 130:929–939
Nishino M, Kurasawa Y, Evans R, Lin SH, Brinkley BR, Yu-Lee LY (2006) NudC is required for Plk1 targeting to the kinetochore and chromosome congression. Curr Biol 16:1414–1421
Obuse C, Iwasaki O, Kiyomitsu T, Goshima G, Toyoda Y, Yanagida M (2004) A conserved Mis12 centromere complex is linked to heterochromatic HP1 and outer kinetochore protein Zwint-1. Nat Cell Biol 6:1135–1141
Ohi R, Sapra T, Howard J, Mitchison TJ (2004) Differentiation of cytoplasmic and meiotic spindle assembly MCAK functions by Aurora B-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 15:2895–2906
Ohkura H, Yanagida M (1991) S. pombe gene sds22+ essential for a midmitotic transition encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein that positively modulates protein phosphatase-1. Cell 64:149–157
Ohkura H, Noriyuki K, Miyatani S, Toda T, Yanagida M (1989) The fission yeast dis2 + gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell 57:997–1007
Park JE, Erikson RL, Lee KS (2011) Feed-forward mechanism of converting biochemical cooperativity to mitotic processes at the kinetochore plate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:8200–8205
Parry DH, Hickson GR, O'Farrell PH (2003) Cyclin B destruction triggers changes in kinetochore behavior essential for successful anaphase. Curr Biol 13:647–653
Perera D, Taylor SS (2010) Sgo1 establishes the centromeric cohesion protection mechanism in G2 before subsequent Bub1-dependent recruitment in mitosis. J Cell Sci 123:653–659
Perpelescu M, Fukagawa T (2011) The ABCs of CENPs. Chromosoma 120:425–446
Peters JM (2006) The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:644–656
Petersen J, Hagan IM (2003) S. pombe aurora kinase/survivin is required for chromosome condensation and the spindle checkpoint attachment response. Curr Biol 13:590–597
Petrovic A, Pasqualato S, Dube P, Krenn V, Santaguida S, Cittaro D, Monzani S, Massimiliano L, Keller J, Tarricone A, Maiolica A, Stark H, Musacchio A (2010) The MIS12 complex is a protein interaction hub for outer kinetochore assembly. J Cell Biol 190:835–852
Pinsky BA, Kotwaliwale CV, Tatsutani SY, Breed CA, Biggins S (2006a) Glc7/protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunits can oppose the Ipl1/aurora protein kinase by redistributing Glc7. Mol Cell Biol 26:2648–2660
Pinsky BA, Kung C, Shokat KM, Biggins S (2006b) The Ipl1-Aurora protein kinase activates the spindle checkpoint by creating unattached kinetochores. Nat Cell Biol 8:78–83
Pinsky BA, Nelson CR, Biggins S (2009) Protein phosphatase 1 regulates exit from the spindle checkpoint in budding yeast. Curr Biol 19:1182–1187
Pomerening JR, Sontag ED, Ferrell JE Jr (2003) Building a cell cycle oscillator: hysteresis and bistability in the activation of Cdc2. Nat Cell Biol 5:346–351
Posch M, Khoudoli GA, Swift S, King EM, DeLuca JG, Swedlow JR (2010) Sds22 regulates aurora B activity and microtubule–kinetochore interactions at mitosis. J Cell Biol 191:61–74
Przewloka MR, Glover DM (2009) The kinetochore and the centromere: a working long distance relationship. Annu Rev Genet 43:439–465
Qi W, Tang Z, Yu H (2006) Phosphorylation- and polo-box-dependent binding of Plk1 to Bub1 is required for the kinetochore localization of Plk1. Mol Biol Cell 17:3705–3716
Reddy SK, Rape M, Margansky WA, Kirschner MW (2007) Ubiquitination by the anaphase-promoting complex drives spindle checkpoint inactivation. Nature 446:921–925
