Abstract
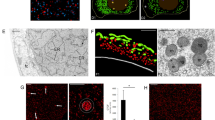
In oocyte nuclei of the scorpionfly, Panorpa communis, we have recently defined a population of nuclear bodies (NBs) that contain some components of Cajal bodies (CBs). In the present study, we used several criteria [presence of coilin, U7 snRNA, RNA polymerase II (pol II) and specific ultrastructure] to identify these NBs as CBs. The essential evidence for CB identification came from experiments with microinjection of fluorescein-tagged U7 snRNA. Consistent with the U7 data, we found pol II and pre-mRNA splicing factor, SC35, in Panorpa oocyte CBs. We show here that the dynamics of CBs differs from that in somatic cells and correlates with the level of oocyte chromosome condensation. We also found that the significant increase of CB size is accompanied by condensation of the chromosomes in the karyosphere, which is indicative of a decline in transcription. Using immunogold microscopy we determined that pol II and coilin are shared by CBs and the granular material associated with condensed chromosomes in the Panorpa karyosphere. The colocalization of pol II, U7 snRNA and splicing factors with CBs at the inactive stage of late oogenesis suggests that the latter may serve as storage domains for components that were earlier engaged in RNA transcription and processing.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliegro MC, Alliegro MA (1998) Protein heterogeneity in the coiled body compartment. Exp Cell Res 239:60–68
Andrade LEC, Chan EKL, Raška I, Peebles CL, Roos G, Tan EM (1991) Human antibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. J Exp Med 173:1407–1419
Andrade LEC, Tan EM, Chan EKL (1993) Immunocytochemical analysis of the coiled body in the cell cycle and during cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:1947–1951
Batalova FM, Stepanova IS, Bogolyubov DS (2000) Cajal bodies in oocyte nuclei of scorpion fly, Panorpa communis. Tsitologiia 42:1037–1047
Bauer DW, Gall JG (1997) Coiled bodies without coilin. Mol Biol Cell 8:73–82
Bellini M (2000) Coilin, more than a molecular marker of the Cajal (coiled) body. BioEssays 22:861–867
Bier K, Kunz W, Ribbert D (1967) Struktur und Funktion der Oocytenchromosomen und Nukleolen sowie der Extra-DNS während der oogenese panoistischer und meroistischer Insecten. Chromosoma 23:214–254
Biliński SM, Kloc M (2002) Accessory nuclei revisited: the translocation of snRNPs from the germinal vesicle to the periphery of the future embryo. Chromosoma 111:62–68
Bogolyubov D, Parfenov V (2001) Immunogold localization of RNA polymerase II and pre-mRNA splicing factors in Tenebrio molitor oocyte nuclei with special emphasis on karyosphere development. Tissue Cell 33:549–561
Bogolyubov D, Parfenov V (2004) Do nuclear bodies in oocytes of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Polyphaga, Tenebrionidae) contain two forms of RNA polymerase II?. Tissue Cell 36:13–17
Bogolyubov D, Alexandrova O, Tsvetkov A, Parfenov V (2000) An immunoelectron study of karyosphere and nuclear bodies in oocytes of mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Polyphaga). Chromosoma 109:415–425
Bogolyubova IO, Parfenov VN (2000) Pre-mRNA splicing factors in nuclei of two-cells mouse embryos. Tsitologiia 42:884–890
Brasch K, Ochs RL (1992) Nuclear bodies (NBs): a newly “rediscovered” organelle. Exp Cell Res 202:211–223
Carmo-Fonseca M, Pepperkok R, Carvalho MT, Lamond AI (1992) Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol 117:1–14
Carvalho T, Almeida F, Calapez A, Lafarga M, Berciano MT, Carmo-Fonseca M (1999) The spinal muscular atrophy disease gene product, SMN: a link between snRNP biogenesis and the Cajal (coiled) body. J Cell Biol 147:715–727
Chouinard LA (1975) A light- and electron-microscope study of the oocyte nucleus during development of the antral follicle in the prepubertal mouse. J Cell Sci 17:589–615