Ricke RM, Jeganathan KB, Malureanu L, Harrison AM, van Deursen JM (2012) Bub1 kinase activity drives error correction and mitotic checkpoint control but not tumor suppression. J Cell Biol 199:931–949
Riedel CG, Katis VL, Katou Y, Mori S, Itoh T, Helmhart W, Galova M, Petronczki M, Gregan J, Cetin B, Mudrak I, Ogris E, Mechtler K, Pelletier L, Buchholz F, Shirahige K, Nasmyth K (2006) Protein phosphatase 2A protects centromeric sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis I. Nature 441:53–61
Rieder CL, Alexander SP (1990) Kinetochores are transported poleward along a single astral microtubule during chromosome attachment to the spindle in newt lung cells. J Cell Biol 110(1):81–95
Rieder CL, Schultz A, Cole R, Sluder G (1994) Anaphase onset in vertebrate somatic cells is controlled by a checkpoint that monitors sister kinetochore attachment to the spindle. J Cell Biol 127:1301–1310
Rieder CL, Cole RW, Khodjakov A, Sluder G (1995) The checkpoint delaying anaphase in response to chromosome monoorientation is mediated by an inhibitory signal produced by unattached kinetochores. J Cell Biol 130:941–948
Rischitor PE, May KM, Hardwick KG (2007) Bub1 is a fission yeast kinetochore scaffold protein, and is sufficient to recruit other spindle checkpoint proteins to ectopic sites on chromosomes. PLoS One 2:e1342
Rosasco-Nitcher SE, Lan W, Khorasanizadeh S, Stukenberg PT (2008) Centromeric Aurora-B activation requires TD-60, microtubules, and substrate priming phosphorylation. Science 319:469–472
Rosenberg JS, Cross FR, Funabiki H (2011) KNL1/Spc105 recruits PP1 to silence the spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Biol 21:942–947
Ryu H, Furuta M, Kirkpatrick D, Gygi SP, Azuma Y (2010) PIASy-dependent SUMOylation regulates DNA topoisomerase IIalpha activity. J Cell Biol 191:783–794
Sakuno T, Tada K, Watanabe Y (2009) Kinetochore geometry defined by cohesion within the centromere. Nature 458:852–858
Salimian KJ, Ballister ER, Smoak EM, Wood S, Panchenko T, Lampson MA, Black BE (2011) Feedback control in sensing chromosome biorientation by the Aurora B kinase. Curr Biol 21:1158–1165
Santaguida S, Vernieri C, Villa F, Ciliberto A, Musacchio A (2011) Evidence that Aurora B is implicated in spindle checkpoint signalling independently of error correction. EMBO J 30:1508–1519
Saurin AT, van der Waal MS, Medema RH, Lens SM, Kops GJ (2011) Aurora B potentiates Mps1 activation to ensure rapid checkpoint establishment at the onset of mitosis. Nat Commun 2:316
Schaar BT, Chan GK, Maddox P, Salmon ED, Yen TJ (1997) CENP-E function at kinetochores is essential for chromosome alignment. J Cell Biol 139:1373–1382
Schmidt JC, Kiyomitsu T, Hori T, Backer CB, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM (2010) Aurora B kinase controls the targeting of the Astrin–SKAP complex to bioriented kinetochores. J Cell Biol 191:269–280
Schmidt JC, Arthanari H, Boeszoermenyi A, Dashkevich NM, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Monnier N, Markus M, Oberer M, Milligan RA, Bathe M, Wagner G, Grishchuk EL, Cheeseman IM (2012) The kinetochore-bound Ska1 complex tracks depolymerizing microtubules and binds to curved protofilaments. Dev Cell 23(5):968–980
Sczaniecka M, Feoktistova A, May KM, Chen JS, Blyth J, Gould KL, Hardwick KG (2008) The spindle checkpoint functions of Mad3 and Mad2 depend on a Mad3 KEN box-mediated interaction with Cdc20-anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C). J Biol Chem 283:23039–23047
Shah JV, Botvinick E, Bonday Z, Furnari F, Berns M, Cleveland DW (2004) Dynamics of centromere and kinetochore proteins; implications for checkpoint signaling and silencing. Curr Biol 14:942–952
Shapiro PS, Vaisberg E, Hunt AJ, Tolwinski NS, Whalen AM, McIntosh JR, Ahn NG (1998) Activation of the MKK/ERK pathway during somatic cell mitosis: direct interactions of active ERK with kinetochores and regulation of the mitotic 3F3/2 phosphoantigen. J Cell Biol 142:1533–1545
Sharp-Baker H, Chen RH (2001) Spindle checkpoint protein Bub1 is required for kinetochore localization of Mad1, Mad2, Bub3, and CENP-E, independently of its kinase activity. J Cell Biol 153:1239–1250
Shepperd LA, Meadows JC, Sochaj AM, Lancaster TC, Zou J, Buttrick GJ, Rappsilber J, Hardwick KG, Millar JB (2012) Phosphodependent recruitment of Bub1 and Bub3 to Spc7/KNL1 by Mph1 kinase maintains the spindle checkpoint. Curr Biol 22:891–899
Sliedrecht T, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Kops GJ (2010) Chemical genetic inhibition of Mps1 in stable human cell lines reveals novel aspects of Mps1 function in mitosis. PLoS One 5:e10251
Stegmeier F, Rape M, Draviam VM, Nalepa G, Sowa ME, Ang XL, McDonald ER 3rd, Li MZ, Hannon GJ, Sorger PK, Kirschner MW, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (2007) Anaphase initiation is regulated by antagonistic ubiquitination and deubiquitination activities. Nature 446:876–881
Stone EM, Yamano H, Kinoshita N, Yanagida M (1993) Mitotic regulation of protein phosphatases by the fission yeast sds22 protein. Curr Biol 3:13–26
Stucke VM, Sillje HH, Arnaud L, Nigg EA (2002) Human Mps1 kinase is required for the spindle assembly checkpoint but not for centrosome duplication. EMBO J 21:1723–1732
Stucke VM, Baumann C, Nigg EA (2004) Kinetochore localization and microtubule interaction of the human spindle checkpoint kinase Mps1. Chromosoma 113:1–15
Stumpff J, von Dassow G, Wagenbach M, Asbury C, Wordeman L (2008) The kinesin-8 motor Kif18A suppresses kinetochore movements to control mitotic chromosome alignment. Dev Cell 14:252–262
Sudakin V, Chan GK, Yen TJ (2001) Checkpoint inhibition of the APC/C in HeLa cells is mediated by a complex of BUBR1, BUB3, CDC20, and MAD2. J Cell Biol 154:925–936
Suijkerbuijk SJ, van Dam TJ, Karagoz GE, von Castelmur E, Hubner NC, Duarte AM, Vleugel M, Perrakis A, Rudiger SG, Snel B, Kops GJ (2012a) The vertebrate mitotic checkpoint protein BUBR1 is an unusual pseudokinase. Dev Cell 22:1321–1329
Suijkerbuijk SJ, Vleugel M, Teixeira A, Kops GJ (2012b) Integration of kinase and phosphatase activities by BUBR1 ensures formation of stable kinetochore–microtubule attachments. Dev Cell 23:745–755
Suzuki A, Hori T, Nishino T, Usukura J, Miyagi A, Morikawa K, Fukagawa T (2011) Spindle microtubules generate tension-dependent changes in the distribution of inner kinetochore proteins. J Cell Biol 193:125–140
Takeda DY, Wohlschlegel JA, Dutta A (2001) A bipartite substrate recognition motif for cyclin-dependent kinases. J Biol Chem 276:1993–1997
Takenaka K, Gotoh Y, Nishida E (1997) MAP kinase is required for the spindle assembly checkpoint but is dispensable for the normal M phase entry and exit in Xenopus egg cell cycle extracts. J Cell Biol 136:1091–1097
Takeuchi K, Fukagawa T (2012) Molecular architecture of vertebrate kinetochores. Exp Cell Res 318:1367–1374
Tanaka TU (2010) Kinetochore-microtubule interactions: steps towards bi-orientation. EMBO J 29:4070–4082
Tanaka TU, Rachidi N, Janke C, Pereira G, Galova M, Schiebel E, Stark MJ, Nasmyth K (2002) Evidence that the Ipl1-Sli15 (Aurora kinase-INCENP) complex promotes chromosome bi-orientation by altering kinetochore–spindle pole connections. Cell 108:317–329