Darzacq X, Jády BE, Verheggen C, Kiss AM, Bertrand E, Kiss T (2002) Cajal body-specific small nuclear RNAs: a novel class of 2′-O-methylation and pseudouridylation guide RNAs. EMBO J 21:2746–2756
Deryusheva S, Gall JG (2004) Dynamics of coilin in Cajal bodies of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4810–4814
Dominski Z, Marzluff WF (1999) Formation of the 3′ end of histone mRNA. Gene 239:1–14
Doyle O, Corden JL, Murphy C, Gall JG (2002) The distribution of RNA polymerase II largest subunit (RPB1) in the Xenopus germinal vesicle. J Struct Biol 140:154–166
Dundr M, Misteli T (2001) Functional architecture in the cell nucleus. Biochem J 356:297–310
Ferreira JA, Carmo-Fonseca M, Lamond AI (1994) Differential interaction of splicing snRNPs with coiled bodies and interchromatin granules during mitosis and assembly of daughter cell nuclei. J Cell Biol 126:11–23
Filek K, Jarek E, Biliński SM (2002) Cajal bodies (coiled bodies) in the nuclei of the house cricket (Acheta domesticus) oocytes. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 40:221–222
Frey MR, Matera AG (1995) Coiled bodies contain U7 small nuclear RNA and associate with specific DNA sequences in interphase human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:5915–5919
Fu X-D, Maniatis T (1990) Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature 343:437–441
Gall JG (2000) Cajal bodies: the first 100 years. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:273–300
Gall JG, Tsvetkov A, Wu Z, Murphy C (1995) Is the sphere organelle/coiled body a universal nuclear component?. Dev Genet 16:25–35
Gall JG, Bellini M, Wu Z, Murphy C (1999) Assembly of the nuclear transcription and processing machinery: Cajal bodies (coiled bodies) and transcriptosomes. Mol Biol Cell 10:4385–4402
Gall JG, Wu Z, Murphy C, Gao H (2004) Structure in the amphibian germinal vesicle. Exp Cell Res 296:28–34
Grande MA, van der Kraan I, de Jong L, van Driel R (1997) Nuclear distribution of transcription factors in relation to sites of transcription and RNA polymerase II. J Cell Sci 110:1781–1791
Gruzova MN (1962) The karyosphere formation in the oogenesis of Panorpa (Mecoptera). Tsitologiia 4:150–159
Gruzova MN (1988) The nucleus during oogenesis with special reference to extrachromosomal structures. In: Detlaff TA, Vassetsky SG (eds) Oocyte growth and maturation. Plenum Press, New York, pp 77–163
Gruzova MN, Parfenov VN (1993) Karyosphere in oogenesis and intranuclear morphogenesis. Int Rev Cytol 144:1–52
Hulsebos TJM, Hackstein JHP, Henning W (1984) Lampbrush loopspecific protein of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 16:9415–9429
Jabłońska A, Biliński SM (2001) Structure of ovarioles in adult queens and workers of the common wasp, Vespula germanica (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Folia Biol 49:191–198
Jády BE, Darzacq X, Tucker KE, Matera AG, Bertrand E, Kiss T (2003) Modification of Sm small nuclear RNAs occurs in the nucleoplasmic Cajal body following import from the cytoplasm. EMBO J 22:1878–1888
Jaglarz MK (2001) Nuclear bodies in the oocyte nucleus of ground beetles are enriched in snRNPs. Tissue Cell 33:395–401
Jörgensen M (1913) Zellenstudien I. Morphologische Beiträge zum Problem des Eiwachstums. Arch Zellforsch 10:1–126
Kopecny V, Biggiogera M, Laurincik J, Pivko J, Grafenaw P, Martin TE, Fu XD, Fakan S (1996) Fine structural cytochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of nucleic acids and ribonucleoprotein distribution in nuclei of pig oocytes and early preimplantation embryos. Chromosoma 104:561–574
Matera AG (1999) Nuclear bodies: multifaceted subdomains of the interchromatin space. Trends Cell Biol 9:302–309
Monneron A, Bernhard W (1969) Fine structural organization of the interphase nucleus in some mammalian cells. J Ultrastruct Res 27:266–288
Morgan GT, Doyle O, Murphy C, Gall JG (2000) RNA polymerase II in Cajal bodies of amphibian oocytes. J Struct Biol 129:258–268