Tanaka K, Mukae N, Dewar H, van Breugel M, James EK, Prescott AR, Antony C, Tanaka TU (2005) Molecular mechanisms of kinetochore capture by spindle microtubules. Nature 434:987–994
Tang Z, Bharadwaj R, Li B, Yu H (2001) Mad2-independent inhibition of APCCdc20 by the mitotic checkpoint protein BubR1. Dev Cell 1:227–237
Tang Z, Shu H, Oncel D, Chen S, Yu H (2004) Phosphorylation of Cdc20 by Bub1 provides a catalytic mechanism for APC/C inhibition by the spindle checkpoint. Mol Cell 16:387–397
Tang Z, Shu H, Qi W, Mahmood NA, Mumby MC, Yu H (2006) PP2A is required for centromeric localization of Sgo1 and proper chromosome segregation. Dev Cell 10:575–585
Tanno Y, Kitajima TS, Honda T, Ando Y, Ishiguro K, Watanabe Y (2010) Phosphorylation of mammalian Sgo2 by Aurora B recruits PP2A and MCAK to centromeres. Genes Dev 24:2169–2179
Taylor SS, McKeon F (1997) Kinetochore localization of murine Bub1 is required for normal mitotic timing and checkpoint response to spindle damage. Cell 89:727–735
Taylor SS, Ha E, McKeon F (1998) The human homologue of Bub3 is required for kinetochore localization of Bub1 and a Mad3/Bub1-related protein kinase. J Cell Biol 142:1–11
Teichner A, Eytan E, Sitry-Shevah D, Miniowitz-Shemtov S, Dumin E, Gromis J, Hershko A (2011) p31comet promotes disassembly of the mitotic checkpoint complex in an ATP-dependent process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3187–3192
Tien JF, Umbreit NT, Gestaut DR, Franck AD, Cooper J, Wordeman L, Gonen T, Asbury CL, Davis TN (2010) Cooperation of the Dam1 and Ndc80 kinetochore complexes enhances microtubule coupling and is regulated by aurora B. J Cell Biol 189:713–723
Tighe A, Staples O, Taylor S (2008) Mps1 kinase activity restrains anaphase during an unperturbed mitosis and targets Mad2 to kinetochores. J Cell Biol 181:893–901
Tooley JG, Miller SA, Stukenberg PT (2011) The Ndc80 complex uses a tripartite attachment point to couple microtubule depolymerization to chromosome movement. Mol Biol Cell 22:1217–1226
Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Andrews PD, Wickramasinghe S, Sleeman J, Prescott A, Lam YW, Lyon C, Swedlow JR, Lamond AI (2003) Time-lapse imaging reveals dynamic relocalization of PP1gamma throughout the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell 14:107–117
Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Andersen J, Lam YW, Moorhead G, Mann M, Lamond AI (2006) Repo-Man recruits PP1 gamma to chromatin and is essential for cell viability. J Cell Biol 172:679–692
Tseng BS, Tan L, Kapoor TM, Funabiki H (2010) Dual detection of chromosomes and microtubules by the chromosomal passenger complex drives spindle assembly. Dev Cell 18:903–912
Tsukahara T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y (2010) Phosphorylation of the CPC by Cdk1 promotes chromosome bi-orientation. Nature 467:719–723
Ubersax JA, Woodbury EL, Quang PN, Paraz M, Blethrow JD, Shah K, Shokat KM, Morgan DO (2003) Targets of the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Nature 425:859–864
Uchida KS, Takagaki K, Kumada K, Hirayama Y, Noda T, Hirota T (2009) Kinetochore stretching inactivates the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 184:383–390
Uzunova K, Dye BT, Schutz H, Ladurner R, Petzold G, Toyoda Y, Jarvis MA, Brown NG, Poser I, Novatchkova M, Mechtler K, Hyman AA, Stark H, Schulman BA, Peters JM (2012) APC15 mediates CDC20 autoubiquitylation by APC/C(MCC) and disassembly of the mitotic checkpoint complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:1116–1123
van der Waal MS, Hengeveld RC, van der Horst A, Lens SM (2012) Cell division control by the chromosomal passenger complex. Exp Cell Res 318:1407–1420
Vanoosthuyse V, Hardwick KG (2009) A novel protein phosphatase 1-dependent spindle checkpoint silencing mechanism. Curr Biol 19:1176–1181
Varma D, Monzo P, Stehman SA, Vallee RB (2008) Direct role of dynein motor in stable kinetochore–microtubule attachment, orientation, and alignment. J Cell Biol 182:1045–1054
Vigneron S, Prieto S, Bernis C, Labbe JC, Castro A, Lorca T (2004) Kinetochore localization of spindle checkpoint proteins: who controls whom? Mol Biol Cell 15:4584–4596
Vorozhko VV, Emanuele MJ, Kallio MJ, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2008) Multiple mechanisms of chromosome movement in vertebrate cells mediated through the Ndc80 complex and dynein/dynactin. Chromosoma 117:169–179
Wan X, O'Quinn RP, Pierce HL, Joglekar AP, Gall WE, DeLuca JG, Carroll CW, Liu ST, Yen TJ, McEwen BF, Stukenberg PT, Desai A, Salmon ED (2009) Protein architecture of the human kinetochore microtubule attachment site. Cell 137:672–684
Wang XM, Zhai Y, Ferrell JE Jr (1997) A role for mitogen-activated protein kinase in the spindle assembly checkpoint in XTC cells. J Cell Biol 137:433–443
Wang HW, Ramey VH, Westermann S, Leschziner AE, Welburn JP, Nakajima Y, Drubin DG, Barnes G, Nogales E (2007) Architecture of the Dam1 kinetochore ring complex and implications for microtubule-driven assembly and force-coupling mechanisms. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:721–726
Wang F, Dai J, Daum JR, Niedzialkowska E, Banerjee B, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ, Higgins JM (2010) Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis. Science 330:231–235
Wang F, Ulyanova NP, van der Waal MS, Patnaik D, Lens SM, Higgins JM (2011) A positive feedback loop involving Haspin and Aurora B promotes CPC accumulation at centromeres in mitosis. Curr Biol 21:1061–1069
Wang F, Ulyanova NP, Daum JR, Patnaik D, Kateneva AV, Gorbsky GJ, Higgins JM (2012) Haspin inhibitors reveal centromeric functions of Aurora B in chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol 199:251–268
Warren CD, Brady DM, Johnston RC, Hanna JS, Hardwick KG, Spencer FA (2002) Distinct chromosome segregation roles for spindle checkpoint proteins. Mol Biol Cell 13:3029–3041
Waters JC, Chen RH, Murray AW, Salmon ED (1998) Localization of Mad2 to kinetochores depends on microtubule attachment, not tension. J Cell Biol 141:1181–1191
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW (2006) Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:658–667
Wei RR, Al-Bassam J, Harrison SC (2007) The Ndc80/HEC1 complex is a contact point for kinetochore–microtubule attachment. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:54–59
Wei R, Ngo B, Wu G, Lee WH (2011) Phosphorylation of the Ndc80 complex protein, HEC1, by Nek2 kinase modulates chromosome alignment and signaling of the spindle assembly checkpoint. Mol Biol Cell 22:3584–3594
Welburn JPI, Vleugel M, Liu D, Iii JRY, Lampson MA, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM (2010) Aurora B phosphorylates spatially distinct targets to differentially regulate the kinetochore–microtubule interface. Mol Cell 38:383–392
Westhorpe FG, Tighe A, Lara-Gonzalez P, Taylor SS (2011) p31comet-mediated extraction of Mad2 from the MCC promotes efficient mitotic exit. J Cell Sci 124:3905–3916