Ogg SC, Lamond AI (2002) Cajal bodies and coilin—moving towards function. J Cell Biol 159:17–21
Parfenov VN, Davis DS, Pochukalina GN, Kostyuchek D, Murti KG (1998) Dynamics of distribution of splicing components relative to the transcriptional state of human oocytes from antral follicles. J Cell Biochem 69:72–80
Parfenov VN, Pochukalina GN, Davis DS, Reinbold R, Schöler HR, Murti KG (2003) Nuclear distribution of Oct-4 transcription factor in transcriptionally active and inactive mouse oocytes and its relation to RNA polymerase II and splicing factors. J Cell Biochem 89:720–732
Ramamurty PS (1963) Über die Herkunft der Ribonucleinsäure in den wachsenden Eizellen der Skorpionsfliege Panorpa communis (Insecta, Mecoptera). Naturwissenschaften 50:383–384
Raška I, Andrade LEC, Ochs RL, Chan EKL, Chang CM, Roos G, Tan EM (1991) Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Exp Cell Res 195:27–37
Rebelo L, Almeida F, Ramos C, Bohmann K, Lamond AI, Carmo-Fonseca M (1996) The dynamics of coiled bodies in the nucleus of adenovirus-infected cells. Mol Biol Cell 7:1137–1151
Schul W, van Driel R, de Jong L (1998) Coiled bodies and U2 snRNA genes adjacent to coiled bodies are enriched in factors required for snRNA transcription. Mol Biol Cell 9:1025–1036
Simiczyjew B (1996) Cyto- and histochemical studies of the ovariole of Panorpa communis (Insecta: Mecoptera). Folia Histochem Cytobiol 34:151–154
Simiczyjew B (2003) Germ cell cluster differentiation in polytrophic ovarioles of hanging-flies (Mecoptera: Bittacidae). Zool Polon 48:71–79
Sleeman JE, Lamond AI (1999) Nuclear organization of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:372–377
Świątek P (1999) Formation of the karyosome in developing oocytes of weevils (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). Tissue Cell 31:587–593
Świątek P, Jaglarz MK (2004) SnRNPs are present in the karyosome capsule in the weevil germinal vesicle. Tissue Cell 36:253–262
Thompson NE, Steinberg TH, Aronson DB, Burgess RR (1989) Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 264:11511–11520
Tsvetkov AG, Gruzova MN, Gall JG (1996) Spheres from the oocyte nuclei of the house cricket and the damselfly contain pre-mRNA splicing and pre-rRNA processing factors. Tsitologiia 38:311–318
Tsvetkov A, Alexandrova O, Bogolyubov D, Gruzova M (1997) Nuclear bodies from cricket and mealworm oocytes contain splicing factors of pre-mRNA. Eur J Entomol 94:393–407
Tuma R, Stolk JA, Roth MB (1993) Indentification and characterization of a sphere organelle protein. J Cell Biol 122:767–773
Wallace RA, Jared DW, Dumont JN, Sega MW (1973) Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. III. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool 184:321–333
Wu Z, Murphy C, Callan HG, Gall JG (1991) Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres and snurposomes. J Cell Biol 113:465–483
Wu CH, Murphy C, Gall JG (1996) The Sm binding site targets U7 snRNA to coiled bodies (spheres) of amphibian oocytes. RNA 2:811–823
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the following people for providing antibodies used in this work: E. K. L. Chan for R288 serum, K. G. Murti for the anti-DNA monoclonal antibody, J. G. Gall for mAbs 8WG16 and anti-SC35. The authors are greatly indebted to J. G. Gall for providing fluorescein-tagged RNA constructs. We also thank Yu. I. Gukina for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grants No. 03-04-49389 and 04-04-48080) and the Russian Science Support Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Matera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batalova, F.M., Stepanova, I.S., Skovorodkin, I.N. et al. Identification and dynamics of Cajal bodies in relation to karyosphere formation in scorpionfly oocytes. Chromosoma 113, 428–439 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0328-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0328-y