Wong OK, Fang G (2007) Cdk1 phosphorylation of BubR1 controls spindle checkpoint arrest and Plk1-mediated formation of the 3F3/2 epitope. J Cell Biol 179:611–617
Wood KW, Sakowicz R, Goldstein LS, Cleveland DW (1997) CENP-E is a plus end-directed kinetochore motor required for metaphase chromosome alignment. Cell 91:357–366
Wurzenberger C, Held M, Lampson MA, Poser I, Hyman AA, Gerlich DW (2012) Sds22 and Repo-Man stabilize chromosome segregation by counteracting Aurora B on anaphase kinetochores. J Cell Biol 198:173–183
Yamagishi Y, Honda T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y (2010) Two histone marks establish the inner centromere and chromosome bi-orientation. Science 330:239–243
Yamagishi Y, Yang CH, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y (2012) MPS1/Mph1 phosphorylates the kinetochore protein KNL1/Spc7 to recruit SAC components. Nat Cell Biol 14:746–752
Yamano H, Ishii K, Yanagida M (1994) Phosphorylation of dis2 protein phosphatase at the C-terminal cdc2 consensus and its potential role in cell cycle regulation. EMBO J 13:5310–5318
Yang M, Li B, Liu CJ, Tomchick DR, Machius M, Rizo J, Yu H, Luo X (2008) Insights into mad2 regulation in the spindle checkpoint revealed by the crystal structure of the symmetric mad2 dimer. PLoS Biol 6:e50
Yasuda S, Oceguera-Yanez F, Kato T, Okamoto M, Yonemura S, Terada Y, Ishizaki T, Narumiya S (2004) Cdc42 and mDia3 regulate microtubule attachment to kinetochores. Nature 428:767–771
Yeh E, Skibbens RV, Cheng JW, Salmon ED, Bloom K (1995) Spindle dynamics and cell cycle regulation of dynein in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 130:687–700
Yue Z, Carvalho A, Xu Z, Yuan X, Cardinale S, Ribeiro S, Lai F, Ogawa H, Gudmundsdottir E, Gassmann R, Morrison CG, Ruchaud S, Earnshaw WC (2008) Deconstructing Survivin: comprehensive genetic analysis of Survivin function by conditional knockout in a vertebrate cell line. J Cell Biol 183:279–296
Zecevic M, Catling AD, Eblen ST, Renzi L, Hittle JC, Yen TJ, Gorbsky GJ, Weber MJ (1998) Active MAP kinase in mitosis: localization at kinetochores and association with the motor protein CENP-E. J Cell Biol 142:1547–1558
Zhang J, Ahmad S, Mao Y (2007) BubR1 and APC/EB1 cooperate to maintain metaphase chromosome alignment. J Cell Biol 178:773–784
Zhao Y, Chen RH (2006) Mps1 phosphorylation by MAP kinase is required for kinetochore localization of spindle-checkpoint proteins. Curr Biol 16:1764–1769
Zhou T, Aumais JP, Liu X, Yu-Lee LY, Erikson RL (2003) A role for Plk1 phosphorylation of NudC in cytokinesis. Dev Cell 5:127–138
Zich J, Sochaj AM, Syred HM, Milne L, Cook AG, Ohkura H, Rappsilber J, Hardwick KG (2012) Kinase activity of fission yeast Mph1 is required for Mad2 and Mad3 to stably bind the anaphase promoting complex. Curr Biol 22:296–301
Acknowledgments
HF is supported by a National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant (R01GM075249), and DW is supported by a NIH Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award Postdoctoral Fellowship (1F32GM103147). We thank Sahand Jamal Rahi for critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 457 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funabiki, H., Wynne, D.J. Making an effective switch at the kinetochore by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Chromosoma 122, 135–158 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0401-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0401-5